Plant diseases: TMV, crown gall disease and barley powdery mildew
I can describe examples of common diseases in plants, how they spread, and ways to reduce the spread.
Plant diseases: TMV, crown gall disease and barley powdery mildew
I can describe examples of common diseases in plants, how they spread, and ways to reduce the spread.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Tobacco mosaic virus is an example of a disease in plants caused by a virus.
- Crown gall disease is an example of a disease in plants caused by a bacterium.
- Barley powdery mildew is an example of a disease in plants caused by a fungus.
- Ways in which plant diseases can be spread, and ways in which the spread can be reduced.
- Impacts of plant diseases, including on biodiversity and human food security.
Keywords
Virus - A non-living infectious agent that replicates inside a host cell.
Fungus - A eukaryotic, spore-producing organism that feeds on organic matter.
Food security - A measure of the quantity and quality of food available to support households and whole communities.
Biodiversity - Variety of living organisms within an ecosystem.
Common misconception
Only human and other animals can catch diseases. Plant diseases are not important.
This lesson explores examples of plant diseases, the pathogens that cause them and how they are spread, and their devastating impacts.
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Plant diseases: TMV, crown gall disease and barley powdery mildew, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 biology lesson on: Plant diseases: TMV, crown gall disease and barley powdery mildew, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 biology lessons from the Health and disease unit, dive into the full secondary biology curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Content guidance
- Depiction or discussion of sensitive content
- Depiction or discussion of violence or suffering
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
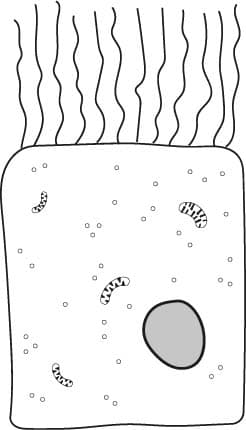
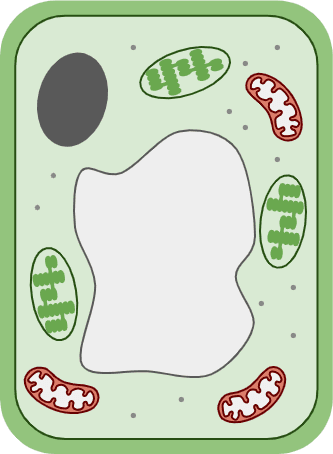
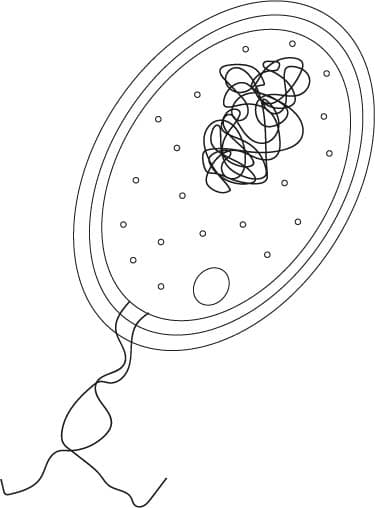
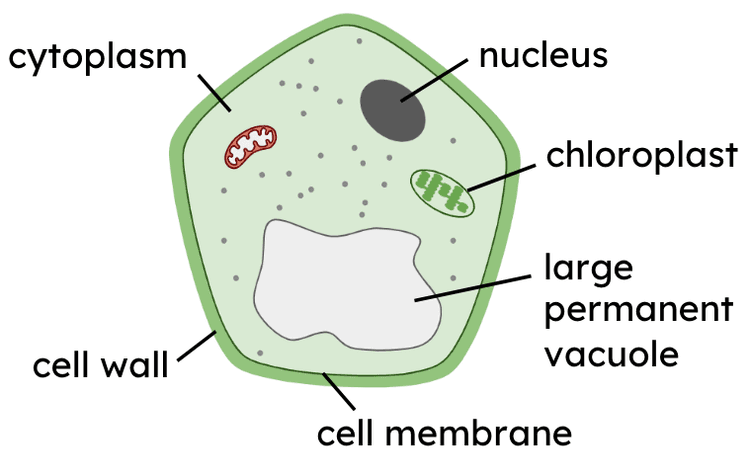
fungus
protist
bacteria
virus
Exit quiz
6 Questions





