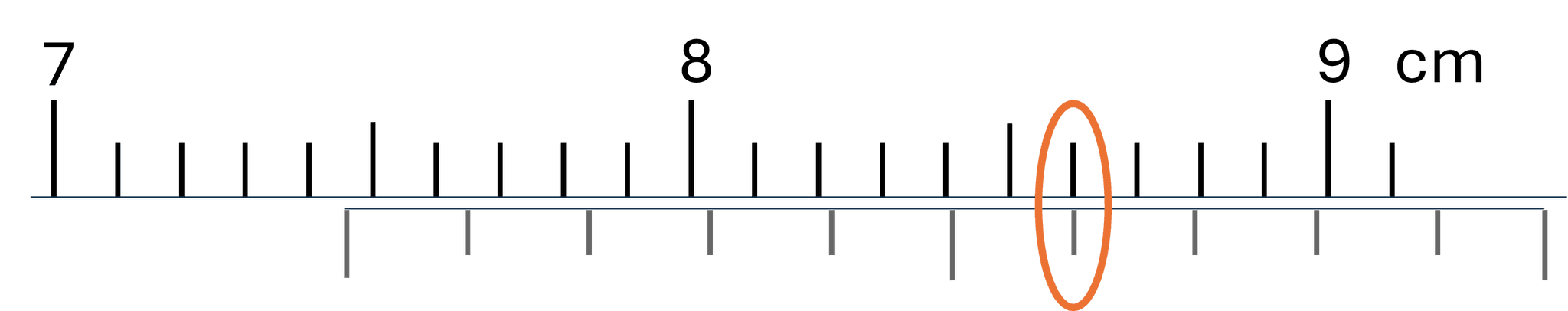Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 10•
- OCR•
- Foundation
Calculating density and measuring volume
I can define density, calculate its value, and describe how to measure volume.


- Year 10•
- OCR•
- Foundation
Calculating density and measuring volume
I can define density, calculate its value, and describe how to measure volume.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Density is calculated using the equation: density = mass ÷ volume.
- Density is measured in kg/m³ or g/cm³.
- The volume of water displaced by a submerged object is equal to the volume of the object.
- The dimensions of a regular cuboid can be measured accurately with Vernier callipers.
- The volume of a regular cuboid is calculated using the equation: volume = length × width × height.
Keywords
Density - the mass per cubic metre (m³) or cubic centimetre (cm³) of a material
Kilograms per cubic metre - the unit for density when mass is measured in kilograms (kg) and volume in cubic metres (m³), written as kg/m³
Grams per cubic centimetre - the unit for density when mass is measured in grams (g) and volume in cubic centimetres (cm³), written as g/cm³
Vernier callipers - a device used to measure length precisely
Micrometer - a device used to measure length to a very high precision
Common misconception
Pupils confuse the mass or weight of an object with density.
Provide pupils with a range of objects of varying sizes they are going to measure the density of and, before starting to do so, ask the pupils to rank the objects in order of density with explanations. Compare results to the list after measurements.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Calculating density and measuring volume, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Calculating density and measuring volume, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Particle explanations of density and pressure unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following quantities does a measuring cylinder measure?
Q2.Which of the following quantities means ‘amount of matter’?
Q3.Here is a mathematical formula: $$c=\frac{d}{e}$$. Rearrange the formula to make $$d$$ the subject.
Q4.Here is a mathematical formula: $$f=\frac{g}{h}$$. Rearrange the formula to make $$h$$ the subject.
Q5.On the left is a set of numbers. On the right are the same numbers after rounding to three significant figures. Match each number on the left with its rounded value on the right.
7.955 -
7.96
7.946 -
7.95
7.9449 -
7.94
7.9032 -
7.90
7.999 -
8.00
Q6.A pupil observes that a beetle runs 5.0 m in 3.0 s, and uses the formula speed = distance ÷ time to calculate the speed. Which of the following is the most accurate way to write the beetle’s speed?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following instruments are used to measure length?
Q2.A displacement can contains water up to its spout. An object is placed in the water and sinks. A beaker collects the water that flows from the spout.
Which of the following statements is correct?
Q3.A paper clip has mass 1.2 g and volume 0.15 cm³. What is the density of the paper clip in g/cm³?
Q4.The diagram shows a Vernier scale. The marking on the lower scale that lines up most closely with a marking on the upper scale has been circled. The reading on the scale is cm.