Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 8
Statistical problems - drawing conclusions
I can effectively summarise and communicate conclusions to a statistical problem.
- Year 8
Statistical problems - drawing conclusions
I can effectively summarise and communicate conclusions to a statistical problem.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Conclusions can be drawn from statistical summaries and graphical representations.
- Conclusions are understood to be limited by any biases.
- Conclusions are understood to only be valid for this sample of data.
Keywords
Population - The population is the entire set of people, creatures, plants or items that make up the whole group which is being studied
Sample - A sample is a subset of the population.
Bias - Bias can be present in any sample collected from a population. e.g. only asking year 7 pupils about a whole school issue.
Statistical summary - A statistical summary sums up the features of a data set
Common misconception
The findings for a data investigation using a sample can always be generalised to the population.
The generalisability of results can depend on how representative the sample is of the population which it is being compared to.
To help you plan your year 8 maths lesson on: Statistical problems - drawing conclusions, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 8 maths lesson on: Statistical problems - drawing conclusions, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 3 maths lessons from the Numerical summaries of data unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.In a data investigation, the __________ is the entire set of people, creatures, plants or items that make up the whole group which is being studied.
Q2. is the relationship between two variables on a scatter graph.
Q3.Extrapolation is the process of estimating unknown values that are .
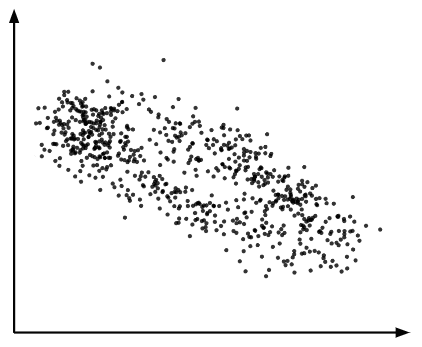
Q4.What type of correlation does the scatter graph show?
Q5.A data investigation finds a positive correlation between temperature and ice cream sales. What does this suggest?
Q6.The mean for the following numbers data set 8.2, 7.4, 11.3, 9.1 is .
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
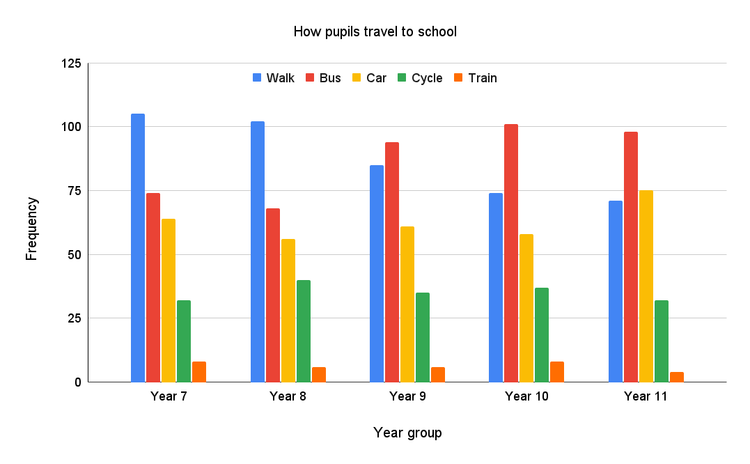
Q1.Which is the least popular mode of transport in this school?
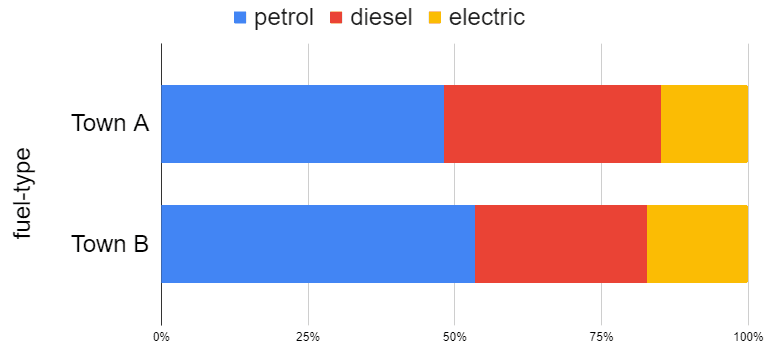
Q2.An investigation surveys residents of two towns about which type of car they drive. The stacked bar chart shows the results. Which is the most popular type of car in this survey?
Q3.The scatter graph shows the population of some towns and the number of phone towers the town has. Each point in the scatter graph represents a town or region. Match each town with its statement.
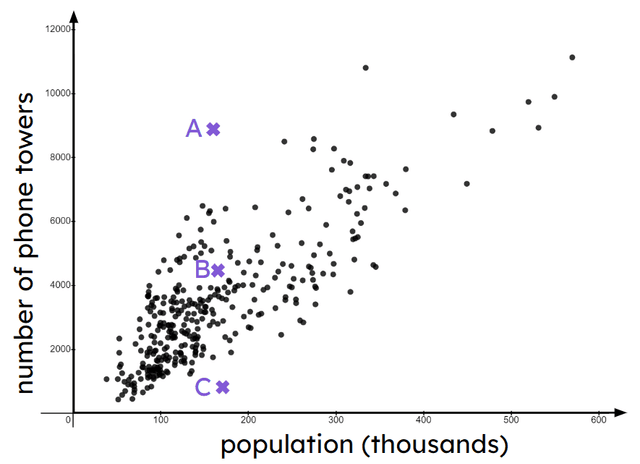
has a high number of phone towers for the population
has the expected number of phone towers for the population
has a low number of phone towers for the population
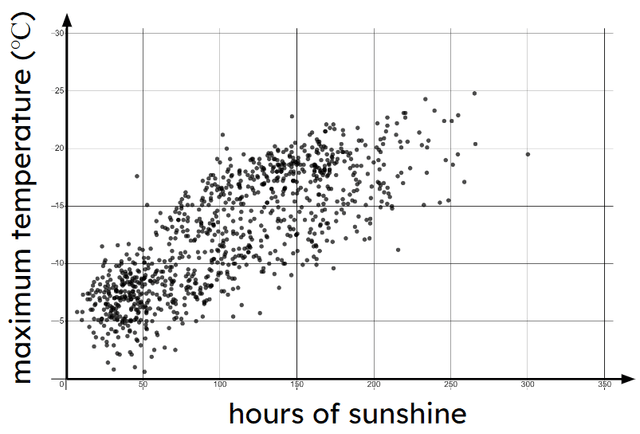
Q4.The scatter graph shows data about the sunshine duration and mean temperature for each month in a city. Which of the statements is the most valid?
Q5.A data investigation surveys 100 people in Oxford about their preferred mode of transport. The most popular mode of transport was bicycle. Which is the most valid conclusion based on these results?