Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 10•
- AQA•
- Higher
Predicting states of matter and limitations of the particle model
I can use the particle model to predict the state of matter of a substance at different temperatures and discuss the limitations of this model for explaining how particles behave.


- Year 10•
- AQA•
- Higher
Predicting states of matter and limitations of the particle model
I can use the particle model to predict the state of matter of a substance at different temperatures and discuss the limitations of this model for explaining how particles behave.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- There are changes in arrangement, movement and energy of particles during state changes.
- There are two types of change; physical and chemical, and the physical state of a substance can be predicted.
- The attraction between particles has a role in determining the amount of energy needed for state changes.
- The particle model has limitations, for example by showing particles as same sized, inelastic spheres.
- The model does not show the attraction between the particles which affects the amount of energy needed to change state.
Keywords
Physical change - A change in which no new substances are formed, such as a change in state, e.g. melting.
Chemical change - Occurs when a reaction takes place and atoms or ions in the reactants are rearranged to make new products/substances.
Particle model - A model that helps us to understand physical properties of substances. It uses circles or spheres to represent particles, i.e. atoms or compounds.
Limitation of a model - A point at which we cannot use the model to help us explain a scientific phenomena.
Common misconception
Pupils often confuse physical and chemical changes and think that all particles look and act like those shown in the particle model.
Give the pupils an array of different examples of physical and chemical reactions and get the pupils to consider if new substances have been produced. Show the pupils, using molymods, how different molecules can be.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Predicting states of matter and limitations of the particle model, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Predicting states of matter and limitations of the particle model, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the States of matter unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Optional: pair of magnets that have different magnetic strengths.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following statements can correctly finish this sentence? Substances in a solid state ...
Q2.Which of the following statements can correctly finish this sentence? Substances in a liquid state …
Q3.Which of the following statements can correctly finish this sentence? Substances in a gas state …
Q4.As particles gain energy, they are able to overcome the between them.

Q5.Which aspects of a particle change when a substance’s state of matter changes?
Q6.Match the following terms to their definitions.
boiling point -
temperature where substance changes from liquid state to gas state
condensing point -
temperature where substance changes from gas state to liquid state
freezing point -
temperature where substance changes from liquid state to solid state
melting point -
temperature where substance changes from solid state to liquid state
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
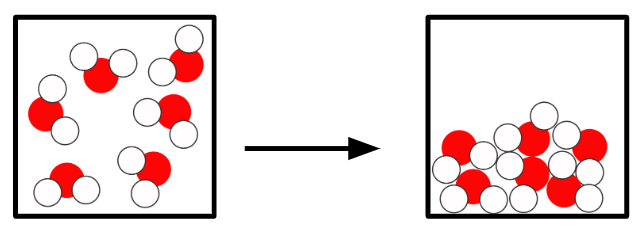
Q1.In the main image, the important information has been replaced with grey boxes. Which of the three answer images is an accurate representation of a chemical change of substances in the same state?
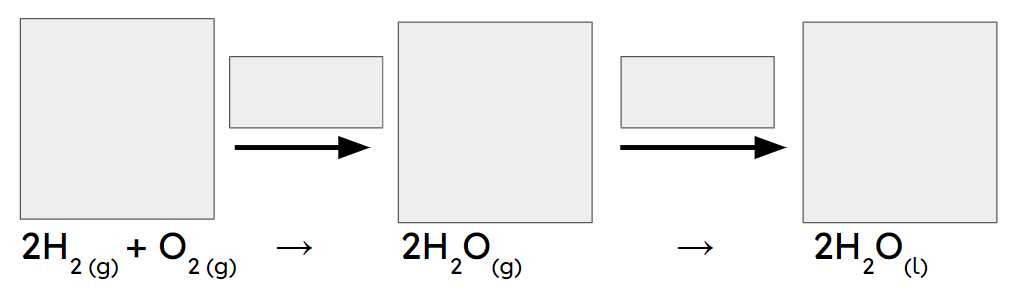
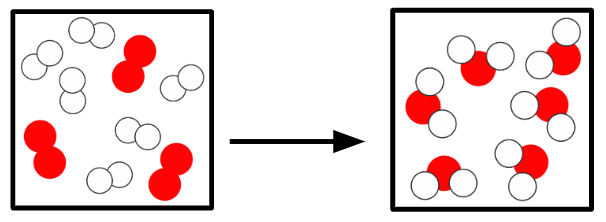
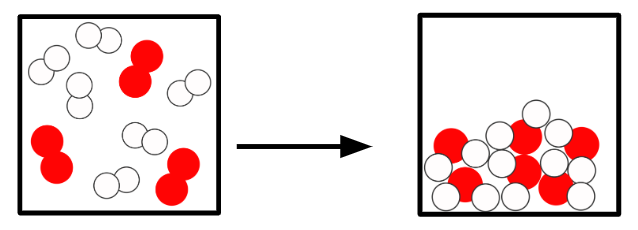
Q2.Sort the following states and the temperatures at which changes of state occur into the correct order, starting with a substance in the gas state.
