The mole
I can describe what a mole is and its link with the Avogadro constant.
The mole
I can describe what a mole is and its link with the Avogadro constant.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Chemical amounts are measured in moles (mol).
- One mole of particles of a substance is defined as the Avogadro constant number of particles.
- The number of particles (atoms, ions, molecules etc.) in one mole of a substance is always the same.
- Use of Avogadro's number to calculate the number of particles of substance when number of moles is known and vice versa.
- The mass of one mole of a monatomic element is equal to the relative atomic mass of that element measured in grams.
Keywords
Mole - A mole of something is 6.02 × 10²³ of it. The mass of a mole of a substance is its relative mass expressed in grams.
Relative formula mass - The relative formula mass (RFM) of a substance is the sum of the relative atomic masses of all the atoms in a formula.
Avogadro's constant - Avogadro's constant is the number of particles in one mole of a substance (6.02 × 10²³ mol⁻¹)
Common misconception
The number one mole represents can be difficult for pupils to grasp and appreciate.
Show many real world examples of 6.02 × 10²³ examples of something - that many basketballs would form a planet the size of the Earth.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: The mole, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: The mole, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Calculations involving masses unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
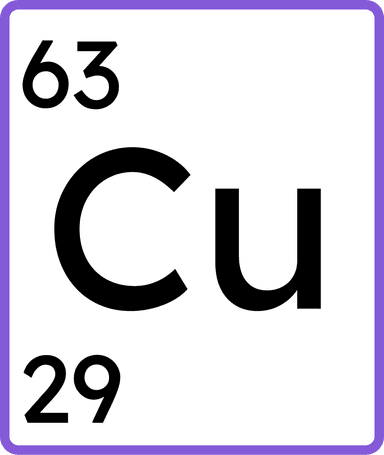
a substance made up of only one type of atom
two more or elements chemically bonded together
a particle with an electrical charge due to the gain/loss of electrons
a particle consisting of two or more atoms joined by covalent bonds
two atoms chemically bonded together
Exit quiz
6 Questions
atom
molecule
molecule
formula unit
formula unit
atom
6 g of carbon
62 g of phosphorus
30 g of neon
84 g silicon
35 g of nitrogen


