Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 2
Use knowledge of the 2, 5 and 10 times tables to solve problems
I can use knowledge of the 2, 5 and 10 times tables to solve problems.
- Year 2
Use knowledge of the 2, 5 and 10 times tables to solve problems
I can use knowledge of the 2, 5 and 10 times tables to solve problems.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Numbers in the 10 times table are also in the 2 and 5 times tables.
- Multiples of 2 are all even numbers.
- Multiples of 10 all have a zero in the ones column.
- Multiples of 5 all have a 5 or a 10 in the ones column.
Keywords
Commutative - Multiplication is commutative. This means the order of the factors can be changed without changing the calculation or product.
Common misconception
Pupils may misunderstand the contexts or language within worded problems and therefore not understand the calculation required to solve.
Model clearly how to identify key phrases and words which will identify the operation and equation required for word problems. Pupils may benefit from representing what is known and what is unknown such as by drawing a bar model.
To help you plan your year 2 maths lesson on: Use knowledge of the 2, 5 and 10 times tables to solve problems, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 2 maths lesson on: Use knowledge of the 2, 5 and 10 times tables to solve problems, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 1 maths lessons from the Representing counting in 5s as the 5 times table and link to the 10 times tables unit, dive into the full primary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which expression matches this array?
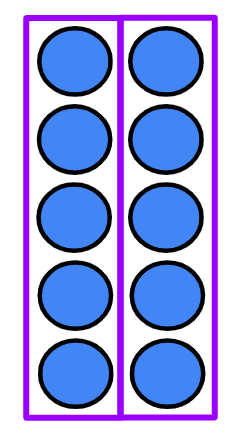
Q2.Look at the array and complete the sentence. There are ___ groups of 6 , this is the same as × 6
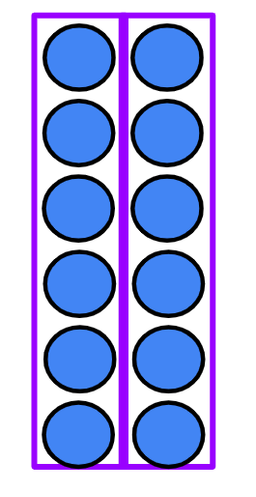
Q3.Which word completes the sentence? The order of the __________ can be changed and the product remains the same. This is known as commutativity.
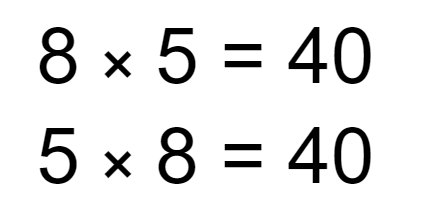
Q4.Look at the arrays. Select the correct expressions that describe the groupings.
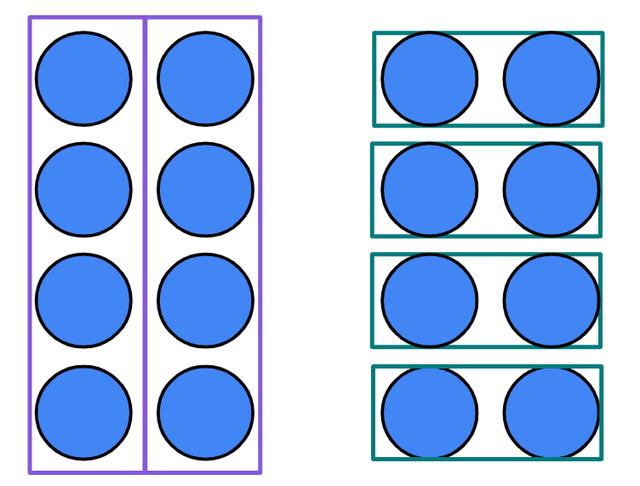
Q5.Look at the array to help you fill in the gap with the same number: × 4 = 4 × ___
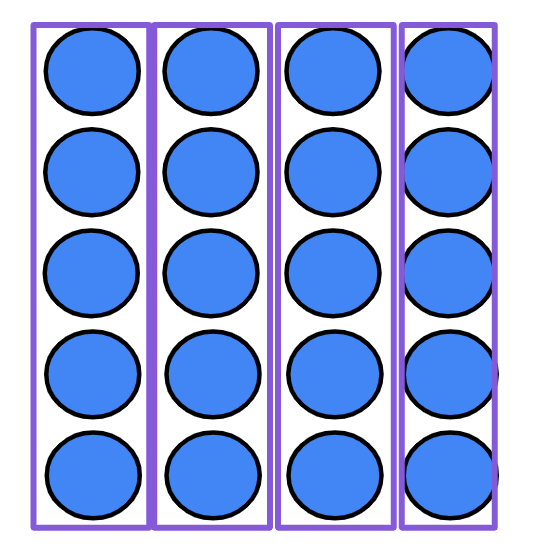
Q6.Aisha and Laura have some coins. They each have 50 p altogether. If Aisha has one 50 pence coin and Laura has five of the same coin, what coins must Laura have? Laura will have 5 pence coins.

Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.2 × 3 = 6, the 2 represents the number of plates, the 3 represents __________. These are our factor pairs.
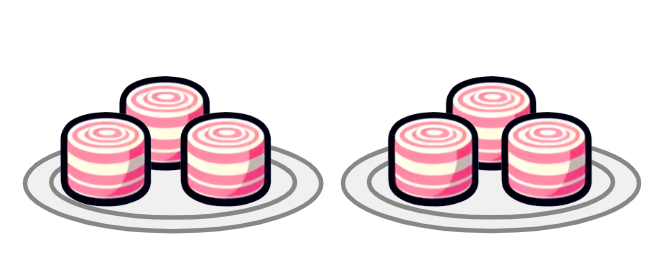
Q2.Look at the image below. Select the multiplication expression that represents the amount of sweets.

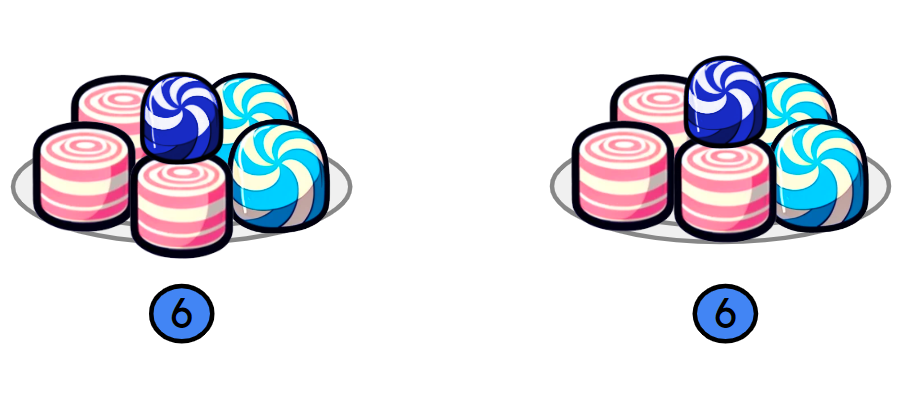
Q3.Select the correct ways to represent the image below.

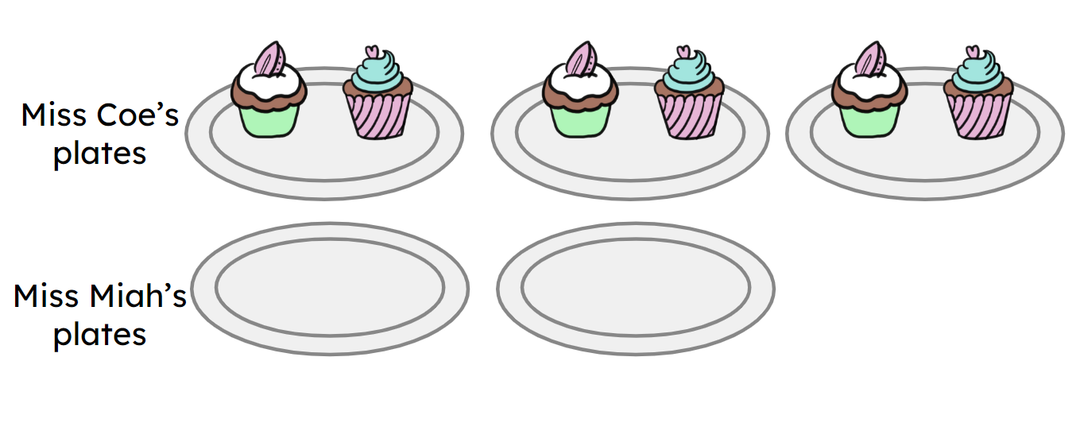
Q4.Miss Coe has organised 3 plates of 2 cupcakes. Miss Miah has 2 plates. If they both have the same amount of cupcakes, how many cupcakes does Miss Miah have on each of her plates? cupcakes.
Q5.A local bakery packs pastries into 4 boxes of 5 pastries. If 5 boxes are used and the same amount of pastries are packed, how many pastries will be in each box? pastries
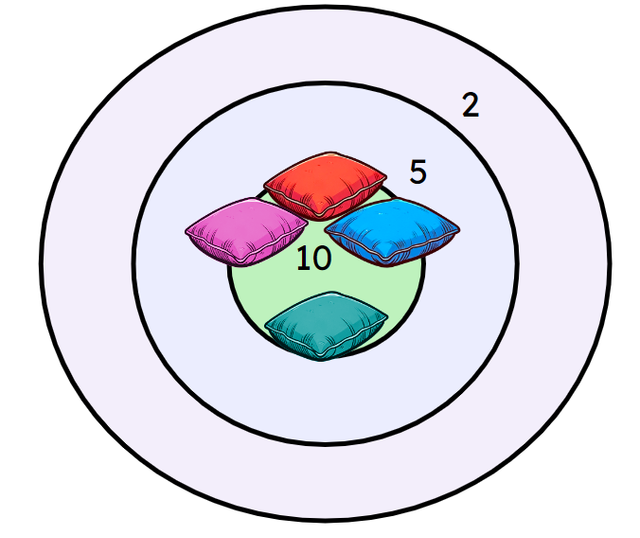
Q6.Aisha plays a bean bag game and throws 4 of her bean bags into the 10 point zone. How many bean bags would she need to score the same amount if all her bean bags were thrown into the 5 point zone?