Human activity and climate change
I can evaluate evidence for human activity causing climate change.
Human activity and climate change
I can evaluate evidence for human activity causing climate change.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
These resources were created for remote use during the pandemic and are not designed for classroom teaching.
Lesson details
Key learning points
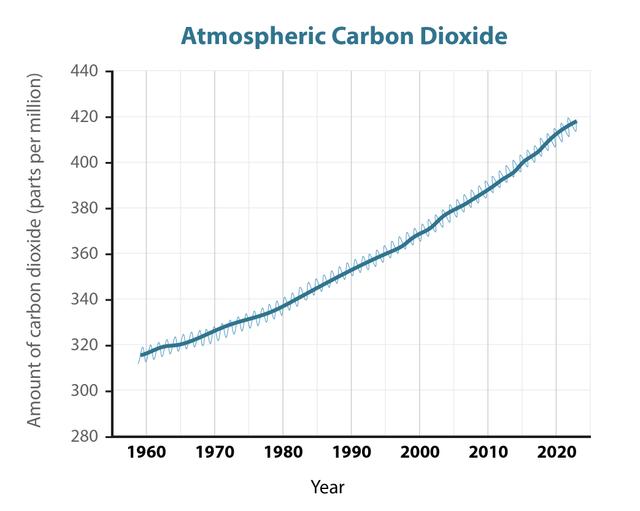
- There is a correlation between increasing amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide and a rising average global temperature.
- Increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide have been caused by human activity.
- Overwhelming evidence shows human activity is responsible for the rapid global warming of the last 200 years.
- Global warming measurements and conclusions are reliable despite some unavoidable uncertainty in measured values.
- Carbon footprints measure the annual greenhouse gas emissions of individuals, industry and nations.
Keywords
Average global temperature - the average of all the temperatures across the world over a year
Atmospheric CO₂ - carbon dioxide that is in the atmosphere
Uncertainty - the biggest possible difference between a measured value and the true value of the quantity being measured
Reliability - the certainty with which a measurement or conclusion will remain the same when it is checked
Common misconception
As individuals we are helpless in combatting climate change. Technology alone can solve climate issues.
Emphasise the impact of collective individual actions, especially in supporting national and international actions (including legislation) that cause appropriate change.
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Human activity and climate change, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Human activity and climate change, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 chemistry lessons from the Atmosphere and changing climate unit, dive into the full secondary chemistry curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
Exit quiz
6 Questions
the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
the amount of greenhouse gases emitted
biggest possible difference between a measurement and the true value
the certainty with which a measurement will be the same when checked