Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- OCR
- Higher
The effect of pH on the rate of an enzyme reaction: data analysis
I can analyse and explain data from an investigation into the effect of changing pH on the rate of an enzyme reaction.
- Year 10
- OCR
- Higher
The effect of pH on the rate of an enzyme reaction: data analysis
I can analyse and explain data from an investigation into the effect of changing pH on the rate of an enzyme reaction.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Interpretation of graphs showing data from an investigation of the effect of pH on the rate of an enzyme reaction.
- Consideration of whether the data increase or decrease confidence in the original prediction or hypothesis.
- Enzyme reaction rate is highest at an optimum pH, at which all active sites are full.
- Enzyme reaction rate decreases at pH values below and above the optimum as the active site becomes denatured.
Keywords
Rate of reaction - How fast a chemical reaction occurs.
PH - A measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is.
End point - The point at which the chemical reaction has finished.
Active site - The part of an enzyme where the substrate binds.
Denatured - A permanent change in the shape of an enzyme which stops it from working.
Common misconception
As pH increases above the optimum, enzymes denature and reaction rate falls, but this is not what happens at pHs below the optimum, so the graph and explanation resemble temperature.
The process of denaturing an enzyme is explored in detail, and a graph of reaction rate is explained carefully to make it clear that the changes to rate occur above and below the optimum pH.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: The effect of pH on the rate of an enzyme reaction: data analysis, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: The effect of pH on the rate of an enzyme reaction: data analysis, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Biological molecules and enzymes unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What is iodine used to test for the presence of?
Q2.Which piece of equipment would you use in this practical to heat the test tubes of starch and amylase to a specific temperature?
Q3.Which of these are examples of continuous sampling?
Q4.What does amylase break starch down into?
Q5.What is this piece of equipment called?
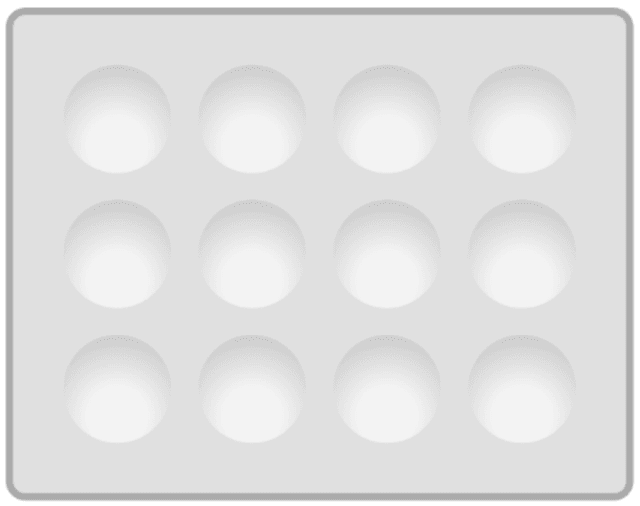

Q6.Which numbered dimple(s) shows that all the starch has been digested?
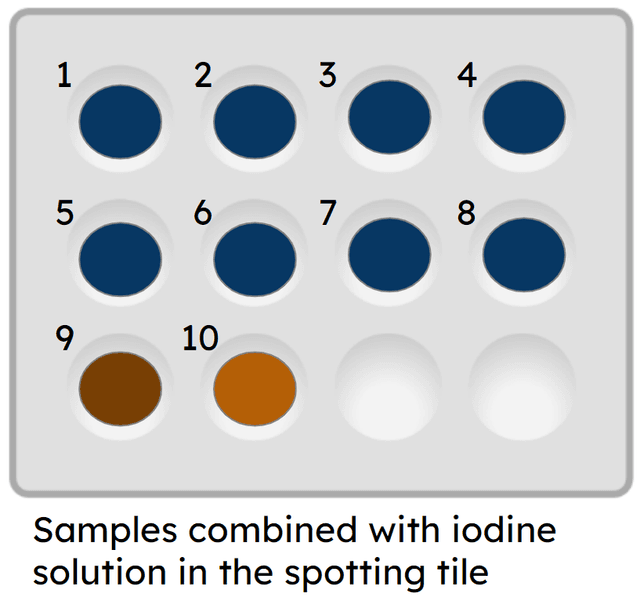
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which statement defines the term ‘rate of reaction’?
Q2.Calculate the missing rate of reaction.

Q3.On which axis would you plot the rate of a reaction, when it is plotted against pH?
Q4.In the graph below which letter shows when an enzyme is at its optimum temperature?
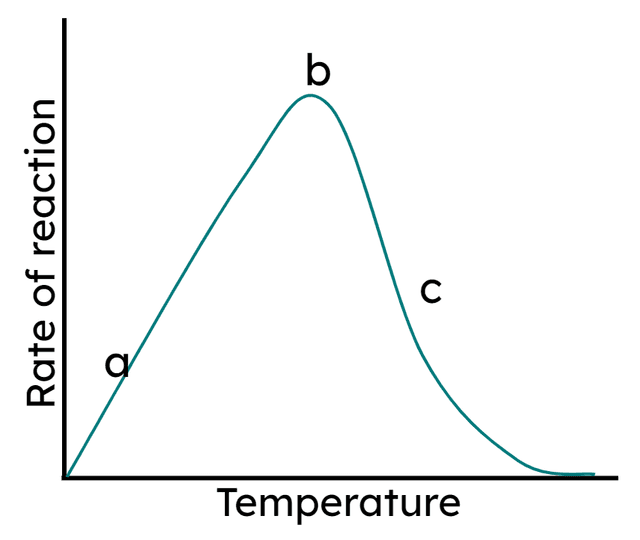
Q5.When enzyme reaction rate is at its highest all the sites are full.



