Cells
I can identify that all cells have some structures in common and I can explain that all organisms are unicellular or multicellular.
Cells
I can identify that all cells have some structures in common and I can explain that all organisms are unicellular or multicellular.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- All organisms (including animals, plants, fungi and micro-organisms) are made up of one or more living cells.
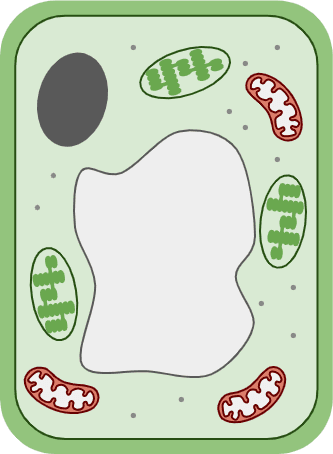
- All cells have some structures in common (cell membrane and cytoplasm) and have a three-dimensional shape.
- Chemical reactions essential to life occur in cytoplasm; the cell membrane regulates the cell’s internal environment.
- Many animals and plants are multicellular; they are made up of many cells organised to form tissues and organs.
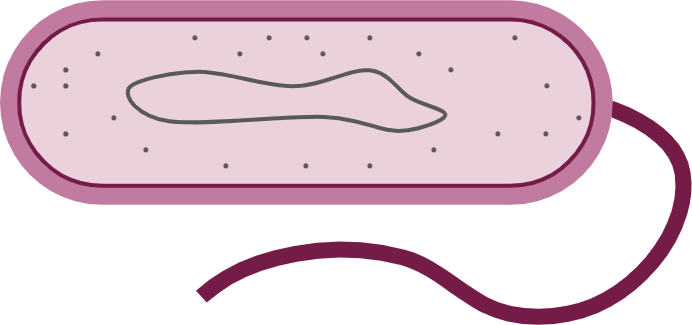
- Micro-organisms such as bacteria are unicellular – they are made of just one cell.
Keywords
Organism - A living thing made of one or more cells.
Cell - The basic unit of all forms of life.
Multicellular - An organism made of many cells.
Micro-organism - An organism that can only be viewed through a microscope.
Unicellular - An organism that consists of a single cell.
Common misconception
Pupils may think that all animals and plant are multicellular and that all unicellular organisms are bacteria.
Lesson explicitly addresses this misconception and the questions in Task A are designed to expose the misconception.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Cells, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Cells, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
Exit quiz
6 Questions
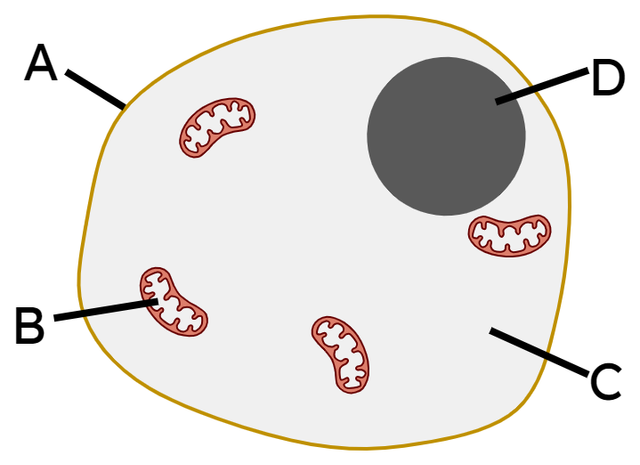
jelly-like substance where chemical reactions take place
contains DNA, which controls the cell activities
where energy is released through aerobic respiration
contains cellulose, which provides strength and support to cell
where protein synthesis occurs
controls what enters and exits the cell
contains sap which helps keep the cell turgid
contains chlorophyll, which is where photosynthesis occurs


