- Year 10•
- Edexcel•
- Higher
The particle model
I can describe the particle model of matter and how it explains the properties of solids, liquids, and gases.


- Year 10•
- Edexcel•
- Higher
The particle model
I can describe the particle model of matter and how it explains the properties of solids, liquids, and gases.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
These resources were created for remote use during the pandemic and are not designed for classroom teaching.
Lesson details
Key learning points
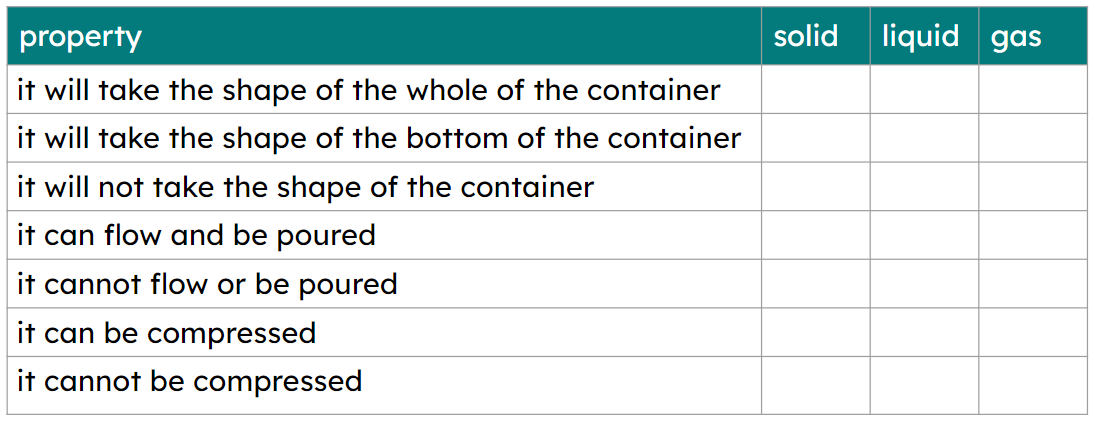
- There are three states of matter: solid state, liquid state, and gas state.
- A substance in the gas state can be compressed because there is empty space between the particles.
- A substance in the liquid or solid state cannot be compressed because the particles are already touching.
- A substance in the gas or liquid state has no fixed shape as the particles can move past each other.
- A substance in the solid state will not flow because the particles vibrate in a fixed position.
Keywords
States of matter - The states of matter are used to describe the three physical states that matter commonly exists in: the solid state, liquid state and the gas state.
Particle model - The particle model is a model used to explain the physical properties of substances by describing the arrangement and movement of particles.
Forces of attraction - Forces of attraction are pulling forces that keep particles close together.
Compress - If you compress a substance, it can be made to take up less space than before. Substances in the gas state can be compressed.
Common misconception
Pupils often think that the particles are embedded in the substance rather than being the substance. Most pupils think that substances in the liquid state will compress a little.
Reinforce that most substances can exist in all three states of matter and when they are in the gas state there is nothing between the particles but empty space.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: The particle model, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: The particle model, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the States of matter unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Sealed syringes filled with air, sand and water.
Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.A substance in the liquid state has particles that are free to move past their neighbouring particles; this means that liquids can and can take the shape of the bottom of a container.
Q2.Starting with the lowest, sort the following substances in order of increasing melting point.
Q3.A substance has a melting/freezing point of 25$$^o$$C. If a sample of this substance is in a container at 25$$^o$$C, which of the following statements is correct?
Q4.There is between the particles of a substance in the gas state.
Q5.Match each of the following states to the correct description of the movement of particles in that state.
gas state -
random movement in all directions
liquid state -
movement past neighbouring particles
solid state -
only vibrational movement around a fixed position
Q6.True or false? Water can evaporate at temperatures lower than 100$$^o$$C. Select a reason for your answer
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following statements about forces of attraction are correct?
Q2.Water can evaporate at temperatures below its boiling point (100$$^o$$C) because some of its particles have enough to overcome the forces of attraction between them.
Q3.Which of the following statements about particles in the solid state are correct?
Q4.Which of the following statements about particles in the liquid state are correct?
Q5.Which of the following statements about particles in the gas state are correct?
Q6.Which two of the properties in the table can apply to two different states (but not necessarily the same two states).