Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- OCR
- Higher
Why chemical reactions occur
I can explain chemical bonding in terms of the transfer or sharing of electrons.
- Year 10
- OCR
- Higher
Why chemical reactions occur
I can explain chemical bonding in terms of the transfer or sharing of electrons.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
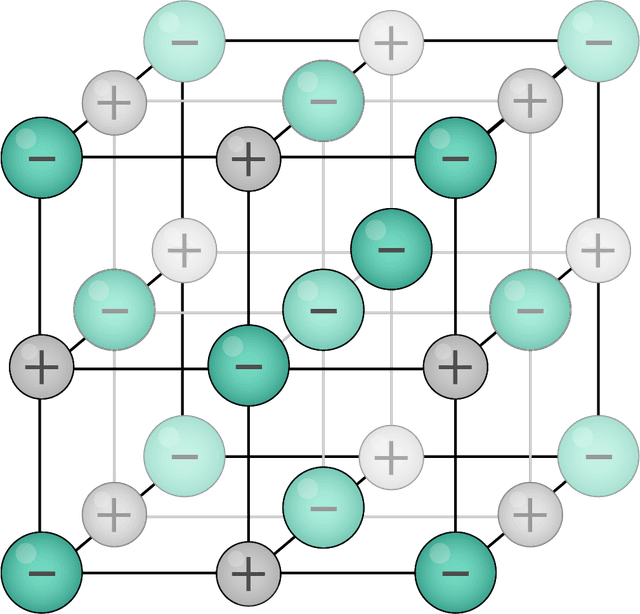
- There are five different types of substance: monatomic, simple covalent (molecules), giant covalent, ionic and metallic.
- The outer shell in most atoms can hold 8 electrons but, in hydrogen and helium, it can only hold 2 electrons.
- Most atoms increase their stability by forming bonds with other atoms so that they have a full outer shell of electrons.
- Some atoms will share electrons with other atoms to increase their stability.
- Some atoms will lose or gain electrons to increase stability forming cations or anions, respectfully.
Keywords
Molecule - A molecule is a particle consisting of a fixed number of (two or more) non-metal atoms covalently bonded together.
Noble gas configuration - When an atom has a full outer shell of electrons, it has a noble gas electron configuration.
Outer shell - The outer shell is the highest energy level in an atom and is usually the furthest from the nucleus.
Cation - A particle with a positive charge.
Anion - A particle with a negative charge.
Common misconception
Atoms react because they 'want' to gain a fuller outer shell of electrons – atoms don't have feelings! Monatomic means one atom and may be confused with the term element, which means one type of atom.
Take care with language and avoid personifying the atoms. Make sure that definitions and terms are used correctly.
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Why chemical reactions occur, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 combined science lesson on: Why chemical reactions occur, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 combined science lessons from the Structure and bonding unit, dive into the full secondary combined science curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the following terms to the correct definition.
Relative mass of an atom, the total mass of its protons and neutrons.
Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element.
The smallest particle of an element that can exist.
A group of atoms chemically bonded together.
Q2.Which of the following are elements?
Q3.Oxygen has an atomic mass of 16.0 and an atomic number of 8. How many electrons does an atom of oxygen have?
Q4.Lithium is in Group 1, period 2 of the periodic table. It has an atomic number of 3. How many electrons are found in the outer shell of a lithium atom?
Q5.Which of the following are examples of diatomic molecules?
Q6.Which of the following statements about subatomic particles are correct?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the following terms to the correct definitions.
The arrangement of electrons in shells, in an atom or ion.
The highest energy level in an atom, contains electrons.
A particle with a positive charge.
A particle with a negative charge.
Q2.In which of the following are electrons donated and accepted?
Q3.Which of the following are monatomic substances?
Q4.What type of bonding forms between non–metal atoms?
Q5.Why is an oxygen atom considered to be unstable?
Q6.Which of the following diagrams shows an ionic substance?