Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- AQA
- Higher
Selective breeding and human food security
I can explain what is meant by selective breeding and why it is important for human food security.
- Year 10
- AQA
- Higher
Selective breeding and human food security
I can explain what is meant by selective breeding and why it is important for human food security.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Some plants and animals have features that are useful to us (e.g. they can provide food and materials, or do work).
- Selective breeding by humans causes particular features to become more (or less) common in the species.
- After many generations, the resulting domesticated species can be quite different to their wild ancestors.
- Examples of the selective breeding of a farm animal and a crop from their wild ancestors.
- The dependence of humans on domesticated animals and crops for food security.
Keywords
Selective breeding - The process in which humans choose individuals with desirable traits and mate them in order to make offspring with these desirable traits.
Crop - Plants grown on a large scale for food or profit.
Domesticated - An animal that has been tamed and is kept as a pet or on a farm.
Farm animal - Animals that are kept on farms for food or work.
Food security - A measure of the quantity and quality of food available to support households or whole communities.
Common misconception
Students often forget that selective breeding is a process that happens over many generations.
This lesson includes examples of how to describe the process of selective breeding.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Selective breeding and human food security, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Selective breeding and human food security, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Fossil evidence, selective breeding and explaining evolution unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Content guidance
- Depiction or discussion of sexual content
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Lesson video
Loading...
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Why are there no fossils younger than 10 000 years?
Q2.Match the words to their meaning.
All the fossils ever found.
A species which has no living individuals remaining anywhere.
Changes in the characteristics of a species over many generations.
An ancestor species shared by several other species.
A species with characteristics between an ancestor and a later species
Q3.Which layer of sedimentary rock will contain the youngest fossils?
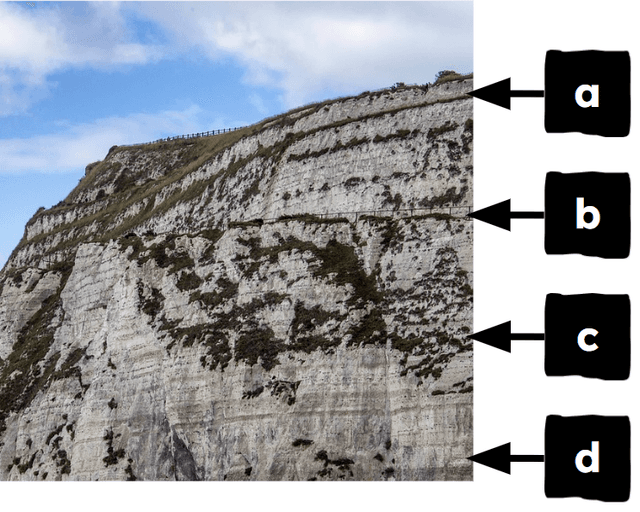
Q4.Scientists think Archeopteryx and modern birds share a common ancestor, but there is a gap in the fossil record. Why are there gaps in the fossil record?
Q5.Which species is the common ancestor?
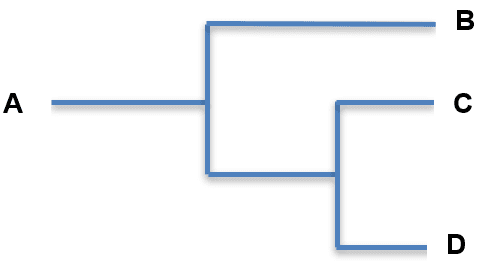
Q6.The diagram shows a suggestion for the evolution of the hippopotamus and some modern whales. Which statement is correct?