Hormonal and non-hormonal methods of contraception
I can compare hormonal and non-hormonal methods of contraception.
Hormonal and non-hormonal methods of contraception
I can compare hormonal and non-hormonal methods of contraception.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Hormones can be used as a contraceptive to prevent pregnancy by disrupting the menstrual cycle.
- Some oral hormone contraceptive pills prevent ovulation. If no egg is released, fertilisation cannot take place.
- Reasons why hormone pills may not be 100% effective (e.g. missing/late dose, taking after ovulation).
- Non-hormonal contraceptives act as a barrier to prevent sperm from reaching the egg, so fertilisation cannot occur.
- Evaluating benefits and risks of hormonal and non-hormonal (barrier) methods of contraception (including STIs).
Keywords
Oral contraceptive pill - A contraceptive method; a pill taken regularly, containing hormones.
Ovulation - Process where an egg is released from an ovary.
Fertilisation - Process where the sperm and the egg fuse in the fallopian tube.
Risk - The chance of something causing harm or leading to unwanted consequences.
STI - Sexually transmitted infection.
Common misconception
The contraceptive pill can protect from STIs; that all contraception is 100% effective; there are no side effects to hormonal contraception.
Discuss barrier methods and their benefit in preventing STIs, oral contraceptive can be affected by user error or illness. Oral contraception has side effects but these are less in modern times.
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Hormonal and non-hormonal methods of contraception, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Hormonal and non-hormonal methods of contraception, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Hormones and human reproduction unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Content guidance
- Depiction or discussion of discriminatory behaviour
- Depiction or discussion of violence or suffering
- Depiction or discussion of sexual content
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
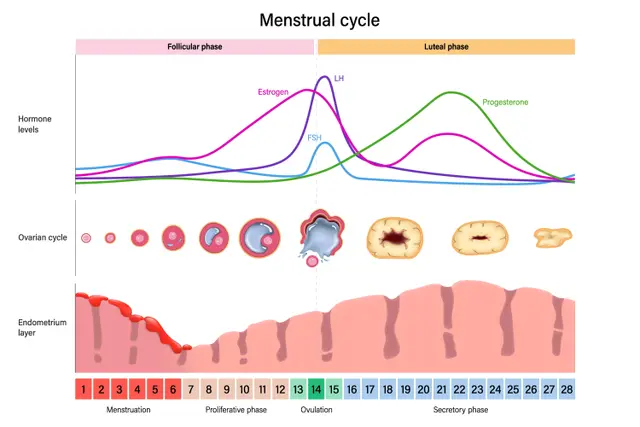
maintains the uterus lining
causes ovulation
causes follicle maturation
Exit quiz
6 Questions







