Human reaction time: practical
I can predict, plan and carry out an investigation into the effect of a factor on human reaction time, and analyse the data to draw a conclusion.
Human reaction time: practical
I can predict, plan and carry out an investigation into the effect of a factor on human reaction time, and analyse the data to draw a conclusion.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Some factors affect human reaction time (e.g. the time taken to catch a ruler after it is dropped).
- Writing a testable prediction or hypothesis about the effect of a factor on human reaction time.
- Identifying independent and dependent variables, range of values to test, and which factors to control and how.
- Safe use of apparatus, and safe and ethical use of human test subjects.
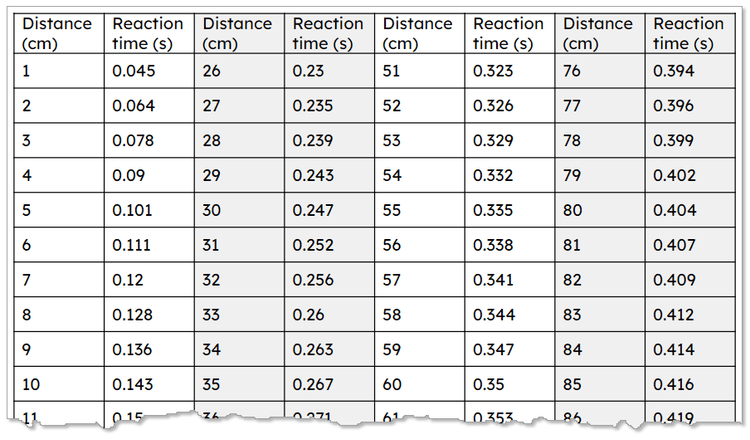
- Interpret data from measurements of human reaction time.
Keywords
Reaction time - The time taken to react to an event.
Ethical - Something that is morally good and does no harm.
Variable - Something that can be changed, measured or controlled in an experiment.
Prediction - A scientific prediction is a testable statement about a possible outcome of an experiment.
Common misconception
Describing and identifying independent, dependent and control variables and following a method with care and accuracy are skills that take time to build and need frequent revisiting.
The variables in the practical and the method are outlined and discussed. Considerations on the ethicality of the experiment due to human subjects, and the presence of anomalous data, are also covered in detail.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Human reaction time: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Human reaction time: practical, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Coordination and control: the human nervous system unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Equipment
Ruler (30 cm or 1 m)
Content guidance
- Risk assessment required - equipment
Supervision
Adult supervision required
Licence
Starter quiz
6 Questions
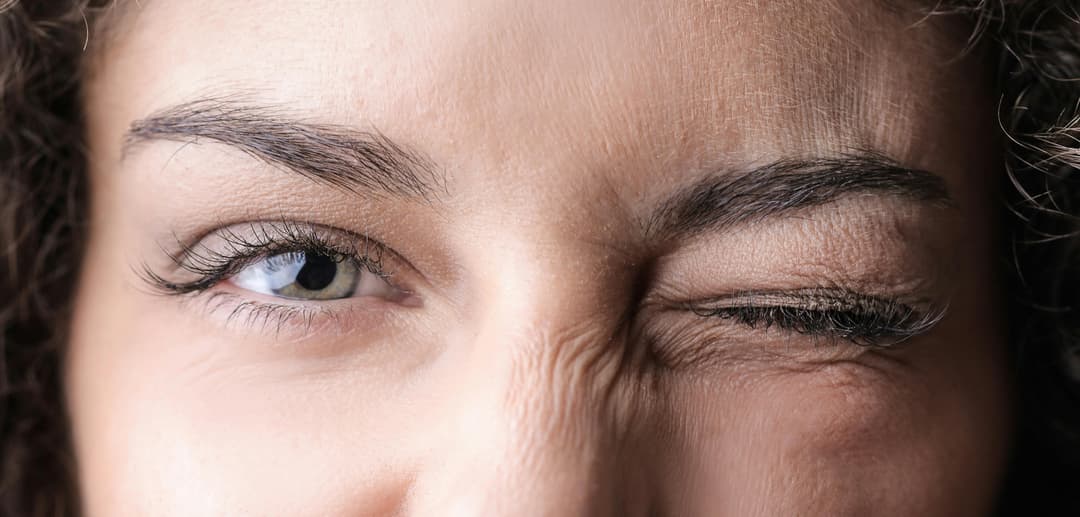


Muscles in the eyelid that contract to make us blink.
Nerve cell that transmits impulses from the CNS to the eye.
Structure in CNS, receives nerve impulses from receptors in the eye.
Exit quiz
6 Questions