Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- OCR
- Foundation
Using a microscope to observe effects of osmosis in plant cells: practical
I can use a light microscope to observe effects of osmosis in plant cells.
- Year 11
- OCR
- Foundation
Using a microscope to observe effects of osmosis in plant cells: practical
I can use a light microscope to observe effects of osmosis in plant cells.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Use a light microscope to observe effects of osmosis in plant cells (including: shrinking/crenation, swelling/bursting)
- The parts of a light microscope and their functions.
- The sequence of steps for setting up a light microscope to observe cells, including changing magnification and focus.
- Explaining observations from microscopy using ideas about osmosis and net movement of water into/out of cells.
Keywords
Light microscope - an instrument that uses visible light and lenses to magnify viewed objects
Selectively-permeable membrane - a membrane that will only allow some substances through and not others
Osmosis - the net movement of water molecules from high to low concentration through a selectively-permeable membrane
Turgid - a cell which is swollen with water and firm
Flaccid - a cell which has lost a lot of water and is soft and limp
Common misconception
The process of osmosis, the direction of movement from high to low water concentration, and the effect that this has on plant cells in terms of turgidity and flaccidity are frequently confused.
Errors are explored, explained and questioned, and clear demonstrations of turgidity and flaccidity and the effects that these have on a plant are demonstrated. This will be reinforced by observation of these processes using a light microscope.
To help you plan your year 11 combined science lesson on: Using a microscope to observe effects of osmosis in plant cells: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 combined science lesson on: Using a microscope to observe effects of osmosis in plant cells: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Coordination and control: maintaining a constant internal environment unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
light microscope, slides with onion epidermis in states of turgor and plasmolysis
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.What is the process by which water moves into the roots of a plant?
Q2.True or false? Osmosis is a type of diffusion.
Q3.Match the cell part to its function.
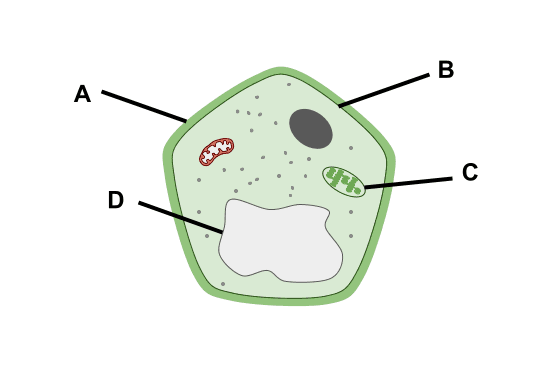
provides support and structure
controls what enters and leaves the cell
the site of photosynthesis
contains cell sap (water and other substances)
Q4.Which tissue inside a plant transports water?
Q5.Which three of the following statements about diffusion are true?
Q6.A concentration is a measurement of how the concentration of something changes from one place to another.
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the part to its function.
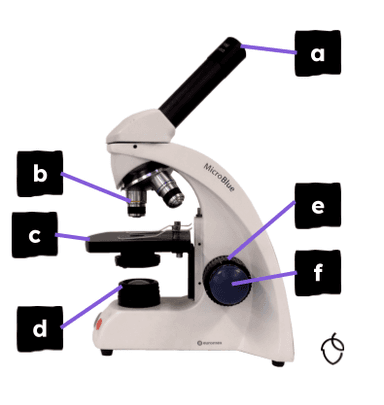
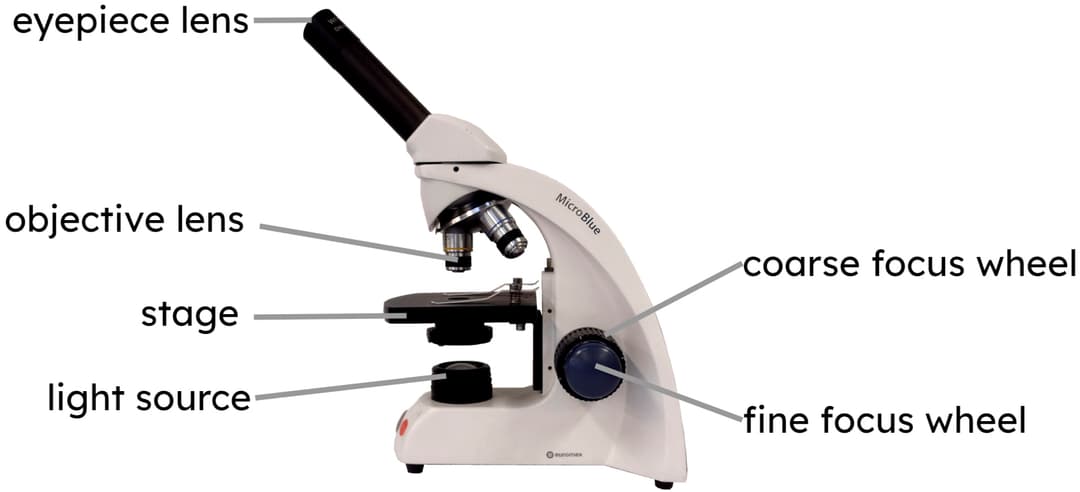
eyepiece lens: viewing lens with ×10 magnification
objective lenses: three lenses with different magnifications
stage: specimen on a slide is placed here
light source: illuminates the specimen so that it can be observed
coarse focus wheel: for adjusting the focus in larger increments
fine focus wheel: for adjusting the focus in smaller increments
Q2.Put these steps in the right order to show how to use a light microscope.