Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 11
- Foundation
Problem solving with loci and constructions
I can use my knowledge of loci and constructions to solve problems.
- Year 11
- Foundation
Problem solving with loci and constructions
I can use my knowledge of loci and constructions to solve problems.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Your knowledge of loci can be applied to your knowledge of bearings
- Your knowledge of loci can be used to help solve area problems
Keywords
Locus/loci - A locus is a set of points that satisfy a given set of conditions. Multiple sets of points are referred to as loci.
Bearing - A bearing is an angle measured in degrees from North in the clockwise direction and written with three figures. E.g. an angle of 82° is written as 082°.
Area - The area is the size of the surface and states the number of unit squares needed to completely cover that surface.
Common misconception
Pupils may not consider that, in some contexts (e.g. a corded lawnmower), the shape of the locus will include sectors of different radii, if a shape/object is creating a barrier.
Have pupils consider the impact of going around the corner of a shape.
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Problem solving with loci and constructions, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Problem solving with loci and constructions, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 maths lessons from the Loci and construction unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Lesson video
Loading...
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.The locus of points __________ from another point can be represented by a circle.
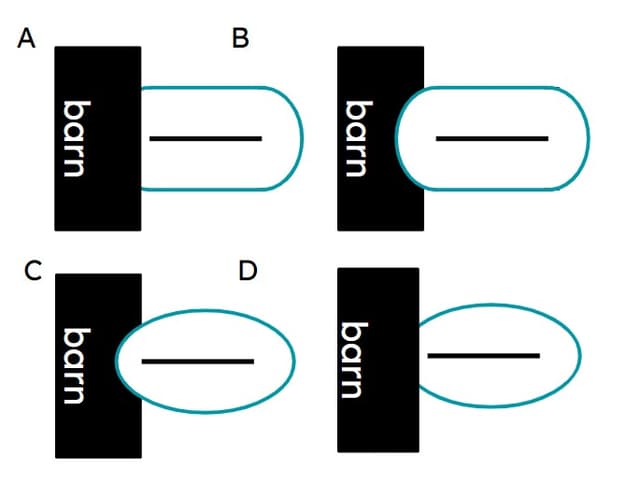
Q2.A goat is tied to a railing by a 1 metre long rope. There is a barn near the railing. Which of these shows the locus of points the goat can walk to?
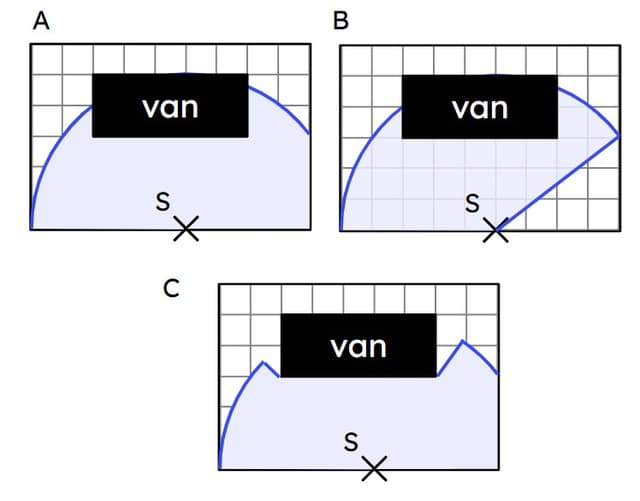
Q3.A motion sensor (S) can film any object up to 5 metres away. It can only detect in locations that it can see in a straight line. Which construction shows the locus of locations the sensor can detect?
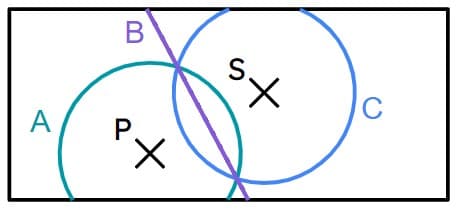
Q4.This map shows two rocks, P and S, out at sea. Any ship must stay 10 metres or more away from each rock. Which locus shows points that are all 10 metres away from rock P? (A, C have radii of 10 m).
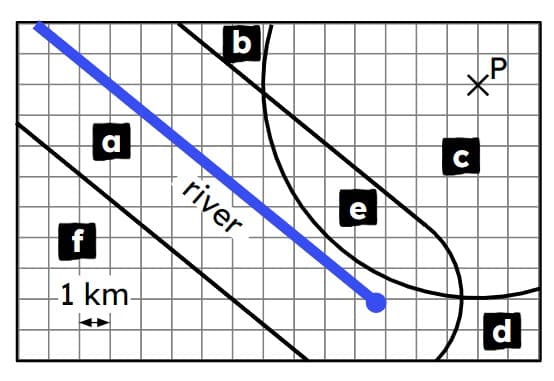
Q5.Laura’s grandma wants to move to a house that is within 7 km of Laura’s house at P, but more than 3 km from the river. Laura's grandma should move to region .
