Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 11•
- AQA•
- Foundation
The effect of different substrates on cellular respiration in yeast: practical
I can investigate the effect of different substrates on cellular respiration in yeast by using a measuring cylinder to collect the gas produced.


- Year 11•
- AQA•
- Foundation
The effect of different substrates on cellular respiration in yeast: practical
I can investigate the effect of different substrates on cellular respiration in yeast by using a measuring cylinder to collect the gas produced.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
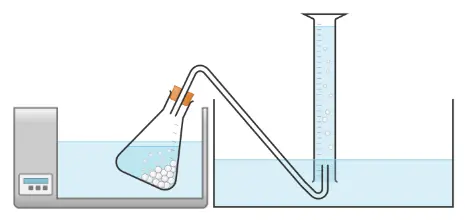
- Living yeast cells immobilised in alginate beads will carry out cellular respiration and produce carbon dioxide gas.
- The gas can be collected and the volume of gas measured using an upturned measuring cylinder under water.
- Identifying independent and dependent variables, and variables to control to increase the validity of the results.
- How to read the volume of gas from the meniscus in the measuring cylinder after a set time.
- Collecting repeat measurements for each substrate, and collecting data for different substrates.
Keywords
Cellular respiration - An exothermic chemical process that transfers energy for life processes, using glucose as fuel.
Independent variable - The factor that we change in an experiment.
Dependent variable - The factor that we measure in an experiment.
Random error - Causes results to differ by different amounts due to a factor other than the independent variable (the factor we changed).
Systematic error - Causes measurements to differ from the true value by the same amount each time they are taken.
Common misconception
Pupils often read the volume of gas incorrectly as they do not measure it from the bottom of the meniscus of the water in the measuring cylinder.
This lesson contains a detailed explanation of how to correctly measure volumes from the meniscus, and why this is important.
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: The effect of different substrates on cellular respiration in yeast: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: The effect of different substrates on cellular respiration in yeast: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Conical flasks, glucose and two other carbohydrate substrates (e.g. sucrose and starch), yeast immobilised in alginate beads, bungs and delivery tubes, measuring cylinders, tank, water bath, timer.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the words to their meanings.
Active site -
part of an enzyme to which a specific substrate can bind
Enzyme -
biological catalyst
Rate -
how much change occurs per unit of time
Lock and key -
a model used to explain the specificity of enzymes
Q2.Which is the best explanation of the term denatured?
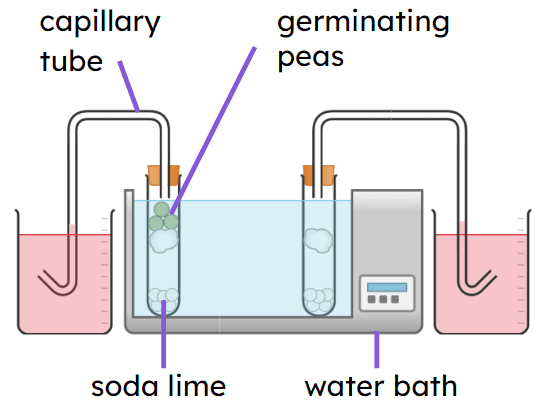
Q3.Some peas are boiled and then cooled back to room temperature. The peas are then used in a respirometer at 30°C. How will the respirometer results for the boiled peas compare to germinating peas?
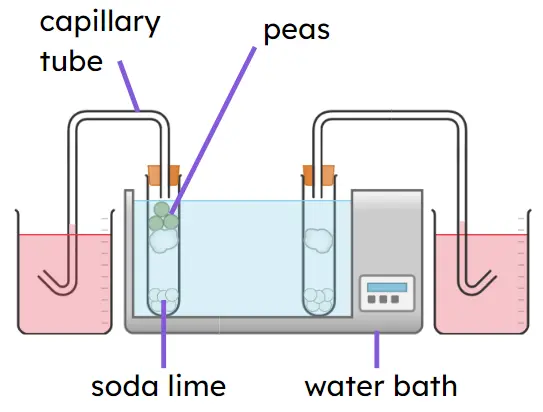
Q4.In three 5 minute tests using a respirometer, the water in the capillary tube moves 10 mm, 12 mm and 8 mm. The mean rate of respiration for these results is mm/min.
Q5.What is oxygen debt?
Q6.For a working muscle cell, what is the major advantage of aerobic cellular respiration compared to anaerobic cellular respiration?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What name do scientist give to errors that cause measurements to differ from the true value by the same amount each time?
Q2.Yeast is used in the production of a variety of food and drinks. Which food or drink is made without yeast?




Q3.The equation for anaerobic respiration in yeast is not balanced. What coefficient (number) needs to be added before the formulae for ethanol and carbon dioxide, to balance the equation?
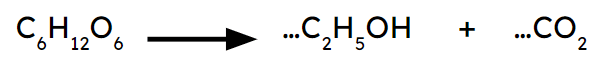
Q4.Starch and cellulose are both large molecules made of thousands of glucose molecules joined together. The enzyme amylase can break down starch but not cellulose. Why?
Q5.The apparatus is used to measure the rate of respiration in yeast, provided with different substrates. When using this apparatus, which of the listed variables is the independent variable?