Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- AQA
- Higher
Observing xylem and phloem using a light microscope: practical
I can use a light microscope to observe xylem and phloem, and calculate the actual size of the structures.
- Year 11
- AQA
- Higher
Observing xylem and phloem using a light microscope: practical
I can use a light microscope to observe xylem and phloem, and calculate the actual size of the structures.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- The parts of a light microscope and their functions.
- The method for using a light microscope to observe xylem and phloem, including changing the magnification and focus.
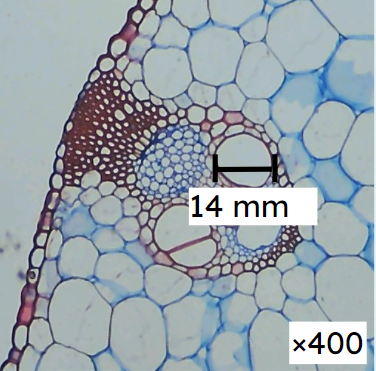
- Light microscopy can be used to observe xylem and phloem in a cross-section of a plant shoot, root or leaf.
- The magnification and actual size of structures observed with a microscope can be calculated.
Keywords
Light microscope - an instrument that uses visible light and lenses to magnify a viewed specimen
Magnification - the number of times greater in size the viewed object is compared to its actual size
Xylem - specialised vessels in plants that transport water and mineral ions
Phloem - specialised vessels in plants that transport sugar, amino acids and other nutrients
Common misconception
Incorrectly calculating the total magnification by adding the magnification of the eyepiece lens to the magnification of the objective lens.
The correct way to calculate the total magnification (by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of the objective lens) is practiced.
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Observing xylem and phloem using a light microscope: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: Observing xylem and phloem using a light microscope: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Transport and exchange surfaces in plants unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Light microscope, pre-prepared microscope slides of cross-sections of plant shoot or leaf.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What are the two main types of vascular tissues in plants?
Q2.What is the function of xylem in plants?
Q3.Which unit is used to measure very small structures, such as cells?
Q4.What unit is smaller than a micrometre?
Q5.What is the function of phloem in plants?
Q6.Match the letters from the image to their names.
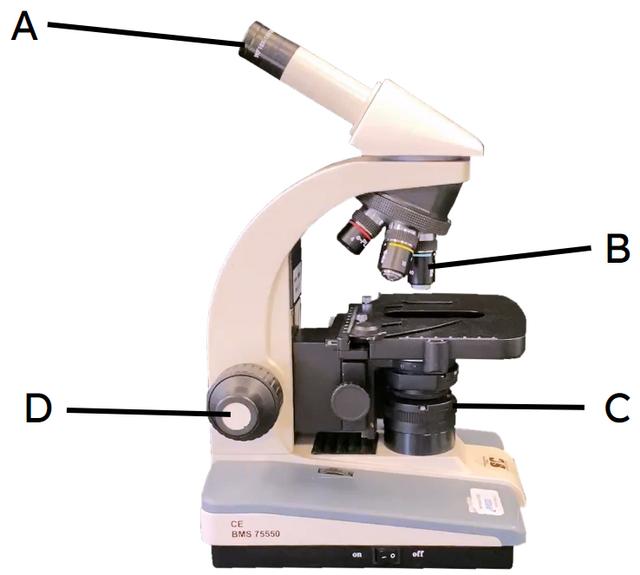
eyepiece lens
objective lenses
light source
focus wheel
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.How do you calculate magnification?
Q2.Which of the following best describes phloem transport?
Q3.What is the total magnification of a microscope with a 100x objective lens magnification and a 40x eyepiece lens magnification.
Q4.A microscope has a total magnification of 400x. If it has a 100x objective lens magnification. What is the eyepiece lens magnification?
Q5.The image size of a specimen is...
Q6.What is the actual size of the xylem vessel that appears to be 14 mm across in this image?