Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- Edexcel
- Foundation
Transport systems in plants: xylem and transpiration
I can explain how water and mineral ions are transported through xylem by transpiration.
- Year 11
- Edexcel
- Foundation
Transport systems in plants: xylem and transpiration
I can explain how water and mineral ions are transported through xylem by transpiration.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
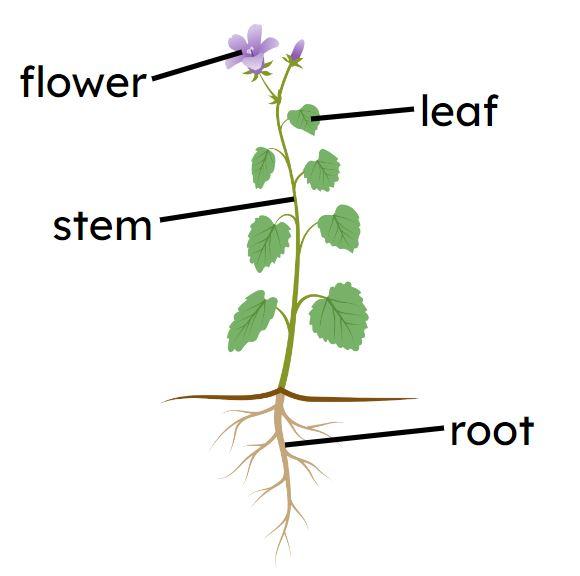
- Water and mineral ions are transported from the roots, up the stem, to the leaves, in vessels made of xylem.
- Xylem is made of dead, empty cells with no cytoplasm, that form a tube with a tough wall made of lignin.
- Water is continually lost from the surface of a plant when water molecules diffuse into the air through open stomata.
- Water is pulled up through xylem tubes to replace the water lost through open stomata; this process is transpiration.
- The water that is pulled through xylem tubes has mineral ions dissolved in it, including nitrate ions.
Keywords
Mineral ions - substances that are essential for healthy plant growth, including nitrates and magnesium
Xylem - specialised vessels in plants that transport water and mineral ions
Stomata - pores in the leaf through which water, oxygen and carbon dioxide can diffuse
Transpiration - the loss of water from a plant’s leaves
Transpiration stream - the continuous movement of water from the roots to the leaves through the xylem
Common misconception
If students fail to understand that water only enters the plant at the roots, and not through the leaves, then the process of transpiration will be very muddled and confused.
The lesson reinforces the pathway that water takes through the plant, clearly stating that water enters at the roots, and showing several times how it moves up through xylem.
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Transport systems in plants: xylem and transpiration, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Transport systems in plants: xylem and transpiration, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Transport and exchange surfaces in plants unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Optional: dyed celery stems.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
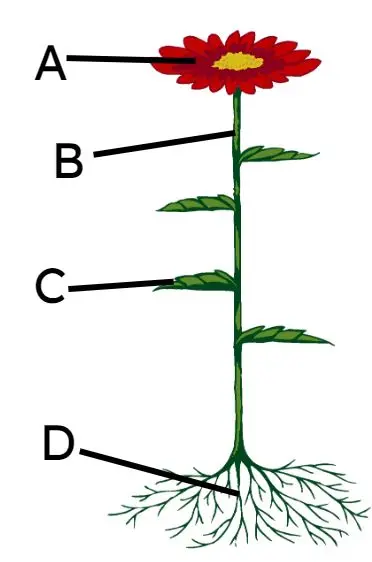
Q1.Which part of a plant absorbs water from the surroundings?
Q2.Producers use water in a process called to make glucose, which requires energy from light.
Q3.Which gas is a reactant in photosynthesis?
Q4.Match each structure to its correct function.
absorb water and minerals from the soil
transport water and minerals from the root to the rest of the plant
pores that open to allow gasses to move in and out of leaves
Q5.How do plants absorb nitrate ions from the soil?
Q6.Plants roots absorb magnesium ions from the soil. Why do plants need magnesium?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What is the name of the part of the plant that has hair cells to absorb water?

Q2.Match each structure to its correct role.
provides a large surface area for the absorption of water and minerals
a tissue in plants that transports water and mineral ions
open and close to enable gas exchange and control water loss
Q3.Stomata are surrounded by two cells that open and close the pore.
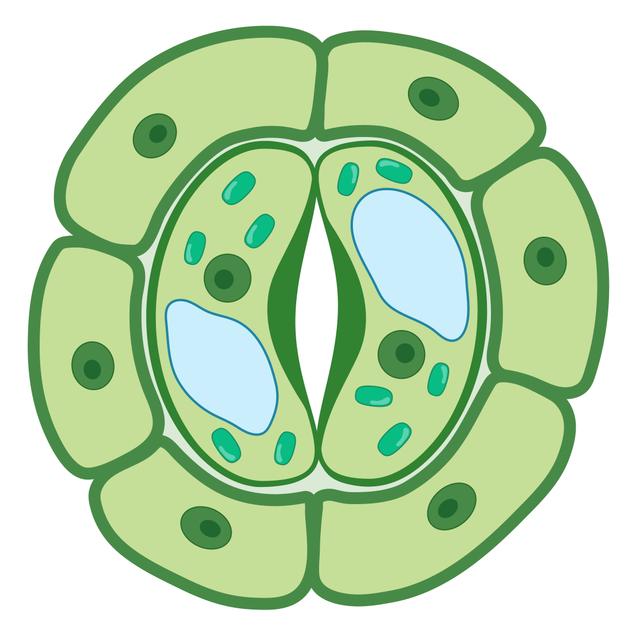
Q4.Which of the descriptions does not apply to xylem?
Q5.Match each term to its correct meaning.
loss of water from the leaves of plants
movement of water from the roots to the leaves of plants
substances needed to make proteins and chlorophyll
plant cells lacking enough water to make them firm
plant cells full of water making them swell and become firm
Q6.In which direction are water and dissolved mineral ions moved through the xylem?