Alkenes
I can describe and explain the reactions and properties of the first four alkenes.
Alkenes
I can describe and explain the reactions and properties of the first four alkenes.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
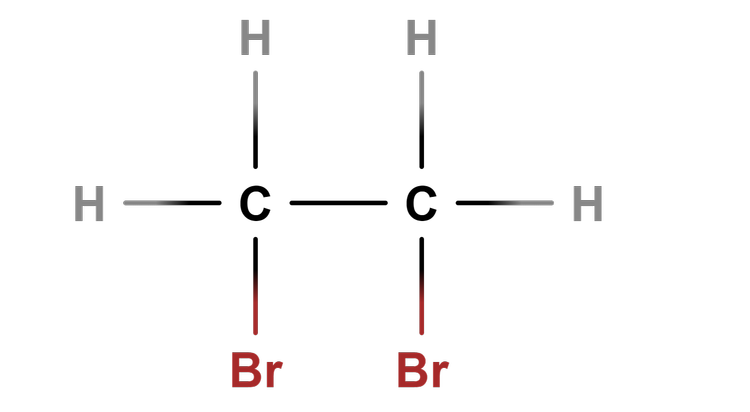
- Reactions of an alkene happen at its functional group, C=C.
- Reactions of an alkene change it from an unsaturated to a saturated molecule.
- Larger alkenes have higher boiling points and are less flammable.
- Alkenes tend to burn with smoky flames due to incomplete combustion.
- Isomers are structures with the same molecular formula, but different arrangement of atoms in space.
Keywords
Functional group - The functional group is the atom or group of atoms responsible for the way a compound reacts.
Unsaturated - Unsaturated compounds contain at least one carbon-carbon double covalent bond.
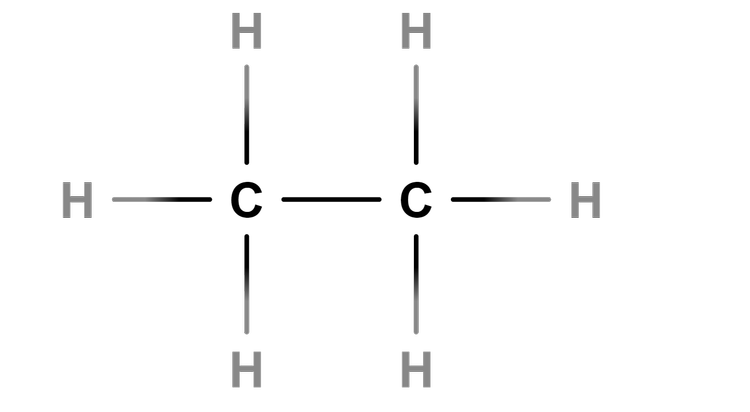
Saturated - Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons as they contain only single bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Isomers - Isomers are structures with the same molecular formula, but different arrangement of atoms in space.
Alkenes - Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain the C=C functional group.
Common misconception
The shortest alkene is one containing only one carbon atom.
Teach that alkenes contain the C=C bond and therefore the shortest alkene is ethene.
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Alkenes, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 chemistry lesson on: Alkenes, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 chemistry lessons from the Organic chemistry unit, dive into the full secondary chemistry curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Molymods (optional to use).
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
Exit quiz
6 Questions
compounds that contain at least one carbon–carbon double covalent bond
compounds that contain only single covalent bonds
hydrocarbons that contain the C=C functional group
the atom or group of atoms responsible for the way a compound reacts