Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 8
Understanding constructing a circle
I can recognise a circle as a collection of points equidistant from a fixed point.
- Year 8
Understanding constructing a circle
I can recognise a circle as a collection of points equidistant from a fixed point.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- A pair of compasses can be used to draw circle with a particular radius.
- All the points on the circle will be the same distance from the centre.
- The centre of a circle is the point that is the same distance from every point on the circle.
- The collection of points an equal distance from a given point form a circle.
Keywords
Fixed point - A fixed point is a point that does not change or move.
Circumference - The circumference of a circle is the perimeter of the circle.
Arc - An arc is part of a curve. An arc of a circle is part of the circle’s circumference.
Equidistant - Points A and B are equidistant from a third point C if the distance AC is equal to the distance BC.
Common misconception
During tasks, pupils may use a ruler to draw or check whether points are equidistant from a centre.
While the tasks could be completed with a ruler, it may be quicker, easier and more accurate to use a pair of compasses.
To help you plan your year 8 maths lesson on: Understanding constructing a circle, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 8 maths lesson on: Understanding constructing a circle, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 maths lessons from the Constructions unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
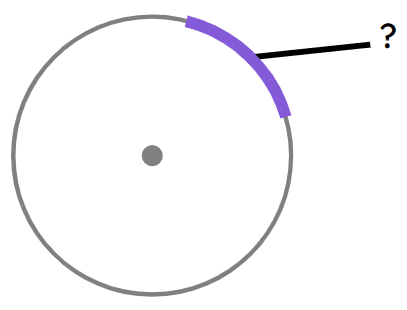
Q1.Which part of the circle is highlighted and labelled with a question mark?
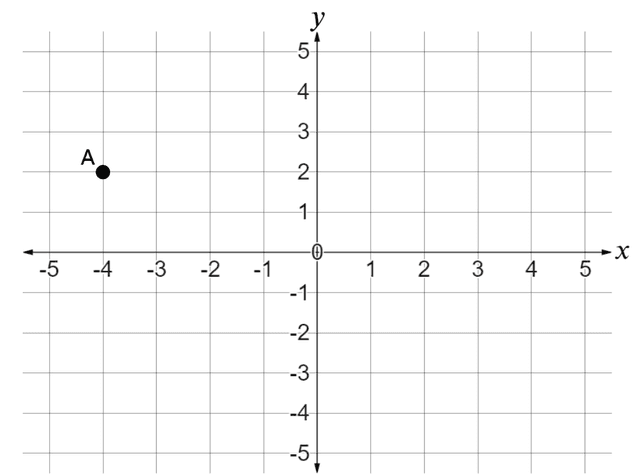
Q2.What are the co-ordinates of point A?
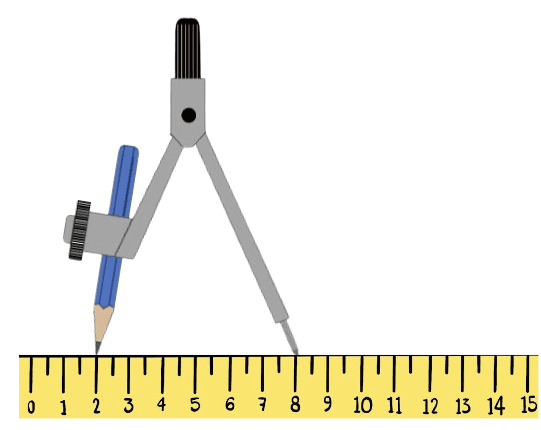
Q3.Izzy tries to draw a circle with a pair of compasses without moving the ruler. The pencil starts at the 2 cm mark on the ruler. Half way around, the pencil touches the cm mark on the ruler.
Q4.The image shows a circle with centre at point A. Sofia draws a circle with radius 2 cm with its centre at point B. How many times will the two circles intersect?
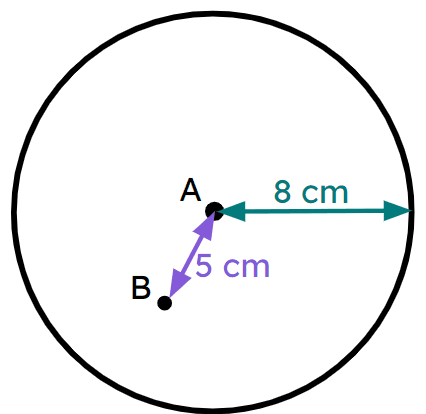
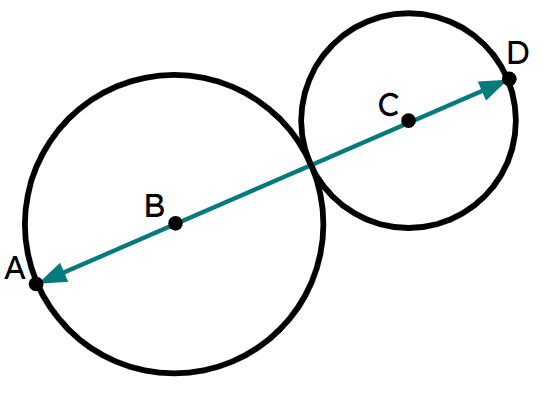
Q5.The diagram is not to scale. Points A, B, C and D lie on a straight line. The distance from A to D is 20 cm. The radius of the large circle is 8 cm; the radius of the small circle is .
