Specialised cells, unspecialised cells and differentiation
I can describe examples of specialised cells in humans and plants, and explain how unspecialised cells become specialised.
Specialised cells, unspecialised cells and differentiation
I can describe examples of specialised cells in humans and plants, and explain how unspecialised cells become specialised.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Most cells in multicellular organisms are specialised – they have structures that are adapted for the jobs the cells.
- Multicellular organisms grow (make new cells by mitosis) and develop (make specialised cells to form tissues/organs).
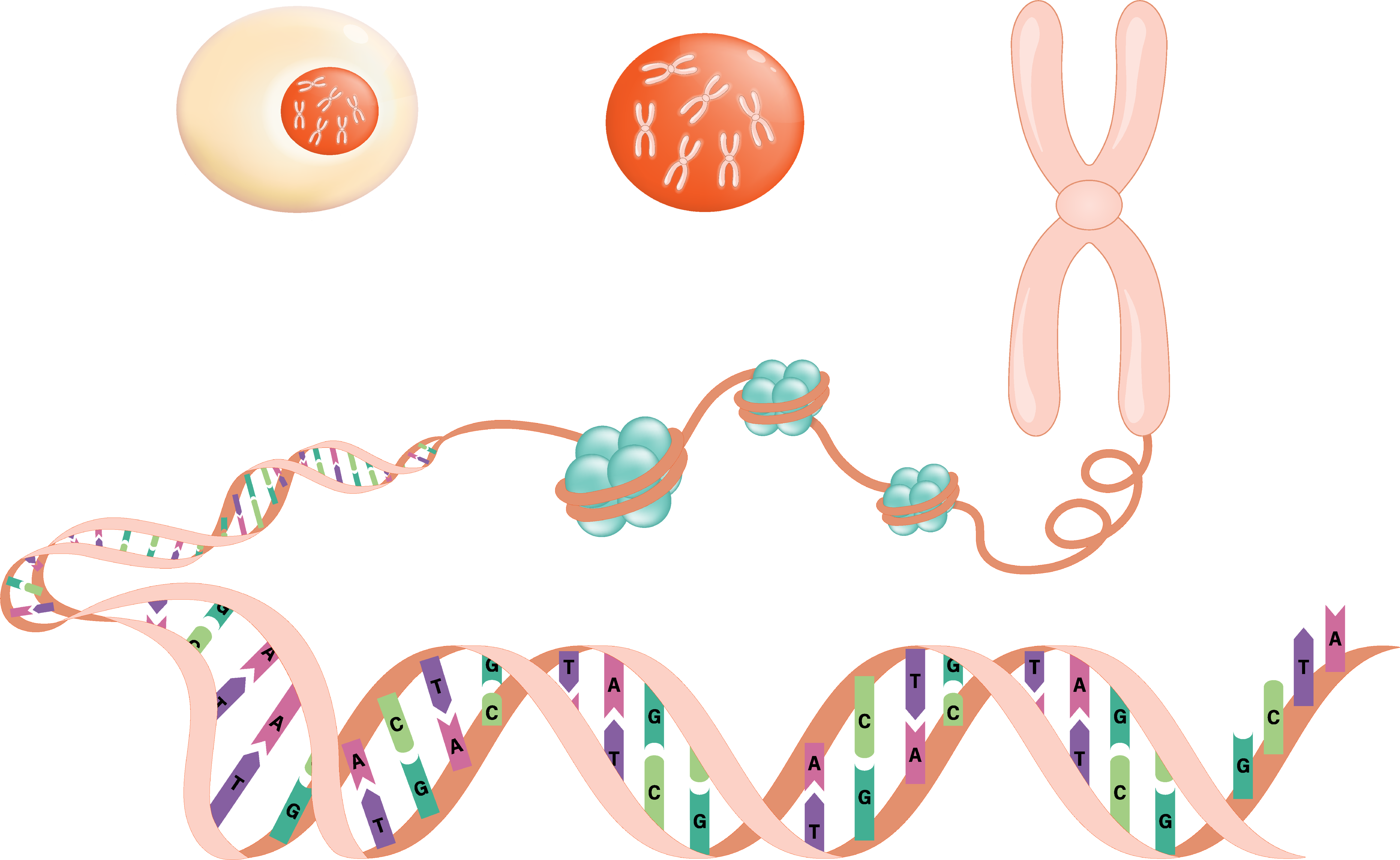
- Unspecialised cells become specialised through a process called differentiation.
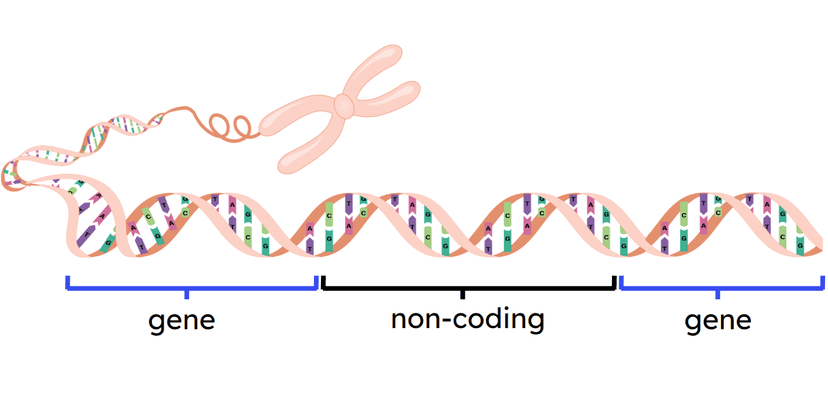
- During differentiation, particular genes in the cell’s genome are switched off or on.
- Specialised cells only use particular genes, so only make the proteins needed for the job they are adapted to do.
Keywords
Multicellular - Animal, plants and fungi made of more than one cell.
Specialised cell - Cells with adaptations to carry out a particular function in a multicellular organism.
Unspecialised cell - Cell with no specific function, but has the capability to turn into different types of cells.
Differentiation - The process of an unspecialised cell becoming a specialised one through the mechanism of turning genes on and off.
Gene - A short section of DNA that carries the genetic code to produce a protein.
Common misconception
Only animals are multicellular; that specialised cells are individual; all DNA in a cell is the same so will produce the same proteins.
Examples of multicellular plants, with specialised cells, tissues and organs provided; show images of cells as tissues rather than just individual. All cells have the same DNA, but it is whether the genes are turned on that makes them specialise.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Specialised cells, unspecialised cells and differentiation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Specialised cells, unspecialised cells and differentiation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Stem cells and differentiation unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions

Exit quiz
6 Questions
Stores nutrients for cell growth.
Lots of mitochondria to provide energy for movement.
Lots of mitochondria to provide energy for contraction.
Folded membrane to increase surface area for absorption.
Gaps in the cell wall to allow sugars to be transported.
Waxy layer for protection.