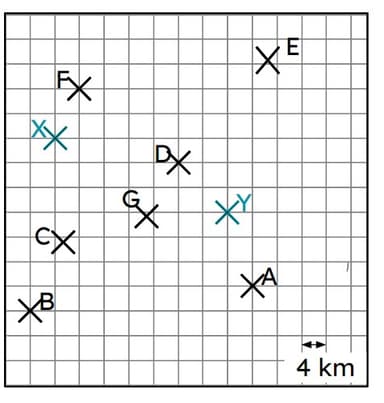
Q6.Two mobile phone masts (X and Y) can broadcast their signal to a maximum of 24 km. The further away from the mast, the weaker the signal is. Which points will receive a signal from both masts?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.A bearing is an angle measured in degrees from __________ in the clockwise direction and written with three figures.
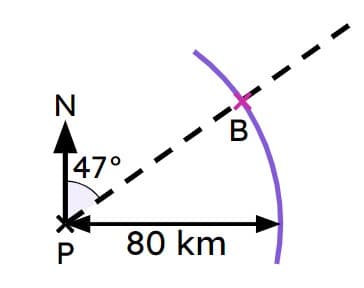
Q2.A boat (B) leaves a port (P) on a bearing of 047° at a speed of 20 km/h. The boat has been travelling for hours.
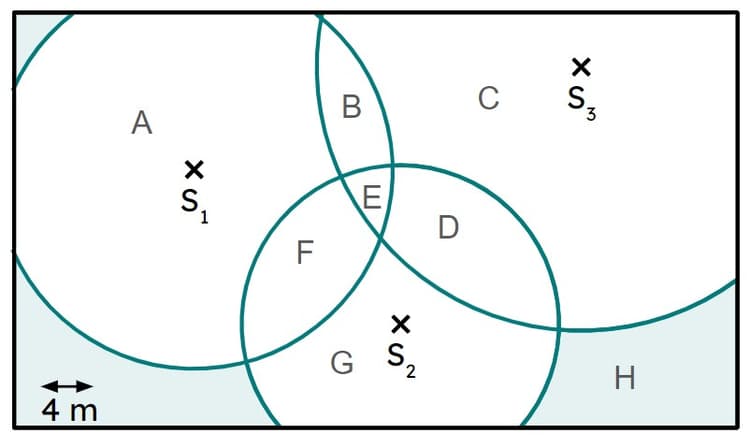
Q3.Three sensors are set up for security. Sensor 1 has a range 15 m, sensor 2 has a range 12 m and sensor 3 has a range 20 m. Sensors 2 and 3 are activated. The intruder is likely to be in region .
Q4.A ship, S, needs to pass through a point that is midway between two buoys. Alex and Sam both do some constructions to find the correct point to pass through. Whose construction is correct?
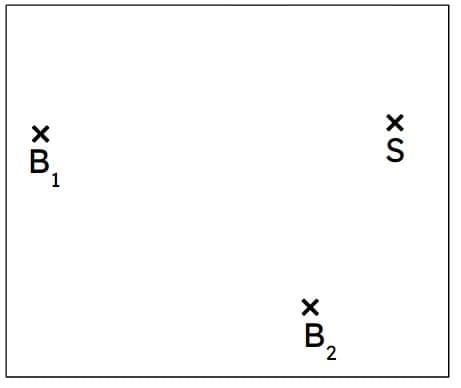
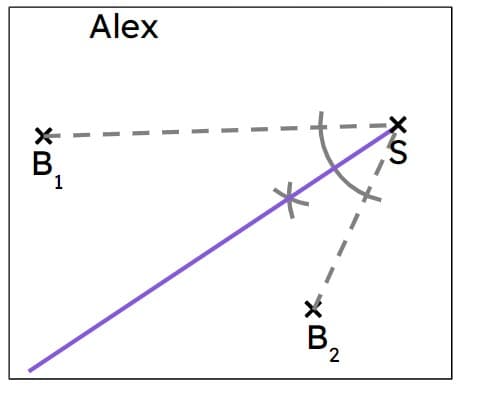
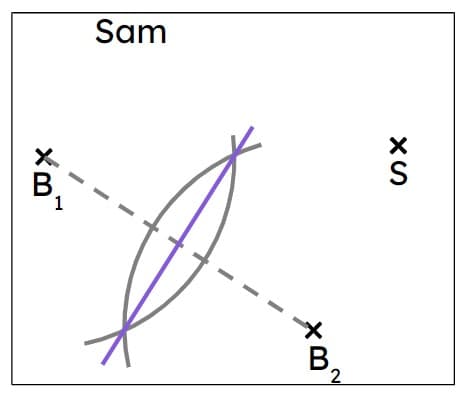
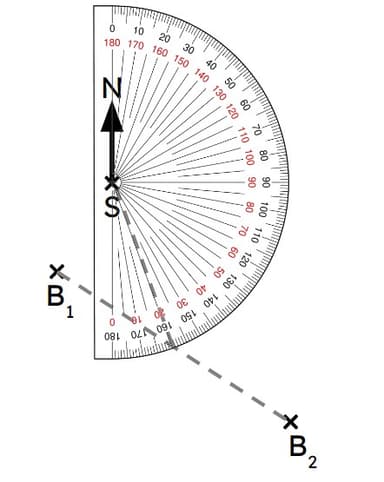
Q5.A ship, S, needs to pass through a point that is midway between two buoys. What bearing should the ship sail on?
Q6.A goat is tethered to a horizontal pole by a rope with a ring attached. The pole is 5 metres long and the rope is 3 metres long. What is the area of region that the goat can graze?