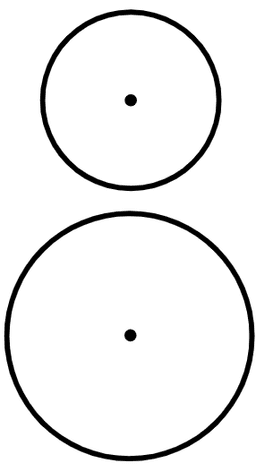
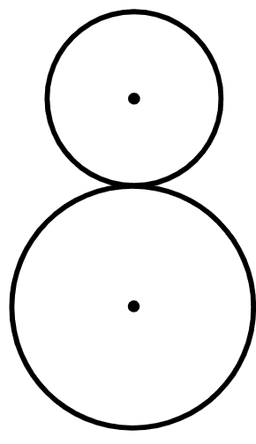
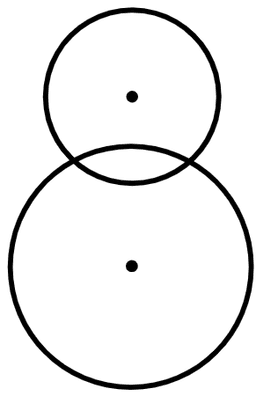
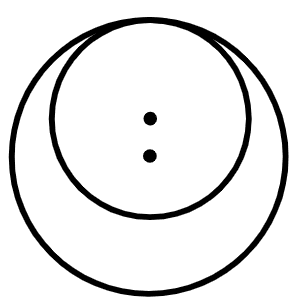
Q6.Laura draws two circles. One has a radius 5 cm, the other has a radius 9 cm. The distance between the centre points of each circle is 16 cm. Which image matches Aisha's drawings?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.A circle is a shape such that every point is to its centre.
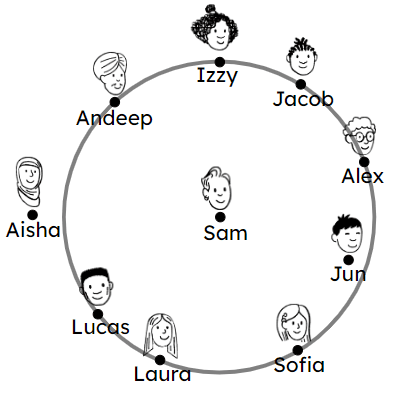
Q2.Sam is stood in the centre of a circle. Which pupil is the closest to Sam?
Q3.The pair of compasses in the image are used to draw a circle around the origin of the co-ordinate grid. Which point would lie on the circle?
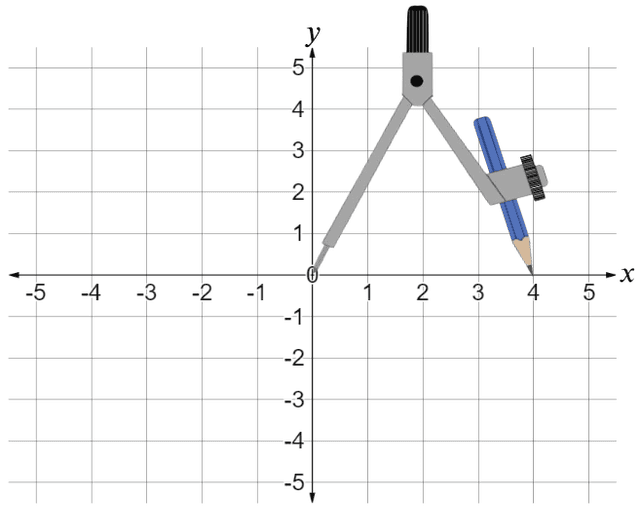
Q4.The pair of compasses in the image are used to draw a circle around the origin of the co-ordinate grid. The diameter of the circle is units.

Q5.The images show a wrecking ball swinging from a fixed point on a crane. Which image correctly shows the movement of the wrecking ball?
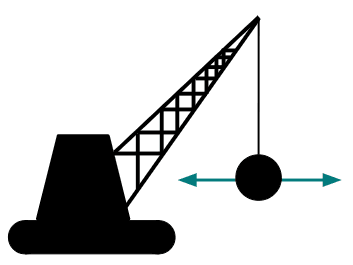
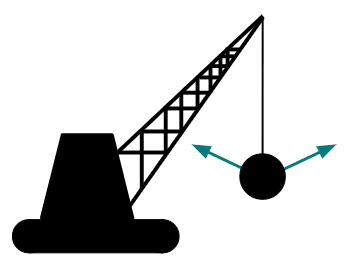
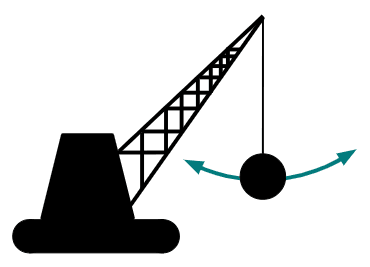
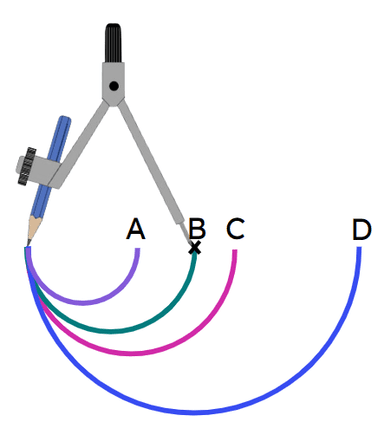
Q6.Which arc will the pair of compass draw?