Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
Estimating population size and distribution using transects: practical
I can investigate the effect of a factor on the distribution of species using a transect.
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
Estimating population size and distribution using transects: practical
I can investigate the effect of a factor on the distribution of species using a transect.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Abiotic factors such as light levels, temperature, soil moisture and pH can be measured.
- Transects can be used to investigate the effects of a changing factor on the distribution and abundance of organisms.
- A transect can be placed along a gradient of a factor (e.g. from shade to full sunlight).
- A belt transect uses quadrats placed along the straight line to measure distribution and abundance.
Keywords
Abiotic factor - Abiotic factors are the non-living components of an ecosystem.
Transect - A transect is a straight line across a habitat that is used to make measurements and observations.
Distribution - The distribution of a species is the geographical area in which a species can be found.
Abundance - Abundance is the number of organisms of a species found within a habitat.
Quadrat - A quadrat is a square frame which is used to sample populations of plants or slow-moving animals.
Common misconception
Quadrats must always be randomly placed to survey organisms.
Quadrats can be systematically placed as part of sampling activities. This is not random sampling but regular sampling.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Estimating population size and distribution using transects: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Estimating population size and distribution using transects: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Living organisms and their environments unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Quadrat, 30 m tape measure, clipboard, paper, pencil, light meter (or app on phone).
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following organisms might you sample using a quadrat?
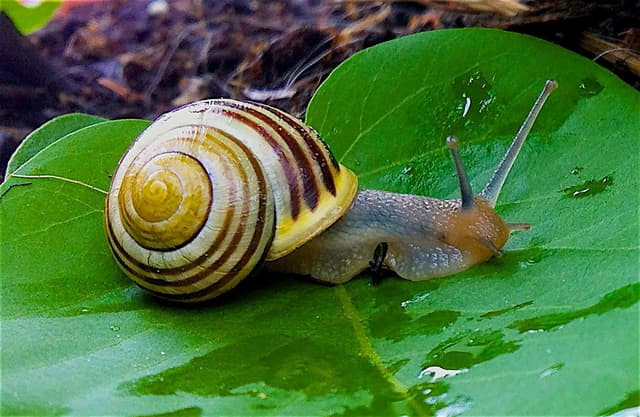
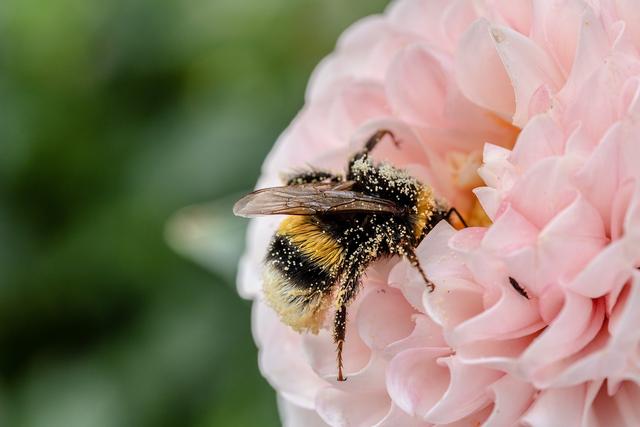




Q2.How many red flowers are there in the quadrat?
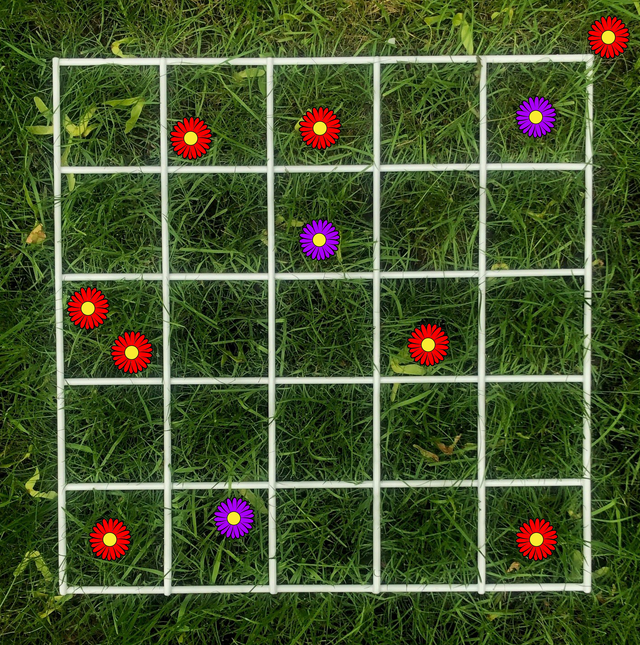
Q3.How might you select random areas to sample using a quadrat?
Q4.When sampling an area using a quadrat, why do you need to make sure that you take as many samples as possible?
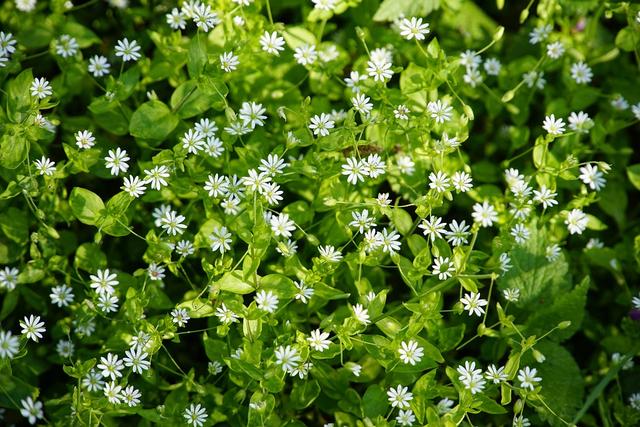
Q5.A pupil records the number of chickweed plants in 5 quadrats. She records the following observations: 4, 7, 9, 5 and 10 plants. What is the mean number of chickweed plants in each quadrat?

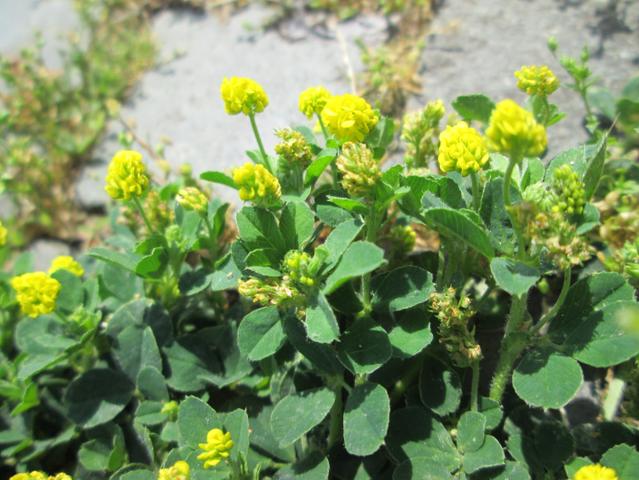
Q6.Black medick plants were sampled using a quadrat (1 m²). After 10 samples, 80 black medick plants were counted. The field is 400 m². What is the estimated population of the plant?

Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.A straight line between two points that is used to take measurements and observations is called a .
Q2.Which of the following are abiotic factors that could be measured in a meadow while sampling an organism?
Q3.Match the words with their definitions.
The number of a species that is found within a habitat.
The range of different species found within a habitat.
The geographical area in which a species can be found.