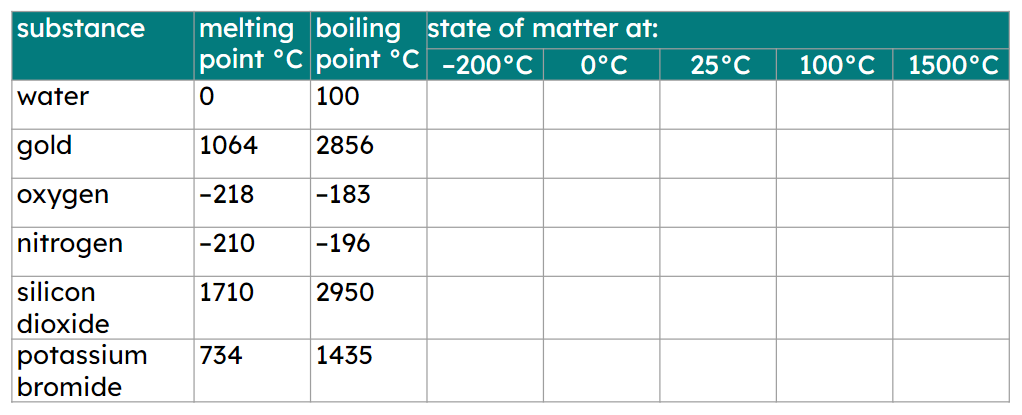
Q3.At which temperature are all of the following substances in a liquid state?
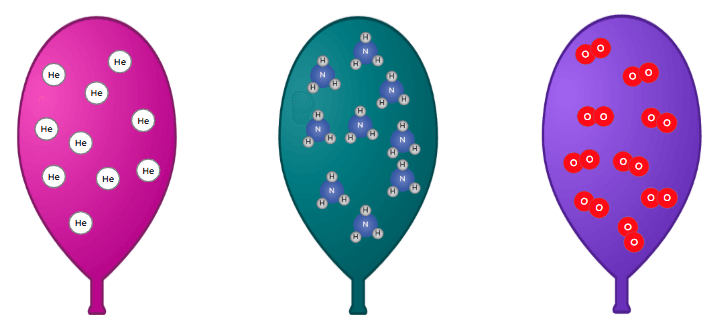
Q4.Three balloons are filled with neon, methane and oxygen, respectively (see image). Why would you expect the substance in the middle balloon to have the highest boiling point?
Q5.Which of the following statements are correct?
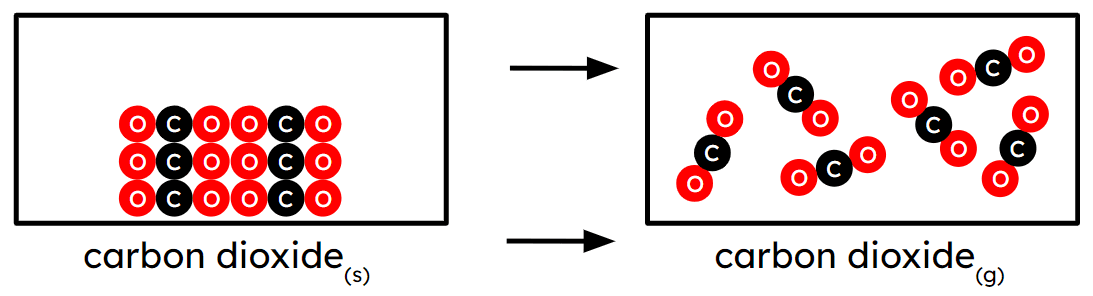
Q6.The image shows the sublimation of carbon dioxide. What are some of the limitations of this representation?