Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 4
Developing reading preferences in Year 4 through personal reflection
I can understand my reader identity by reflecting on my reading experiences.
- Year 4
Developing reading preferences in Year 4 through personal reflection
I can understand my reader identity by reflecting on my reading experiences.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Reader identity is the process of reflecting on what you enjoy or do not enjoy reading
- Reading can take many forms; it does not have to be restricted to a book
- Reading is a skill that you use every single day
- A reading preference can include what we read and where we read.
Keywords
Reading preference - A reading preference can include what we read and where we read.
Form - Form is the way that a text can be presented.
Treasure hunt - A treasure hunt is an activity where you search for hidden items or clues.
Common misconception
Pupils may think reading is restricted to a book.
By completing a reading treasure hunt, pupils can explore reading in a range of forms.
To help you plan your year 4 English lesson on: Developing reading preferences in Year 4 through personal reflection, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 4 English lesson on: Developing reading preferences in Year 4 through personal reflection, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 2 English lessons from the Developing reading preferences in Year 4 unit, dive into the full primary English curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which of the following forms are released weekly, with a story spread across a number of weeks?
Q2.A __________ is a person who writes poems.
Q3.True or False? A poetry collection must contain poems by the same poet.
Q4.Match the following terms to their definitions.
the person responsible for crafting the words that make up a text
the person responsible for creating the pictures that make up a text
an organisation which edits, designs and prints the book
the name given to a piece of writing, such as a book, story or poem
Q5.Match the following terms to their definitions.
a reflection on who you are as a reader and why you read
a way of thinking about and understanding something
a group of readers who read, share and discuss their reading
Q6.Match the following terms to their definitions.
reading that we enjoy and do of our own free will
reading to gain information or verify knowledge
reading to gain information that we enjoy doing
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Match the keywords to their definitions.
what we read and where we read
the way that a text can be presented
an activity where you search for hidden items
Q2.Select examples below of when a reader might read.
Q3.Select examples below of where a reader might read.
Q4.What type of reading is required to read the image below?
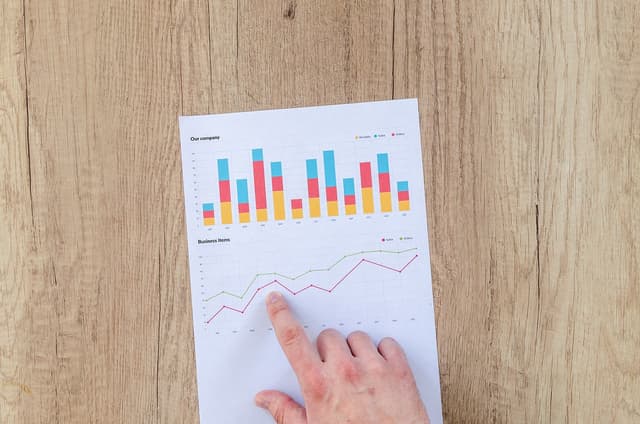
Q5.What type of reading is required to read the image below?