Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- OCR
- Higher
Potable water
I can explain what potable water is and describe how it can be obtained from groundwater and sea water.
- Year 10
- OCR
- Higher
Potable water
I can explain what potable water is and describe how it can be obtained from groundwater and sea water.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- 'Potable' and 'pure' water are not the same material.
- Water used in analysis must not contain any dissolved ions.
- The method used to obtain potable water depends on the water source.
- Filtration and sterilisation are used to obtain potable water from groundwater and fresh water sources.
- Desalination of sea water creates potable water by distillation or reverse osmosis.
Keywords
Pure - A single element or compound that is not mixed with any other substance.
Potable - Water that is safe to drink.
Sterilisation - The process of killing bacteria and other living microorganisms.
Desalination - The process of removing dissolved salts from seawater.
Reverse osmosis - The movement of solvent through a semipermeable membrane by applying excess pressure on the solution. This process can remove dissolved solutes from water.
Common misconception
Pupils tend to think that all water is the same. Pupils tend to forget that non-visible substances are also found in water.
Stress that pure water only contains H₂O molecules. Other waters may include varying amounts of dissolved salts, other solids or micro-organisms. Stress that microbes must be killed for water to be potable, but are too difficult to remove.
To help you plan your year 10 chemistry lesson on: Potable water, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 chemistry lesson on: Potable water, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 chemistry lessons from the Separating substances unit, dive into the full secondary chemistry curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
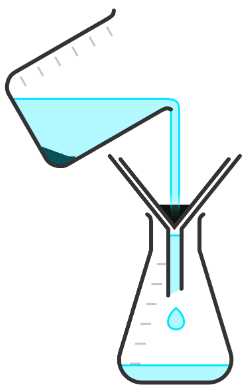
Q1.The equipment setup shown below shows which separation technique?
Q2.Match each letter on the diagram below to the correct label.
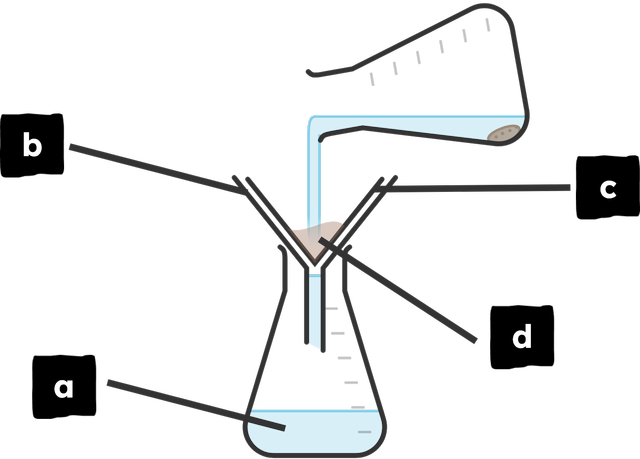
filtrate
funnel
filter paper
residue
Q3.A single element or compound that is not mixed with any other substance is said to be .
Q4.A substance that dissolves into another substance is described as .
Q5.When a substance dissolves into a liquid (e.g., water), a __________ forms.
Q6.Which of the following techniques can be used to fully isolate components of a mixture or solution?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Water is essential for life.
Which of the following are domestic uses of water?
Q2.All sources of water contain varying amounts of micro-organisms and what other material?
Q3.Water that is safe to drink is classified as .
Q4.Match each step of making potable water, from either groundwater or freshwater, to the correct description.
a grid acts like a sieve, removing large insoluble objects
small, insoluble particles 'settle out', forming a sediment
very small particles are removed by passing through fine layers
microbes are killed


