Distillation: fractional distillation
I can explain how fractional distillation works and how it differs from simple distillation in separating mixtures of fluids.
Distillation: fractional distillation
I can explain how fractional distillation works and how it differs from simple distillation in separating mixtures of fluids.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Fractional distillation is an extension of simple distillation, and is mostly used to separate mixtures of liquids.
- A main distinction between fractional and simple distillation is that the former uses a fractionating column.
- Fractional distillation has multiple real-world examples, including the fractional distillation of air.
- Fractional distillation produces fractions; these can be pure or mixtures of chemicals with very similar boiling points.
Keywords
Fraction - A fraction is a component of a mixture that has been separated by fractional distillation.
Fractional distillation - Fractional distillation is a method used to separate miscible fluids (liquids or gases) with different boiling points into individual components (fractions).
Miscible - Fluids that dissolve in another fluid are described as miscible in that fluid.
Boiling point - The temperature at which a substance changes between a liquid state and a gas state is known as its boiling point.
Fractionating column - A fractionating column is a piece of apparatus within which a temperature gradient develops. It is used during fractional distillation.
Common misconception
Pupils sometimes think that heating a substance strongly and for extended periods will improve the quality of separation via distillation.
Stress that distillation is a skill which requires careful control of heating so only one substance is in the condenser at a time. Understanding the link between application of heat to the mixture, boiling point and reading a thermometer is essential
To help you plan your year 10 chemistry lesson on: Distillation: fractional distillation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 chemistry lesson on: Distillation: fractional distillation, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 chemistry lessons from the Separating substances unit, dive into the full secondary chemistry curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Content guidance
- Depiction or discussion of sensitive content
Supervision
Adult supervision recommended
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
at a fixed temperature.
over a range of temperatures.
of one element or compound only.
of more than one element and/or compound.
not be separated.
be separated.
Exit quiz
6 Questions
separate two miscible liquids with very different boiling points.
to separate multiple miscible fluids with a range of boiling points.
to create a temperature gradient to separate fluids into fractions.
pure substances, or mixtures with similar boiling points.
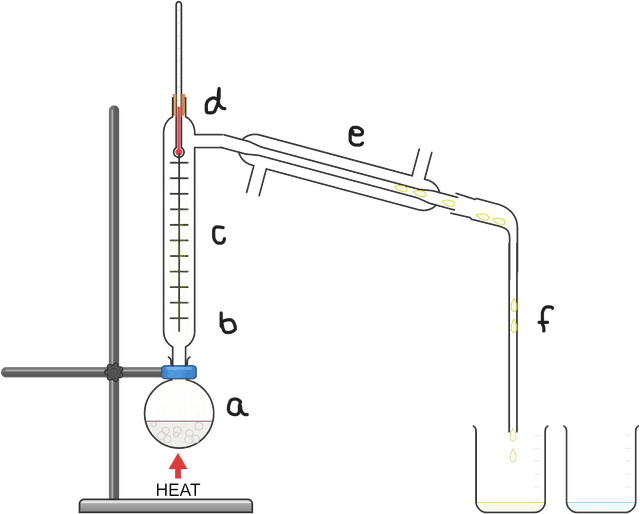
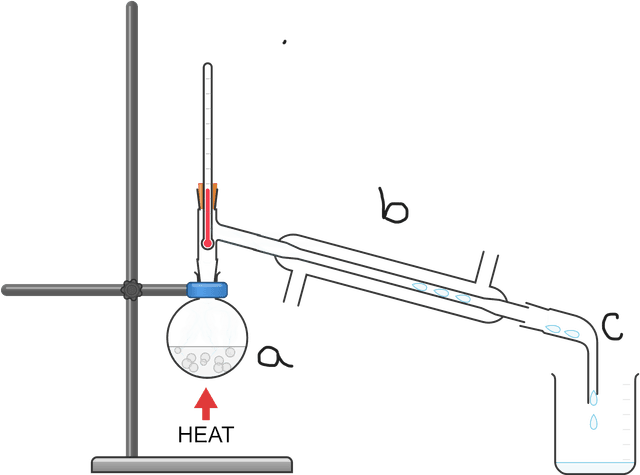
miscible fluid mixture is heated and starts to boil forming a vapour
the vapour passes up the fractionating column, heating the bottom
most substances cool as they rise up the column and drip back down
lower boiling point substances pass as gases into the condenser
these gases are cooled in the condenser back into the liquid state
the condensed liquid is collected as the distillate fraction


