Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
Alleles, genotype, and phenotype
I can explain how the genotype affects the phenotype of an organism.
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
Alleles, genotype, and phenotype
I can explain how the genotype affects the phenotype of an organism.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- An individual inherits two copies of each gene in a pair of chromosomes.
- Versions of genes are called alleles, they can be recessive or dominant, indicated with a capital or lowercase letter.
- The combination of alleles that an organism has is called its genotype.
- Different alleles of a gene are associated with different versions of the same characteristic called the phenotype.
- Some phenotypes are determined only by genotype, others are also affected by the environment.
Keywords
Allele - A genetic variant in a gene creates an allele (a different version of the gene), which produces a different phenotype.
Dominant - One or both dominant alleles in the genotype for the characteristic to be expressed in the phenotype.
Recessive - Two recessive alleles in the genotype for the characteristic to be expressed in the phenotype.
Genotype - The combination of alleles an organism has for a characteristic (i.e. phenotype).
Phenotype - Features that result, at least partly, from the genetic code of an organism’s genes.
Common misconception
A dominant condition is 'stronger' and that only the strongest characteristic is inherited from one parent.
Two genes are inherited, so both alleles contribute to the genotype. In some cases one is dominant and therefore will always be expressed (through protein structure) in the phenotype, the recessive allele is still present.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Alleles, genotype, and phenotype, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Alleles, genotype, and phenotype, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Inheritance, genotype and phenotype unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Phenotype refers to an organism’s observable characteristics. Which factors can affect an organism’s phenotype?
Q2.Starting with the smallest, put these in size order.
Q3.What is the genome in a unicellular organism?
Q4.Which is the best description of a DNA molecule?
Q5.True or false? All genes code for enzymes.
Q6.Put these in order to describe the production of a red pigment in a petal.
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Adult body cells contain two copies of each chromosome. Gametes are sex cells. Which statement about gametes is true?
Q2.The diagram shows a chromosome pair. Four genes are shown. One gene is labelled on the left chromosome. Which position (A, B, C or D) shows the location of this gene on the right chromosome?
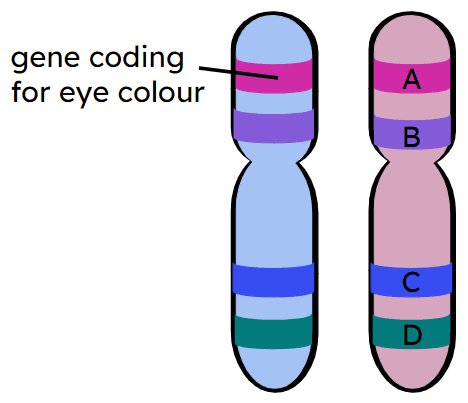
Q3.Alleles are ...
Q4.A plant’s flowers are either red or white. Plants with the genotypes RR and Rr have red flowers. Which allele is recessive?
Q5.Match each word to its correct meaning.
A genetic variant of a gene coding for a different phenotype.
Only one copy of this type of allele will cause a phenotypic feature.
The combination of alleles an organism has for a feature.
Observable features that are at least partly caused by genes.
Two copies of this allele are needed to cause a phenotypic feature.


