Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- AQA
- Foundation
Comparing materials and their properties
I can compare the properties of glass, clay ceramics, polymers, composites, and metals; and explain how the properties of materials are related to their uses.
- Year 11
- AQA
- Foundation
Comparing materials and their properties
I can compare the properties of glass, clay ceramics, polymers, composites, and metals; and explain how the properties of materials are related to their uses.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Production processes for industrial materials are under continuous development, with new materials discovered.
- Several factors direct a choice of materials: performance, production processes, cost, aesthetics, and others.
- Composites are mixtures of materials made up of a matrix and a reinforcement.
- Qualitative data describes properties, while quantitative data measures properties numerically.
Keywords
Material - A physical substance that things can be made from.
Composite - A mixture of materials (matrix and reinforcement), combined to produce a material with properties of both.
Matrix - In a composite material, it is the substance that binds the reinforcement material together.
Reinforcement - In a composite material, it is the substance that is bound together by the matrix material.
Quantitative data - Information that can be counted or measured, and given a numerical value.
Common misconception
Students often think: all glass types have the same properties and uses; polyethene types are identical in structure and use; and composites are simple mixtures (not engineered materials).
Clarify that soda-lime and borosilicate glass differ in production and use. Explain the distinct processes and uses of LDPE and HDPE. Describe how composites are engineered to achieve specific properties.
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Comparing materials and their properties, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Comparing materials and their properties, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 chemistry lessons from the Industrial chemistry unit, dive into the full secondary chemistry curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the keywords to the correct definitions.
a mixture of two or more elements; at least one element is a metal
a hard, brittle, heat-resistant material
made from at least two types of materials, with improved properties
makes up everything around us; can be natural or human-made
shiny, hard material that is good thermal and electrical conductor
long chained molecules formed by joining together monomers
Q2.Which picture shows a model of a branched polymer?

Q3.Which picture shows a model of a polymer with plasticisers?




Q4.A chemical bond is a strong force that holds atoms together in a compound. A chemical bond takes a lot of energy to overcome and break.
Which of the following statements are correct?
Q5.A practical method for scientists to determine the physical properties of materials is by conducting tests. How can you distinguish between plain and reinforced concrete if the pieces look similar?
Q6.Which picture shows a model of a cross-linked polymer?




Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match these key terms to the correct definitions.
materials combined to produce materials with improved properties
a physical substance that things can be made from
in composite: substance that binds reinforcement material together
information that can be counted or measured, and given numerical value
in composite: substance bound together by the matrix material
Q2.Soda-lime glass is made from readily available materials. Borosilicate glass requires rarer compounds but its property makes it possible to use in high heat applications such as lab glassware.
Q3.Considering performance, sustainability or aesthetics can lead to discovery of new materials. Composites are typically more expensive than aluminium. What makes carbon fibre better for aircraft wings?
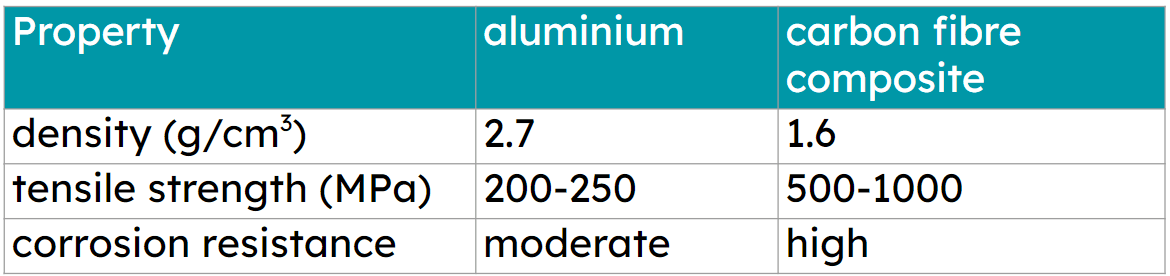
Q4.Quantitative data is essential for precise comparisons and decision-making in material selection. Which of the following properties can provide quantitative data for this?
Q5.Match these terms to the correct descriptions.
ability of material to withstand pushing force without being squashed
non-numerical information describing properties e.g. texture or colour
numerical information of measurable properties e.g. time or distance
ability of material to withstand pulling force without stretching
ability of material to absorb shock without breaking
Q6.Thermosoftening polymers can be reheated, melted and reshaped multiple times due to their linear chain structure. Thermosetting polymers decompose instead of melting because of their .



