Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
The effect of temperature on the rate of decomposition by an enzyme: data analysis and evaluation
I can analyse, explain and evaluate the results of an experiment investigating how temperature affects the rate of decomposition of milk by an enzyme.
- Year 10
- AQA
- Foundation
The effect of temperature on the rate of decomposition by an enzyme: data analysis and evaluation
I can analyse, explain and evaluate the results of an experiment investigating how temperature affects the rate of decomposition of milk by an enzyme.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Calculate rate of reaction where rate = 1/time taken to reach the end point.
- Plot a graph of results (x-axis = temperature and y-axis = rate, or time taken to reach end point).
- Interpret the results and evaluate how well they support the hypothesis.
- Explain the results using ideas about the effect of temperature on the rate of enzyme activity.
Keywords
Rate - The rate is how quickly something takes place. The rate of a reaction is a measure of how much change occurs per unit of time.
End point - The point at which a reaction is complete, often indicated by a change in colour of an indicator.
Hypothesis - A precise, measurable and testable statement based on observations about how something works.
Active site - The part of an enzyme where the substrate binds.
Denature - A permanent change in the shape of an enzyme which stops it from working.
Common misconception
As pH increases above the optimum, enzymes denature and reaction rate falls; but this is not what happens at pHs below the optimum, so the graph and explanation resemble temperature.
The process of denaturing an enzyme is explored in detail, and a graph of reaction rate is explained carefully to make it clear that the changes to rate occur above and below the optimum pH.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: The effect of temperature on the rate of decomposition by an enzyme: data analysis and evaluation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: The effect of temperature on the rate of decomposition by an enzyme: data analysis and evaluation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Living organisms and their environments unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Lesson video
Loading...
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.In most reactions, what will an increase in temperature result in?
Q2.What type of microscopic organisms carry out decomposition?
Q3.In enzyme catalysed reactions, how will an increase in temperature affect the rate of the reaction?
Q4.What is meant by the 'optimum' temperature in an enzyme catalysed reaction?
Q5.Why are moisture levels important in the rate of decomposition?
Q6.What happens to manure (animal waste) that is put onto a field by a farmer?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.In an experiment to determine the effect of temperature on the rate of decomposition by an enzyme, it takes 5 seconds for the indicator to reach the end point. What is the rate of the reaction?
Q2.A range of equipment and chemicals are used in the experiment to determine the effect of temperature on the rate of decomposition by an enzyme. Match the words with their function in the experiment.
enzyme (works on lipids)
indicator (used to measure the end point)
found in milk (the substrate)
the product (decreases pH of the solution)
Q3.At which of the following points are enzymes being denatured?
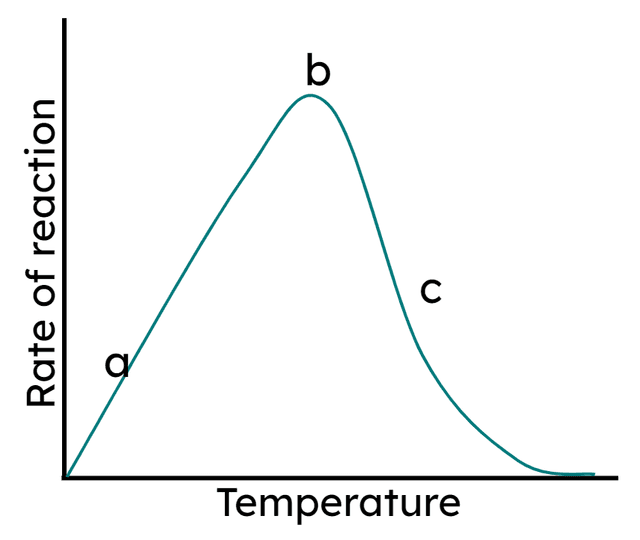
Q4.Point b in the graph is known as the enzyme's optimum temperature. Which of the following statements explains what is happening at point 'b'?

