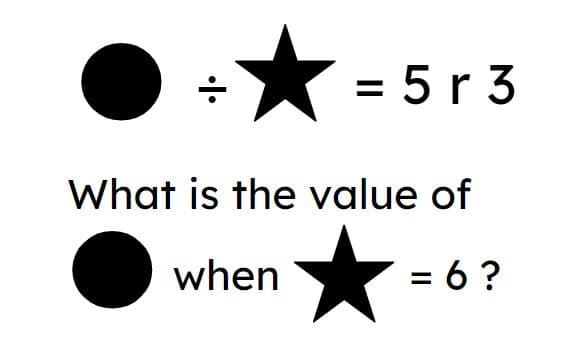Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 4
Use knowledge of division equations and remainders to solve problems
I can use knowledge of division equations and remainders to solve problems.
- Year 4
Use knowledge of division equations and remainders to solve problems
I can use knowledge of division equations and remainders to solve problems.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- If the dividend is a multiple of the divisor, there will be no remainder.
- If the remainder is greater than the divisor, another equal group can be made.
- If the remainder is known, the possibilities for a missing divisor can be found.
- If the divisor is known, the possibilities for a missing remainder can be found.
- This knowledge can help when solving missing number equations.
Keywords
Dividend - The dividend is the whole amount to be divided into groups or divided into equal parts. It is what we are dividing.
Divisor - The divisor is the number in each group or the number of equal parts that the whole is divided into or between. It is what we are dividing by.
Remainder - A remainder is the amount left over after division when the dividend does not divide exactly by the divisor.
Common misconception
Children may either choose to use a multiple higher than the dividend, e.g. 53 ÷ 9 = , or choose a multiple that is too low, e.g. 57 ÷ 8 = , which results in a remainder greater than the divisor.
When solving equations, refer back to the largest multiple that is less than or equal to the dividend and use number lines to allow children to visualise this.
To help you plan your year 4 maths lesson on: Use knowledge of division equations and remainders to solve problems, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 4 maths lesson on: Use knowledge of division equations and remainders to solve problems, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 2 maths lessons from the Division with remainders unit, dive into the full primary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Complete the sentence. If the dividend in a calculation is not a multiple of the divisor,
Q2.Which of the following will not have a remainder?
Q3.Which of these numbers will have a remainder when the divisor is 8?
Q4.58 books are sorted onto 9 shelves in the classroom. Are there any books left over?
Q5.We know that multiples of 6 are even and have a digit sum that is divisible by 3 Which of these numbers will have a remainder when divided by 6?
Q6.We know that multiples of 4 must be even and, if halved, will reach an even number. Which of these numbers will have a remainder when divided by 4?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Pencils are put into pots of 7 Which of the total number of pencils won’t divide equally into pots of 7?
Q2.When dividing 21 into equal groups, which group size will give a remainder?
Q3.Which of these equations is incorrect?
Q4.Jun has fewer that 40 counters. When divided into groups of 7 there are no remainders and when divided into groups of 5 there are no remainders. How many counters must Jun have?
Q5.Look at the image.

Q6.Look at the image.