Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- OCR
- Higher
The importance of maintaining constant conditions in the body
I can explain why it is important for humans to maintain constant conditions inside the body.
- Year 11
- OCR
- Higher
The importance of maintaining constant conditions in the body
I can explain why it is important for humans to maintain constant conditions inside the body.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- If conditions in the body change too much this can be dangerous to our health.
- Changes in body temperature affect the rate of chemical reactions and can impact enzyme activity.
- Changes in body temperature can lead to hypo- or hyperthermia and death.
- Changes in water balance in the body can lead to dehydration and death.
- Use of antagonistic effects to maintain a constant environment.
Keywords
Enzyme - a protein that acts as a biological catalyst
Internal body temperature - the optimal internal temperature of our body, which is about 37°C
Homeostasis - the regulation of the internal conditions to maintain optimum conditions for enzyme action and all cell functions
Antagonistic - effectors and effects that work against each other
Common misconception
It is common for pupils to misunderstand the links between increased or decreased body temperature and the impact on enzyme function.
Explanations of the effect of temperature on enzyme activity, the link between body temperature and enzyme function, and conditions such as hyper- and hypo-thermia are made and explored in this lesson.
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: The importance of maintaining constant conditions in the body, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 biology lesson on: The importance of maintaining constant conditions in the body, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Coordination and control: maintaining a constant internal environment unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Optional: Bunsen burner, tripod, gauze, heat proof mat, thermometer, beaker, ice cubes.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Below is a simplified diagram of an enzyme. What is shown by A?

Q2.Which of the following are effectors?
Q3.True or false? Enzymes are catalysts.
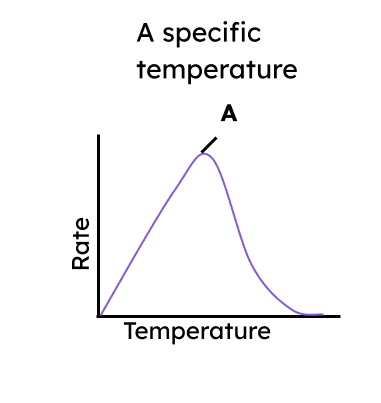
Q4.The graph shows the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction. Point A represents the temperature for the enzyme.
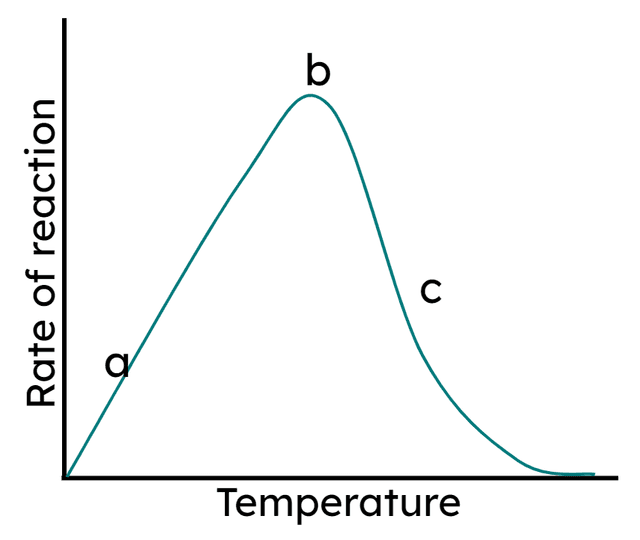
Q5.The graph shows the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction. Why is the rate of reaction decreasing at point c?
Q6.If a significant increase in body temperature is sustained, it can lead to ...
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.The maintenance of a constant internal environment is known as .
Q2.True or false? All enzymes work optimally at pH 7 and 37 °C.
Q3.What name is given to enzymes whose active site has changed shape and no longer fits to its substrate?
Q4.Order the statements below to describe how the body responds to an increase in body temperature.
Q5.The Oak pupils are discussing the control of water levels in the body. Who is correct?






