Discovery and uses of carbon nanostructures
I can describe the scientific discovery process and relate the uses of nanostructures to their properties, structure and bonding.
Discovery and uses of carbon nanostructures
I can describe the scientific discovery process and relate the uses of nanostructures to their properties, structure and bonding.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Scientists discovered and isolated fullerenes accidentally, which led to exciting new possibilities in chemistry.
- Research into the allotropes of carbon is an important part of chemistry's history, earning multiple Nobel Prizes.
- Graphene is so thin that it's nearly transparent, allowing most light to pass through.
- Fullerenes, nanotubes, and graphene have a wide range of real-world uses in fields like electronics and medicine.
- Scientific discoveries have the power to change the world, even if their significance takes time to be fully understood.
Keywords
Fullerene - A molecular allotrope of carbon. Each atom is covalently bonded to three others, forming nanoparticles with hollow spheres or tubes.
Graphene - An allotrope of carbon consisting of a sheet that is one-atom-thick. Each atom is covalently bonded to three others arranged in hexagonal rings.
Nanotube - A cylindrical fullerene, essentially a tube of graphene. A nanoparticle known for its strength and electrical conductivity.
Common misconception
Students may think that all carbon allotrope discoveries were recent and that these materials are primarily used in cutting-edge, futuristic applications.
Emphasise the timeline of discoveries (graphite > fullerenes > nanotubes > graphene), highlighting theoretical predictions preceding isolation. Discuss current uses (e.g. nanotubes in sporting equipment) alongside potential future breakthroughs.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Discovery and uses of carbon nanostructures, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Discovery and uses of carbon nanostructures, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Chemistry of carbon unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
A substance made from only one type of atom.
A substance made from two or more elements chemically bonded together.
The temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid.
Substances that allow electricity to pass through them easily.
Can be directly observed or measured without a chemical reaction.
Exit quiz
6 Questions
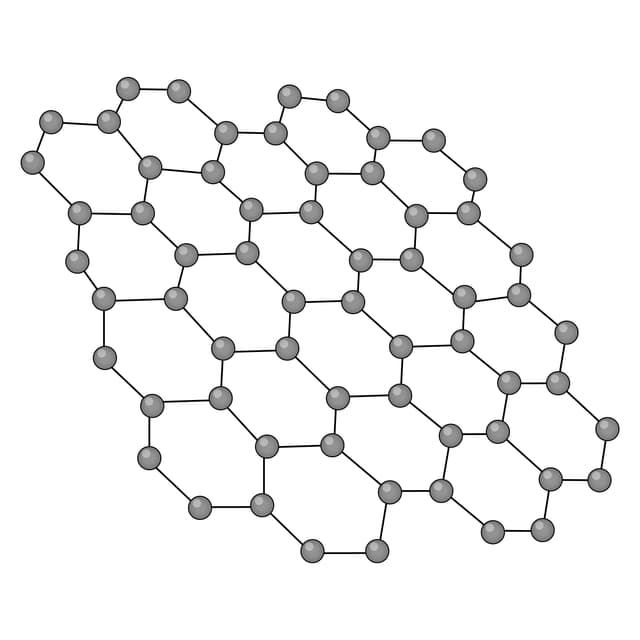
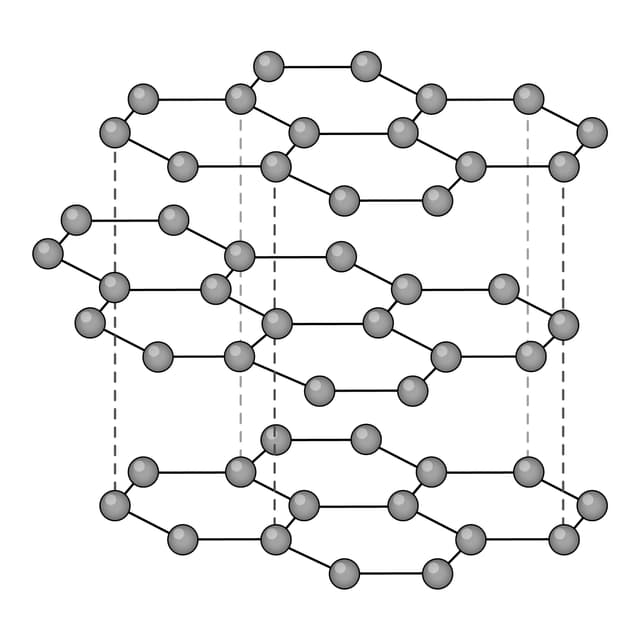
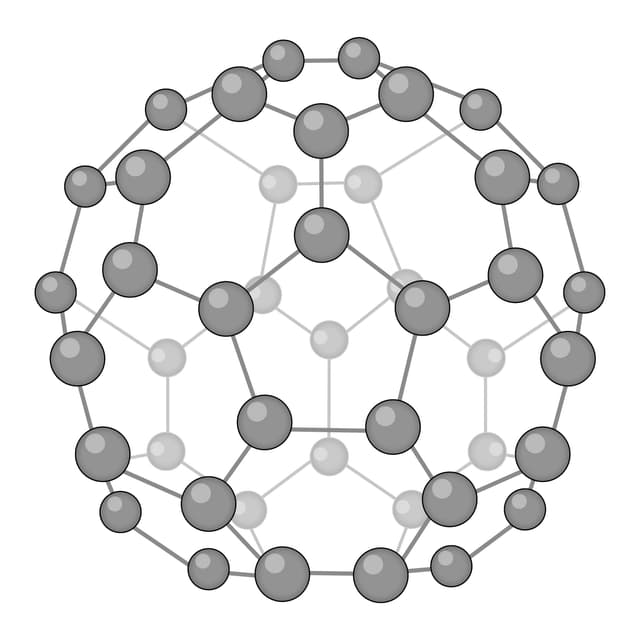
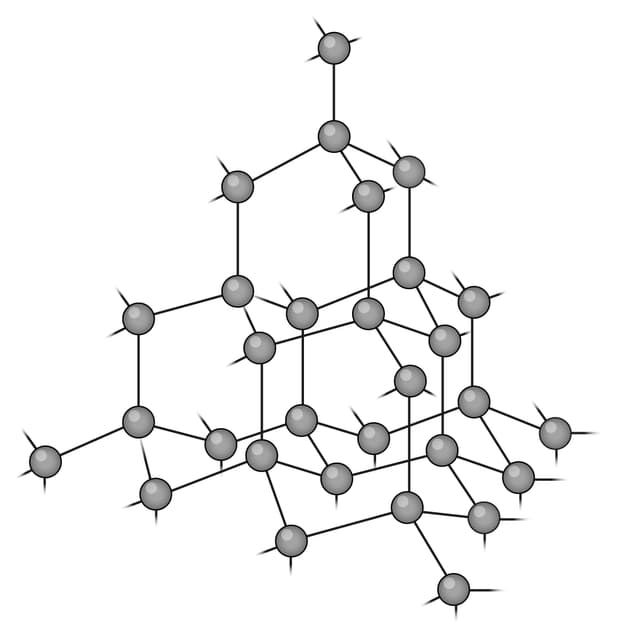
An allotrope of carbon consisting of a sheet that is one atom thick.
An allotrope of carbon that forms hollow spheres or tubes.
A fullerene that can form a cylinder.


