Light microscopy: observing and drawing cells
I can use a light microscope to observe and produce scientific drawings of cells.
Light microscopy: observing and drawing cells
I can use a light microscope to observe and produce scientific drawings of cells.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
These resources were created for remote use during the pandemic and are not designed for classroom teaching.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- A light microscope can be used to observe animal and plant cells.
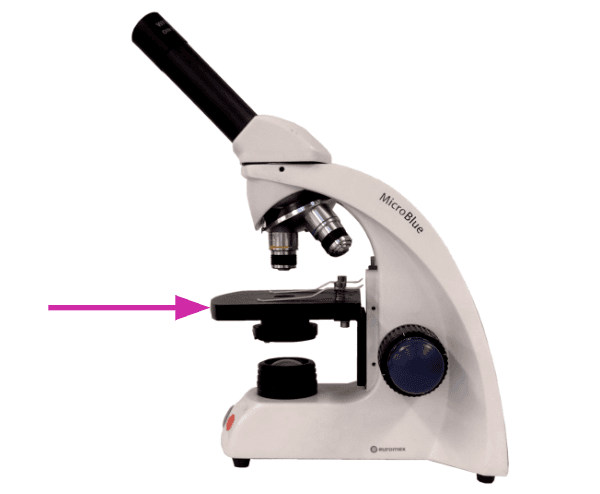
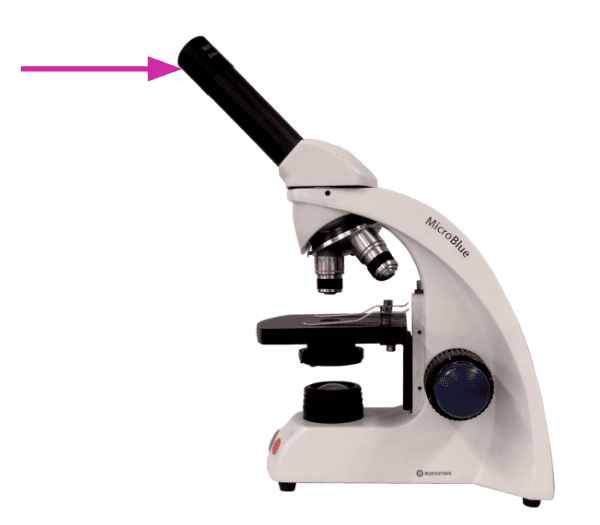
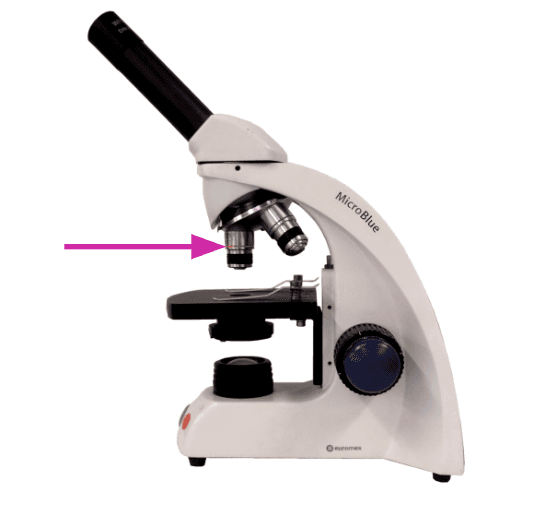
- The parts of a light microscope and their functions.
- The sequence of steps setting up a light microscope to observe cells, including changing the magnification and focus.
- Observations from a light microscope can be recorded in a labelled scientific line drawing with an indication of scale.
- The magnification and real size of structures observed with a microscope can be calculated.
Keywords
Light microscope - A type of microscope that uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects.
Lens - A piece of glass or other transparent material with curved sides, used in a microscope to magnify objects.
Magnification - Making small objects appear larger in order to see more detail.
Focus - A point where light rays converge to form an image.
Common misconception
Cells are inert 'building blocks' like bricks. Microscopes can see structures as small as molecules.
The lesson explores what cells are, including that they are living units, and considers what can and can't be seen using a light microscope.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Light microscopy: observing and drawing cells, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Light microscopy: observing and drawing cells, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Light microscopes, pre-prepared slides.
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
Exit quiz
6 Questions