Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- AQA
- Higher
- Year 10
- AQA
- Higher
The genetic code
I can describe how instructions for making proteins are coded into DNA.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- DNA is a polymer of four different nucleotides (A, C, G and T).
- Proteins are polymers of amino acids.
- The sequence of nucleotides in a gene determines the order of amino acids in a protein.
- Each set of three nucleotides is a triplet code that corresponds to an amino acid, this code is universal.
- Different organisms have different sequences of nucleotides in their DNA, but share this common coding system.
Keywords
DNA - A large chemical molecule made of smaller chemical groups, it carries the genetic code of all living organisms.
Polymer - A chemical made up of smaller repeating chemical groups.
Protein - A chemical substance whose structure is coded for by the genetic code in genes.
Amino acid - A small chemical group that makes up a protein polymer, there are 20 types.
Nucleotide - A chemical group that make up the building blocks of DNA, the four types are coded A, T, C and G.
Common misconception
Genes, DNA and chromosomes are used interchangeably rather than understanding their separate definitions; also that organisms such as animals and plants are not related.
Use images to show the difference between DNA, genes and chromosomes; display a phylogenetic tree so the common ancestry of all living organisms can be visualised and so the commonality of DNA between all life.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: The genetic code, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: The genetic code, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the DNA and the genome unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Starting with the largest, put the structures in order of decreasing size.
Q2.What does the order of nucleotide bases in a gene determine?
Q3.What is the name of the type of molecule that acts as a catalyst in living organisms?
Q4.The diagram shows a single nucleotide. Which part of the nucleotide joins the two strands of a DNA molecule together?
Q5.One strand of a DNA molecule has the base sequence A A T C G A G C A.
Which is the complementary base sequence on the other strand of the DNA molecule?
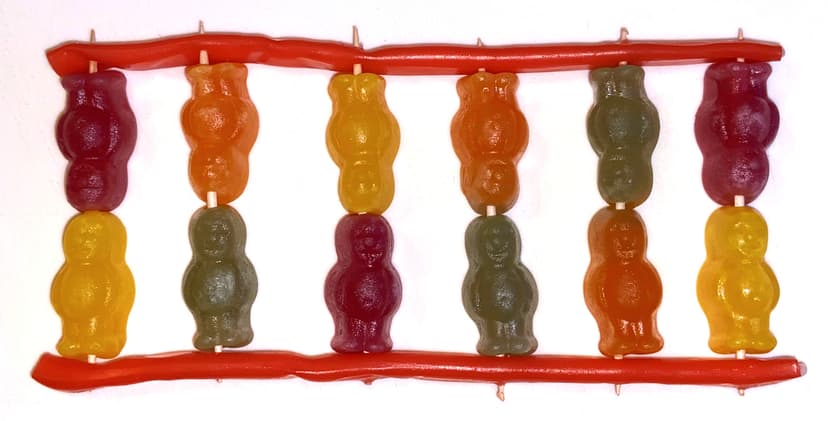
Q6.The photograph shows a model of DNA made from jelly babies and liquorice sticks.
In this model, which parts of the nucleotide molecules are represented by the liquorice sticks?

Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match each word to its meaning.
a polymer that carries the genetic code for all living organisms
small chemical group; 4 types (ATCG) are joined together to make DNA
long chain molecule made of small chemical groups joined together
a polymer that can be structural or functional, coded for by a gene
Q2.The diagram shows a nucleotide. DNA molecules have four types of nucleotides.
Which sub units are the same in all four types?



