Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- OCR
- Higher
Ammonia: NPK fertiliser production and other applications
I can describe applications of industrial chemistry in agriculture, specifically in the production of ammonium salts for fertilisers.
- Year 11
- OCR
- Higher
Ammonia: NPK fertiliser production and other applications
I can describe applications of industrial chemistry in agriculture, specifically in the production of ammonium salts for fertilisers.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Fertilisers contain nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium compounds to promote plant growth.
- Ammonia is a feedstock for manufacture of fertilisers, explosives, plastics, dyes and cleaning products.
- Ammonia can be used to manufacture ammonium salts and nitric acid.
- The laboratory preparation of ammonium salts is not the same as the industrial preparation.
Keywords
Fertiliser - a mixture of soluble chemicals added to soil that replace the mineral ions needed by plants, to promote plant growth
Eutrophication - a term used to describe when nutrients accumulate in bodies of water, which results in an increased growth of microorganisms that reduce the oxygen availability in the water
Salt - an ionic compound formed from positive and negative ions electrostatically attracted to each other
Batch process - a manufacturing method made up of discrete stages, rather than a product being constantly produced
Continuous process - a manufacturing method where a product is constantly produced
Common misconception
Ammonia and ammonium are the same thing.
Carefully compare the different chemical formulae, structures, and distinct uses in fertilisers vs. industrial applications. Use visual aids to reinforce these differences.
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Ammonia: NPK fertiliser production and other applications, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Ammonia: NPK fertiliser production and other applications, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 chemistry lessons from the Industrial chemistry unit, dive into the full secondary chemistry curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Name the industrial process used to make ammonia.
Q2.Which of the following are properties of ammonia?
Q3.Which of the following shows ammonia?
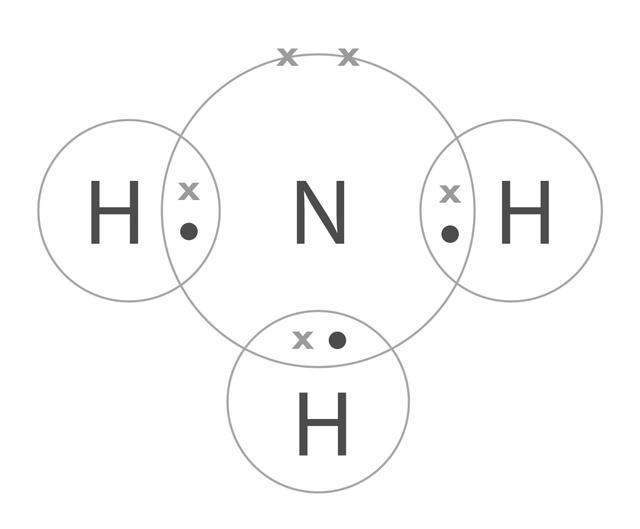
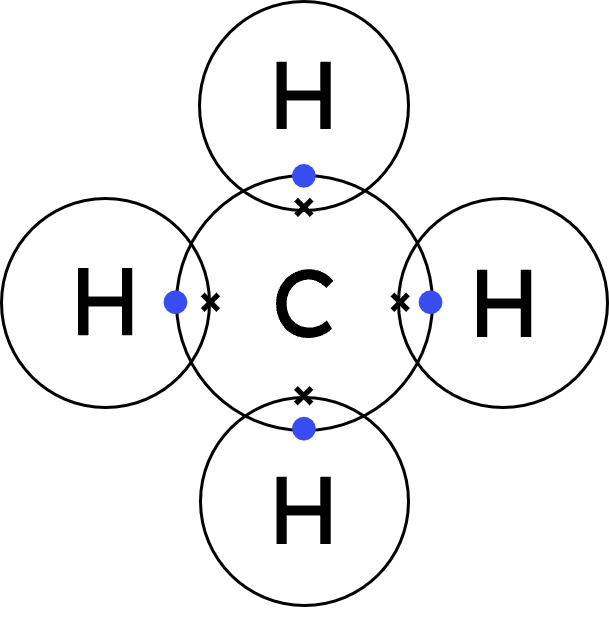
Q4.Nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to form ammonia. Which of the following shows this balanced chemical reaction?
Q5.When the symbol ⇌ is used in an equation it means that the reaction is .
Q6.What happens to the unreacted hydrogen and nitrogen gases used in the Haber process?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the following terms to the correct definition.
Mixture of soluble chemicals added to soil to replace mineral ions.
Process where nutrients accumulate in body of water, removing oxygen.
Manufacturing process made of discrete stages or steps.
Manufacturing process where a product is constantly produced.
A raw material used to provide reactants for an industrial reaction.


