Models of single-gene inheritance: family tree diagrams
I can construct and interpret family tree diagrams showing information about inheritance of a feature.
Models of single-gene inheritance: family tree diagrams
I can construct and interpret family tree diagrams showing information about inheritance of a feature.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
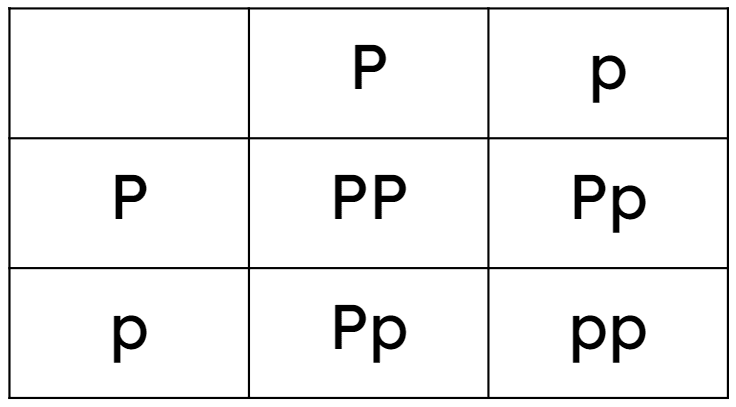
- Offspring inherit two alleles, one from each parent, the combination of these alleles is the genotype.
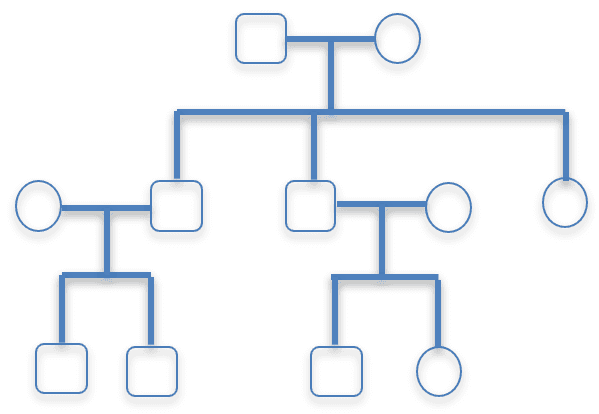
- The phenotypes of members of a family can be shown in a diagram such as a family tree (pedigree).
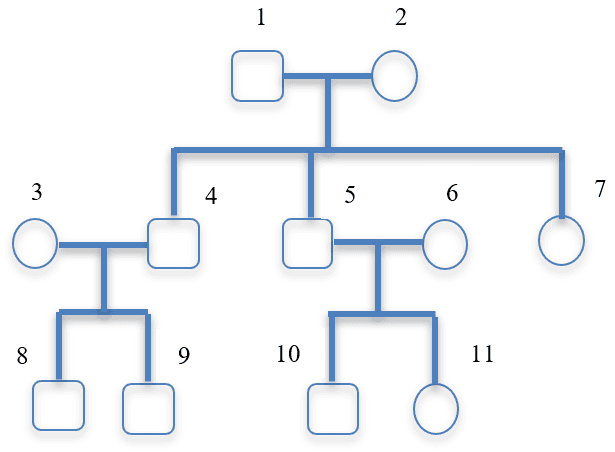
- A family tree diagram is a model of inheritance, showing whether a characteristic was passed from parents to offspring.
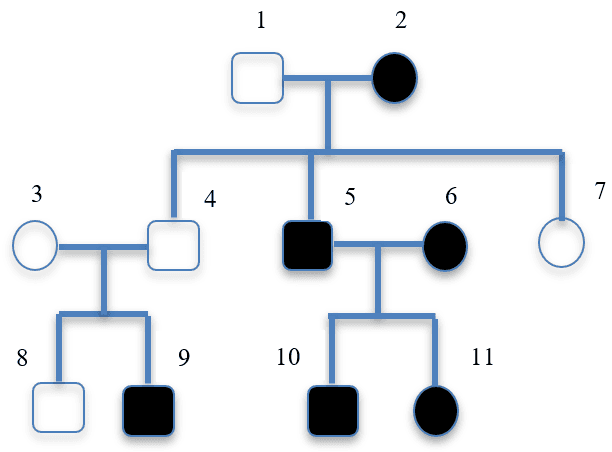
- A family tree can be used to work out an individual’s genotype if their phenotype and relatives’ genotypes are known.
- A family tree can be used to determine the history and probability of genetic disorders: cystic fibrosis and polydactyly
Keywords
Family tree - A family tree diagram is a model of inheritance, showing whether a characteristic was passed from parents to offspring.
Genotype - The genotype is the combination of alleles that an individual has for each gene.
Phenotype - The phenotype is the physical characteristics of an organism.
Carrier - A carrier of a recessive genetic disorder does not express the disorder in their phenotype, but has one recessive allele in their genotype that can be passed to offspring.
Inheritance - Inheritance is the passing of genetic information from parents to offspring by reproduction.
Common misconception
The dominant allele is stronger than the recessive allele preventing its expression or that the recessive allele is an absence of the dominant allele, also that all genetic disorders are recessive.
Linking the allele to change in protein structure, showing that proteins are produced in the case of dominant and recessive alleles. Examples of dominant and recessive disorders provided.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Models of single-gene inheritance: family tree diagrams, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Models of single-gene inheritance: family tree diagrams, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Inheritance, genotype and phenotype unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
Exit quiz
6 Questions
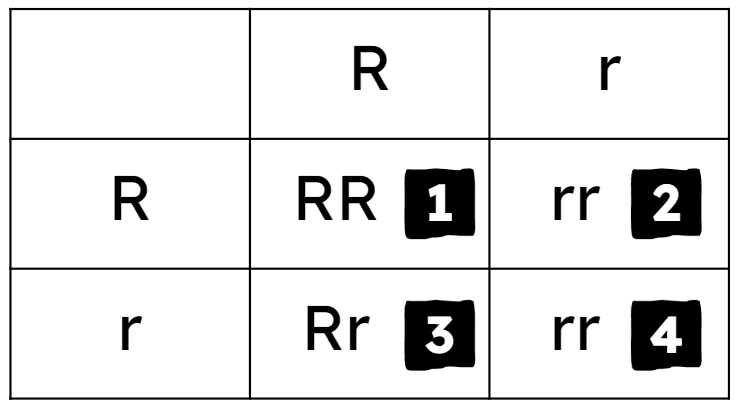
homozygous dominant
heterozygous
homozygous recessive