Year 9
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- In this lesson, we will develop an understanding of Pythagoras' theorem by drawing upon our tilted squares knowledge.
Licence
This content is made available by Oak National Academy Limited and its partners and licensed under Oak’s terms & conditions (Collection 1), except where otherwise stated.
6 Questions
Q1.
Look at the diagram below and fill in the gap: The area of the larger square is equal to the ........... of the area of the two smaller squares.
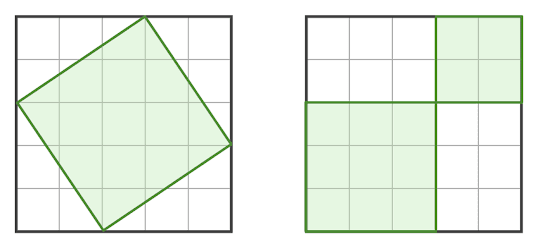
difference
product
Q2.
What is the side length of the larger square?
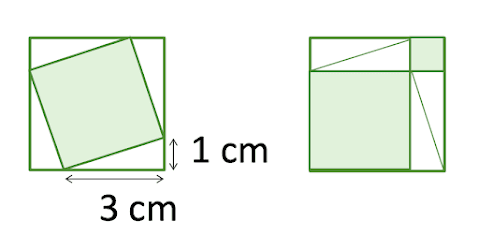
√8
10
8
Q3.
What is the side length of the larger square?
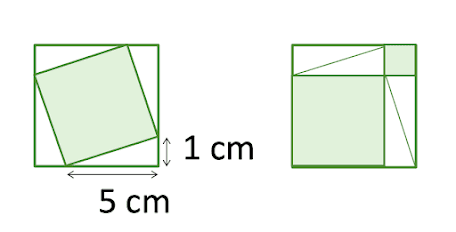
√12
12
26
Q4.
What is the side length of the larger square?
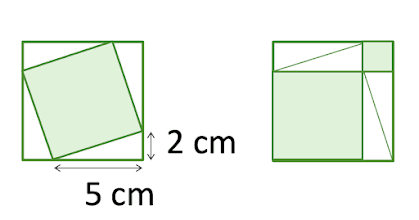
√7
29
7
Q5.
If the pink triangle has a base of 10 and a height of 2. What is the area of the green tilted square?
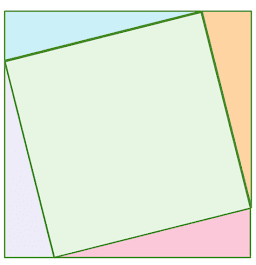
√104
√20
20
Q6.
If the pink triangle has a base of 10 and a height of 2. What is the side length of the green square?
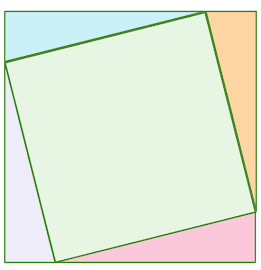
√29
104
29
4 Questions
Q1.
What is the name of the longest side of a right-angled triangle?
base
height
Q2.
Which diagram shows the hypotenuse correctly highlighted and labelled?
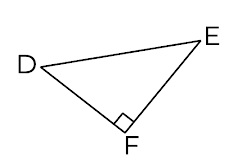
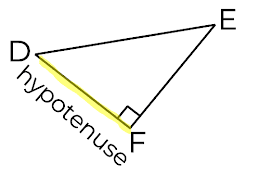
Option 1
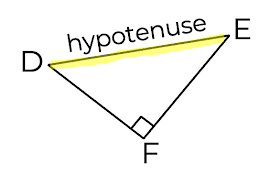
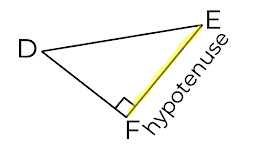
Option 3
Q3.
A right-angled triangle has the sides a, b and c. Choose the correct formula for finding the length of side a.
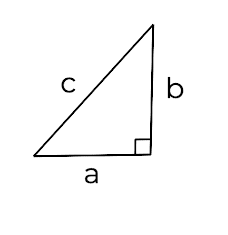
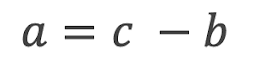
Option 1
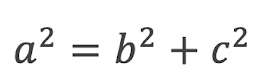
Option 2
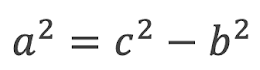
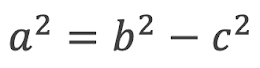
Option 4
Q4.
Work out the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle shown below.
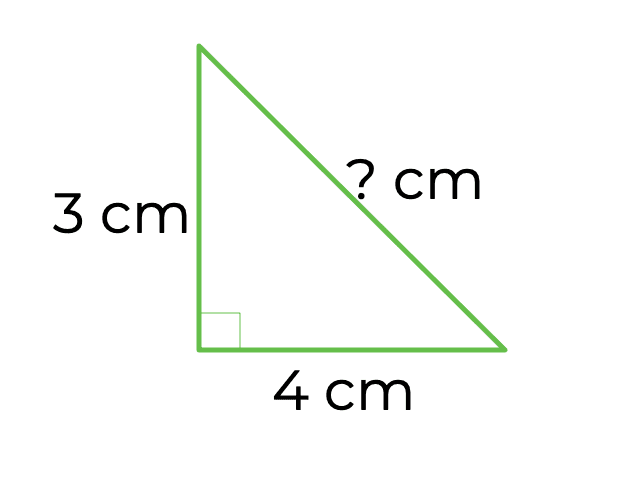
14 cm
25 cm
7 cm

