Explaining effects of substrate concentration and temperature on enzyme rate
I can explain how and why the rate of an enzyme reaction is affected by substrate concentration and temperature.
Explaining effects of substrate concentration and temperature on enzyme rate
I can explain how and why the rate of an enzyme reaction is affected by substrate concentration and temperature.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- The rate of a reaction is the amount of change (e.g. substrate broken down or product made) per unit of time.
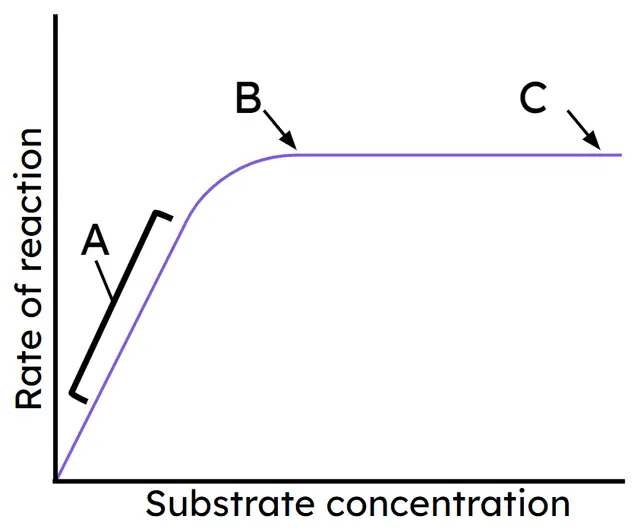
- Enzyme reaction rate increases as substrate concentration increases until an optimum when all active sites are full.
- Enzyme reaction rate increases with temperature due to more collisions, until an optimum when all active sites are full.
- Enzyme rate decreases as temperature increases above the optimum as bonds break and the active site becomes denatured.
- Interpretation of graphs showing effects of substrate concentration and temperature on enzyme reaction rate.
Keywords
Rate of reaction - A measure of how much change occurs per unit of time.
Concentration - A measure of the quantity of a dissolved substance in a given volume of solution.
Optimum - The conditions where maximum rate of reaction occurs.
Bond - A force of attraction between atoms in a compound.
Denatured - A permanent change in the shape of an enzyme that stops it from working properly.
Common misconception
Enzymes die rather than denature.
The word denature is clearly introduced and a CfU explores the word die vs denature.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Explaining effects of substrate concentration and temperature on enzyme rate, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Explaining effects of substrate concentration and temperature on enzyme rate, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Biological molecules and enzymes unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions


Exit quiz
6 Questions
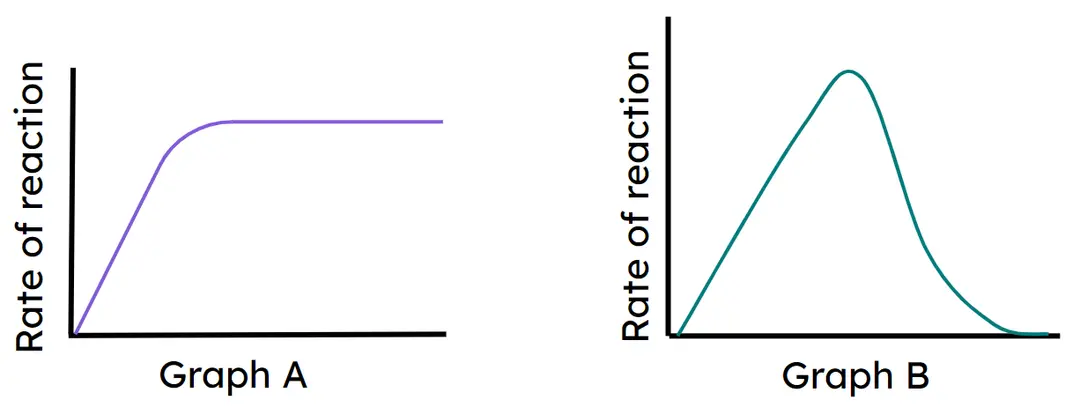
graph B
graph A