Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- AQA
- Higher
Climate change and biodiversity: changes in the distribution of organisms
I can evaluate evidence of the impacts of environmental changes on the distribution of organisms.
- Year 11
- AQA
- Higher
Climate change and biodiversity: changes in the distribution of organisms
I can evaluate evidence of the impacts of environmental changes on the distribution of organisms.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Increasing amounts of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are associated with climate change.
- Changes in ecosystems can affect mean temperature and water availability.
- Changes in ecosystems can leave organisms less well adapted to survive and thrive there.
- Evaluation of data linking changes in atmospheric gases and changes in biodiversity.
- Evaluation of data linking changes in water availability and changes in biodiversity.
Keywords
Greenhouse gas - a gas responsible for the greenhouse effect by absorbing and re-radiating infrared radiation that warms the atmosphere
Climate change - a long-term shift in weather patterns
Distribution - where species are located
Abundance - how many individuals of a species are present
Biodiversity - the range of different living organisms (species) that live in a place
Common misconception
A common misconception is that a small increase in greenhouse gases and a small rise in Earth's temperature will not have much impact on organisms on Earth beyond land ice melting.
The lesson discusses how small changes in weather patterns can have a significant impact on organisms as their habitats change and no longer provide them with food, shelter and a place to reproduce.
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Climate change and biodiversity: changes in the distribution of organisms, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Climate change and biodiversity: changes in the distribution of organisms, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Maintaining biodiversity and human impacts unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following are examples of conservation?
Q2.The destruction of habitats through deforestation causes...
Q3.Eutrophication reduces biodiversity in aquatic habitats when...

Q4.A species which is naturally found in an area is called a species.
Q5.Why might a population of an invasive species grow quickly?
Q6.What are reasons why species become endangered?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Why might a species become extinct as a result of climate change?
Q2.What does the term 'distribution of a species' mean?
Q3.Why is climate change causing sea levels to rise?
Q4.Which of the following is not a main factor that affects the distribution of organisms?
Q5.A species of plant is found in mountains at altitudes between 800 m and 1000 m where the temperature is colder. What will happen to the species of plant as the Earth's temperature increases?

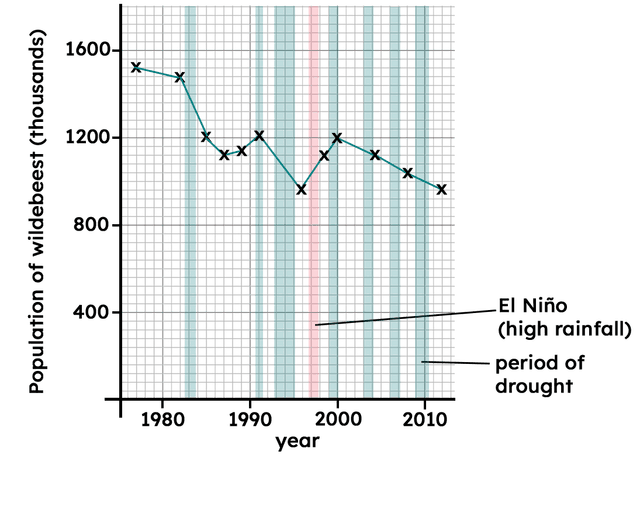
Q6.What trends or patterns are shown in the graph of the population of wildebeest from 1990-2010?