Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- Edexcel
- Foundation
Neurones and synapses
I can describe the structures and functions of neurones and the synapses between neurones.
- Year 10
- Edexcel
- Foundation
Neurones and synapses
I can describe the structures and functions of neurones and the synapses between neurones.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
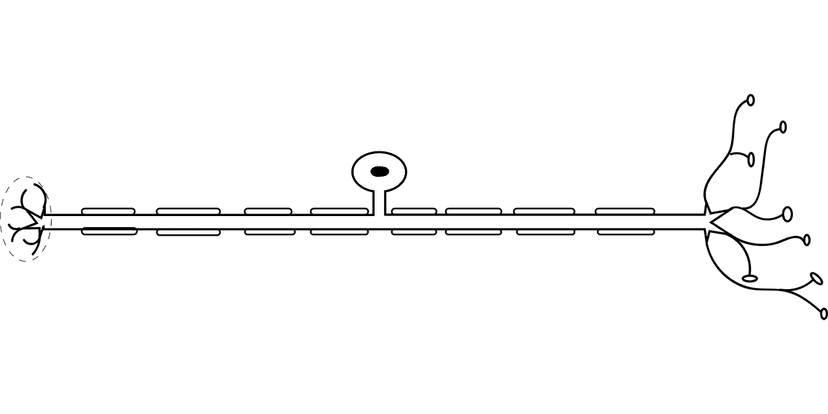
- Neurones are specialised cells that transmit nerve impulses
- The common structures of neurones, including cell body and axon
- A myelin sheath on some neurones increases the speed of the nerve impulse
- Nerve impulses pass from one neurone to another across a gap called a synapse
- An impulse arriving at a synapse releases neurotransmitters that diffuse across the gap to receptors on the next neurone
Keywords
Neurone - A nerve cell which transmits electrical impulses between different parts of the body.
Axon - The part of a neurone which carries the signal.
Myelin sheath - A fatty coating on the neurone which insulates it.
Synapse - The junction between two neurones.
Neurotransmitter - A chemical transmitter which crosses the synapse and triggers the onward response.
Common misconception
There is usually a lot of confusion over the synapse and how the signal moves from electrical, to chemical, to electrical again. There are many new key words involved, which makes it even harder.
The synapse has been broken down into several stages with clear diagrams and carefully used key words. There are plenty of opportunities to practise using the terminology and explaining the process, including applying it to a real-world scenario.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Neurones and synapses, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Neurones and synapses, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Coordination and control: the human nervous system unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What are nerve cells called?
Q2.What is the role of the nervous system?
Q3.Which of the following are effectors?
Q4.Which of the following is not a stimulus?
Q5.Match the word to its meaning.
Cells that detect a change in the environment.
A change in the environment.
A nerve cell which transmits electrical impulses.
A muscle or gland which carries out a response.
Q6.Put these in order to show how a message moves through the nervous system, starting with detecting the stimulus.
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the part of the cell to its name.
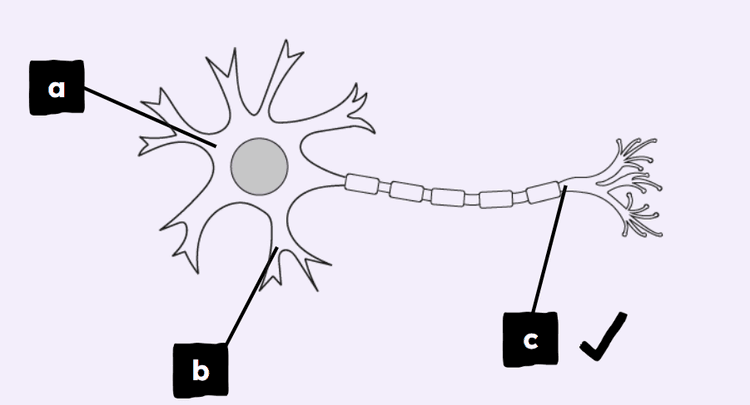
dendron
cell body
axon
Q2.Match the type of neurone to its function.
Transmits electrical impulses between neurones within the CNS.
Transmits electrical impulses from the receptor to the CNS.
Transmits electrical impulses from the CNS to the effector.
Q3.What sort of tissue is the myelin sheath made of?
Q4.What effect does having a myelin sheath have on nerve impulses?
Q5.What are the chemicals called that diffuse across the synapse?
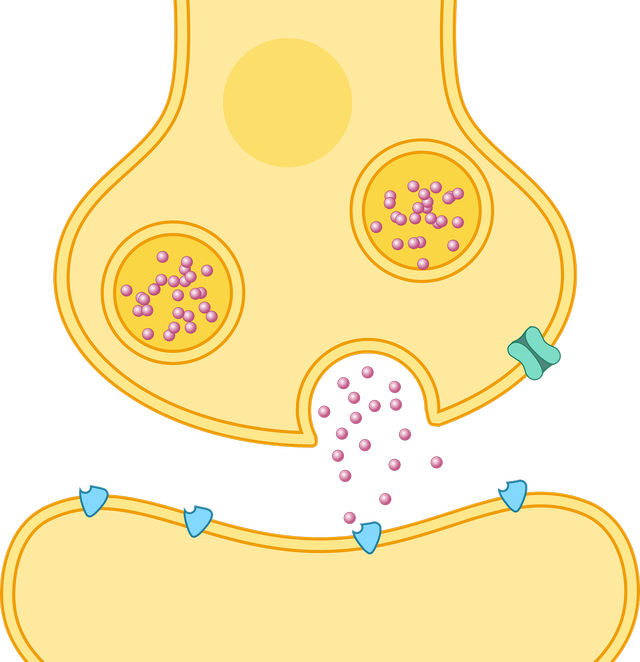
Q6.Put these steps in order, to show how a nerve impulse passes from one neurone to another.



