Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- AQA
- Higher
Evaluating the global use of vaccination
I can evaluate the benefits and risks of vaccinations, and explain the role herd immunity plays in reducing the spread of disease.
- Year 11
- AQA
- Higher
Evaluating the global use of vaccination
I can evaluate the benefits and risks of vaccinations, and explain the role herd immunity plays in reducing the spread of disease.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Vaccines have had a positive effect on public health (e.g. the eradication of smallpox).
- Vaccination is not risk free as it can have side effects, but the benefits outweigh the risks.
- New vaccines are trialled, and are only approved for use when the benefits of the vaccination outweigh the risks.
- It is necessary to vaccinate a high proportion of a population against a pathogen to provide herd immunity.
- Herd immunity helps protect those who can’t or won’t have the vaccination.
Keywords
Vaccination - The process of administering a vaccine to an individual to create immunity to a pathogen.
Vaccine - A formulation that contains an inactive pathogen, or parts of it.
Immunity - Immunity is established after the body is first exposed to a pathogen's antigens, and enables white blood cells to respond quickly to the antigen when the body is re-exposed to it.
Risk - A possible negative outcome.
Herd immunity - When a high proportion of the population have been vaccinated against a disease, the spread is reduced and unvaccinated individuals may be protected.
Common misconception
The MMR vaccination causes autism.
The study by Dr Wakefield is highly flawed, and has been discredited. Many subsequent studies have found no link between the MMR vaccination and autism. Measles is a highly infectious disease that can have devastating consequences.
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Evaluating the global use of vaccination, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Evaluating the global use of vaccination, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Defences against pathogens, the human immune system and vaccination unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Content guidance
- Depiction or discussion of sensitive content
Supervision
Adult supervision recommended
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.White blood cells called lymphocytes make proteins called against pathogens.
Q2.Lymphocytes make antibodies that are specific to one on a pathogen.
Q3.Which statement about vaccines and vaccination is correct?
Q4.When a person has been vaccinated against a pathogen, they are protected by cells that remain in their body.
Q5.The protection provided by memory cells is called __________.
Q6.After vaccination, if the pathogen from the vaccine enters the body again, memory cells quickly respond by making .
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match each word to its correct meaning.
a formulation containing an inactive pathogen
the process of injecting a formulation containing an inactive pathogen
long-lasting protection against a pathogen
Q2.Which disease has been eradicated through the use of a global vaccination programme?
Q3.Who is correct?



Q4.A vaccine is only approved for widespread use when evidence shows that …
Q5.When a very high percentage of the population has been vaccinated against a pathogen, this provides immunity.
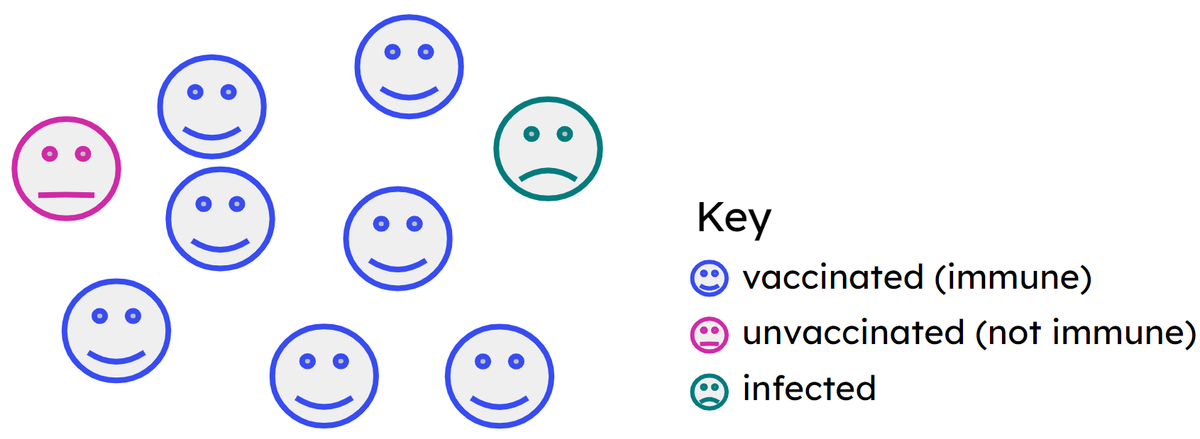
Q6.Which statements explain why herd immunity is important?



