Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- Edexcel
- Foundation
The inheritance of biological sex in humans
I can explain how the inheritance of chromosomes determines biological sex in humans.
- Year 10
- Edexcel
- Foundation
The inheritance of biological sex in humans
I can explain how the inheritance of chromosomes determines biological sex in humans.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
These resources were created for remote use during the pandemic and are not designed for classroom teaching.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- During sexual reproduction, an individual’s biological sex is determined by the chromosomes they inherit.
- In humans, the 23rd pair of chromosomes are sex chromosomes; XX in females and XY in males.
- A gene on the Y chromosome triggers the development of testes, which make male sex hormones (androgens).
- Interpreting, completing and constructing Punnett squares showing the inheritance of human sex chromosomes.
Keywords
Sexual reproduction - The process of producing offspring where a male and a female provide half the genetic material via gametes.
Biological sex - Male or female as determined by the combination of sex chromosomes inherited (i.e. XX female, XY male).
Sex chromosome - The chromosomes that determine the reproductive and secondary sexual characteristics (i.e. X and Y).
Sex hormone - Chemical messengers, secreted by glands, that help to control the reproductive and secondary sexual characteristics.
Common misconception
Males only have Y chromosomes.
Males have one Y and one X chromosome.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: The inheritance of biological sex in humans, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: The inheritance of biological sex in humans, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Inheritance, genotype and phenotype unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
None required.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which is the best definition of genotype?
Q2.Horses can breed with donkeys to produce offspring called mules. Horse body cells have 64 chromosomes and those of a donkey have 62. How many chromosomes will the zygote that grows into a mule have?
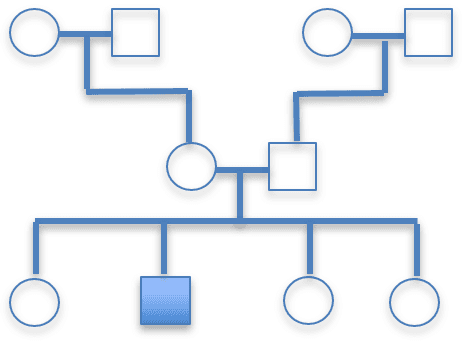
Q3.Tay-Sachs is a single gene disorder caused by a recessive allele. Here is a family tree. It shows three generations. The shaded male has Tay-Sachs. Which statement is true?
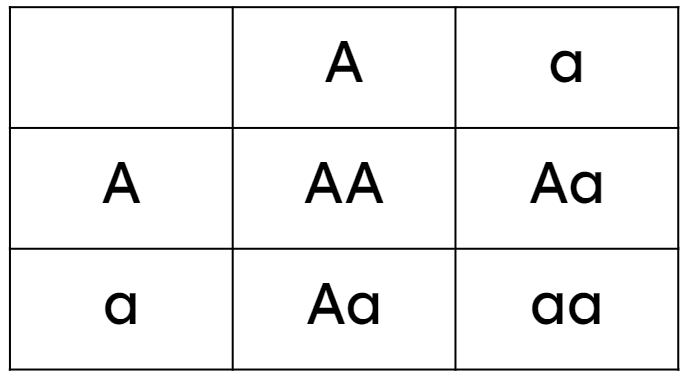
Q4.Albinism is caused by a recessive allele. The Punnett square shows the possible genotypes resulting from two carriers having a child. What is the probability that a child will be a carrier?
Q5.A student thinks you can tell the genotype of an individual by looking at its phenotype. When is this statement true?
Q6.Although it wasn’t recognised at the time, Mendel made a significant contribution to our modern understanding of inheritance. What was this contribution?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match each term to its correct meaning.
Production of offspring by the fusion of gametes.
In humans, features determined by the 23rd chromosome pair.
In humans these can be X or Y.
Chemical messengers that control reproduction and physical characters.
Q2.What percentage of the chromosomes in the nucleus of a zygote comes from the father?
Q3.In humans, biological sex is determined by ...
Q4.Put the statements in order to describe how sex chromosomes cause the development of male biological sex.
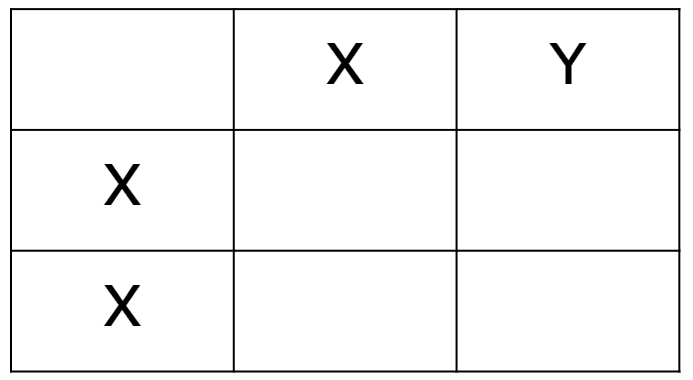
Q5.The incomplete Punnett square show the inheritance of biological sex in humans. What combination of sex chromosomes cannot be produced in a fertilised egg cell?