Ozone layer: a story of global success
I can describe why the ozone layer was nearly destroyed, but through a global community and international resolution it was saved.
Ozone layer: a story of global success
I can describe why the ozone layer was nearly destroyed, but through a global community and international resolution it was saved.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
These resources were created for remote use during the pandemic and are not designed for classroom teaching.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- The ozone layer protects life from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) were once used, and when they entered our atmosphere reacted with ozone (O₃).
- Ozone levels decreased, but scientific communication led to action being taken to prevent further loss of ozone.
- The work of analytical scientists suggests the ozone layer is now reforming.
Keywords
Ozone - Ozone is made up of oxygen atoms. It has the molecular formula O₃.
Ozone layer - The ozone layer refers to an area in the stratosphere where there is a high concentration of ozone.
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation - Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation which is emitted from the Sun.
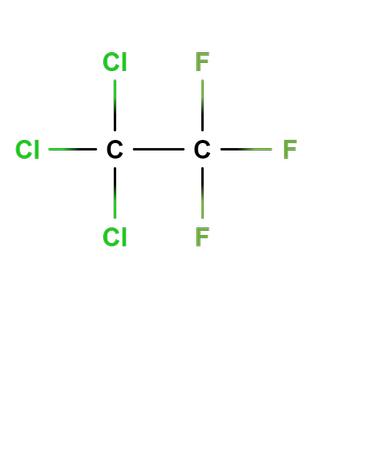
Chlorofluorocarbons - Chlorofluorocarbons are compounds consisting of chlorine, fluorine and carbon atoms only.
Analytical scientists - Analytical scientists use a range of scientific techniques to study the chemical composition of substances.
Common misconception
Ozone layer and climate change are linked/the same thing.
Ozone layer depletion was caused by human activity, but not through use of burning fossil fuels/greenhouse gas emissions. Both are atmospheric issues, but not the same issue.
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Ozone layer: a story of global success, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Ozone layer: a story of global success, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 chemistry lessons from the Atmosphere and changing climate unit, dive into the full secondary chemistry curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
a layer of gas surrounding a planet
a type of electromagnetic radiation which is emitted from the Sun
compound consisting of chlorine, fluorine and carbon only
an area in the atmosphere where there is a high concentration of ozone
Exit quiz
6 Questions