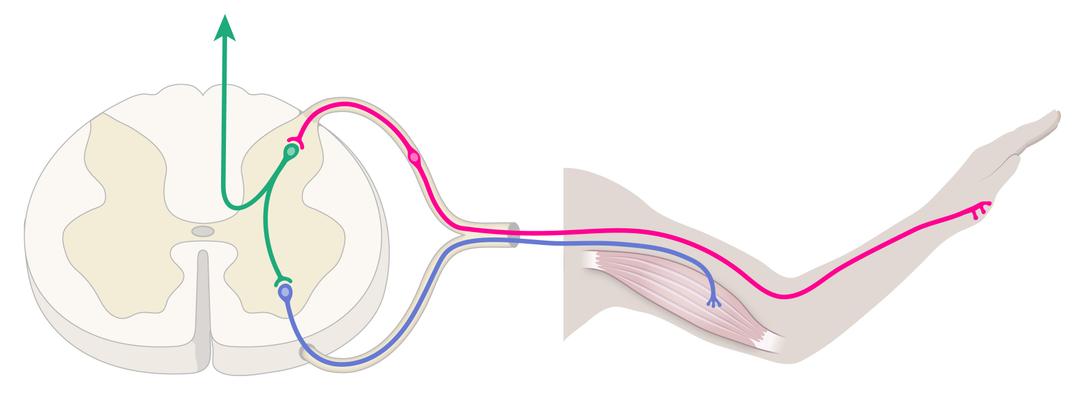
The structure and function of a reflex arc
I can describe what a reflex response is and the path a nerve impulse takes through a reflex arc in the nervous system.
The structure and function of a reflex arc
I can describe what a reflex response is and the path a nerve impulse takes through a reflex arc in the nervous system.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Reflex responses are fast and involuntary, and are essential to the survival of many organisms.
- Reflex responses do not involve a processing centre (e.g. the brain) in the CNS.
- In a reflex arc, the nerve impulse travels across a synapse from the sensory neurone to a relay neurone in the CNS.
- The nerve impulse travels across a synapse from the relay neurone to a motor neurone in the PNS.
- Sometimes the brain can modify (e.g. stop) a reflex response via a neurone to the motor neurone of the reflex arc.
Keywords
Involuntary - Something that occurs without you realising or controlling it.
Reflex response - An involuntary, fast neural response to a situation.
Reflex arc - The fixed neural pathway that controls the reflex response.
Relay neurone - An intermediate neurone that sits within the central nervous system.
Common misconception
What constitutes a reflex response, and how they are generated in the body is often confused and muddled, leading to an incorrect mix between a standard neural pathway and the reflex pathway.
The reflex pathway is clearly stated and explained, and it is compared to the standard neural pathway. Plenty of examples of reflexes are given, including those that occur in other organisms, and there is a quick practical to try too.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: The structure and function of a reflex arc, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: The structure and function of a reflex arc, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Coordination and control: the human nervous system unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
Exit quiz
6 Questions