Myths about teaching can hold you back
Learn why
New
New
Lesson 3 of 13
- Year 9
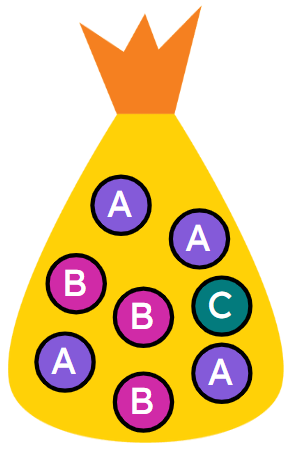
Calculating theoretical probabilities from lists (one event)
I can find theoretical probabilities from a list of possible outcomes for one event.
Lesson 3 of 13
New
New
- Year 9
Calculating theoretical probabilities from lists (one event)
I can find theoretical probabilities from a list of possible outcomes for one event.
These resources will be removed by end of Summer Term 2025.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
These resources were created for remote use during the pandemic and are not designed for classroom teaching.
Lesson details
Assessment exit quiz
Download quiz pdf