Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- AQA
- Foundation
Transport systems in plants: phloem and translocation
I can explain how sugars are transported through phloem by translocation.
- Year 11
- AQA
- Foundation
Transport systems in plants: phloem and translocation
I can explain how sugars are transported through phloem by translocation.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Sugars, amino acids and other organic substances (nutrients) are transported in phloem.
- Translocation starts at a source, such as a leaf where sugars are made.
- Sugars are transported into phloem by active transport across the membranes of the living phloem cells.
- Water moves into the phloem cells by osmosis, which increases the pressure and pushes the sugars along the phloem tube.
- Sugars are transported out of the phloem by active transport at a sink, such as a developing root, stem or flower.
Keywords
Phloem - specialised vessels in plants that transport sugar, amino acids and other nutrients
Translocation - the process of transporting sugars and nutrients through the phloem
Source - the location that the sugars or nutrients are loaded during translocation
Sink - the location that the sugars or nutrients are unloaded during translocation
Active transport - the net movement of particles against a concentration gradient using energy
Common misconception
Students get confused between transport in the xylem (water and minerals) and the phloem (sugars).
These sections are covered in separate lessons, each with clear explanations and reinforcing tasks to support learning.
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Transport systems in plants: phloem and translocation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Transport systems in plants: phloem and translocation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Transport and exchange surfaces in plants unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Licence
Lesson video
Loading...
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
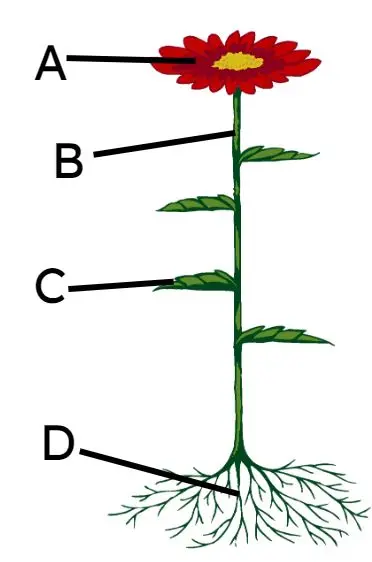
Q1.Which part of the plant pictured - A, B, C or D - absorbs water for photosynthesis?
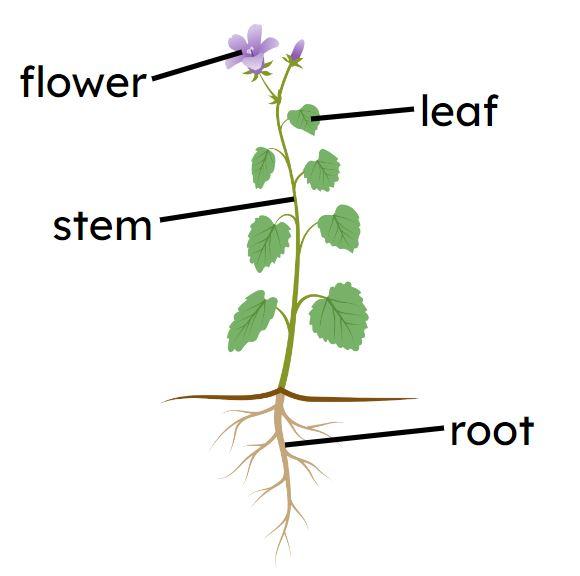
Q2.Which part of the plant is adapted to make a lot of glucose by photosynthesis?
Q3.Name the vessels that transport water from the roots to the leaves in plants.
Q4.What may happen to a non-woody plant if the rate of uptake of water by the roots is less than the rate of transpiration?
Q5.When it is dark at night, plants close their stomata. How will this affect life processes in the plant?
Q6.Which statement explains why the majority of stomata are on the underside of leaves?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Some of the __________ produced by photosynthesis is used in cellular respiration to transfer energy for life processes.
Q2.Which of these statements is correct?
Q3.Match each keyword to the correct meaning.
the loss of water from a plant's leaves
the transport of sugars and other nutrients in plants
specialised tissue for the transport of water and minerals
specialised tissue for the transport of sucrose and amino acids
Q4.Cells in plant leaves are like factories for the production of biological molecules. Match each biological molecule to the components from which it is made.
glucose and nitrate ions
thousands of glucose molecules joined together
glucose and magnesium
