Myths about teaching can hold you back
- Year 10
- Foundation
Sampling methods
I can see why samples are used and why different selection methods exist.
- Year 10
- Foundation
Sampling methods
I can see why samples are used and why different selection methods exist.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Samples are used when using the whole population would be impractical/destructive.
- There are various sampling methods.
- A simple random sample is one of the easiest samples to collect.
Keywords
Simple random sample - A simple random sample is where every item in a population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
Common misconception
Names in a hat is the simplest way to perform a simple random sample.
This can be true for very small populations but becomes time consuming quickly.
To help you plan your year 10 maths lesson on: Sampling methods, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 10 maths lesson on: Sampling methods, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 maths lessons from the Sampling unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Select all the examples of quantitative discrete data.
Q2.Data that has been previously collected for a different or unknown purpose are called data.
Q3.Lucas collects some data on shoe sizes. Which of these statements are correct?
Q4.Match each type of data to an example.
type of pet
number of pets in each household
mass of each pet
Q5.Laura measures the temperature outside her school every morning at 10 am for a month. What type of data has Laura collected?
Q6.Aisha writes an article for the school magazine about sport. She uses data from the local sports centre on what exercise classes they offer. What type of data has Aisha used?
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.The is the entire set of people, creatures, plants or items that make up the whole group which is being studied.
Q2.A simple sample is where every item in a population has an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
Q3.Investigation: A vet wants to check a sample of sheep from a farm to see if they are all healthy. What is the population in the vet's investigation?
Q4.A teacher asks each pupil in a class of 30 to write down any two numbers between 1 and 30. The teacher uses RanInt#(1, 15) on her calculator to pick 5 pupils. Will this give a simple random sample?
Q5.These six pupils are assigned a range of numbers. A simple random sample of two pupils will be taken using these numbers. The range of integers that Jun should be assigned is .
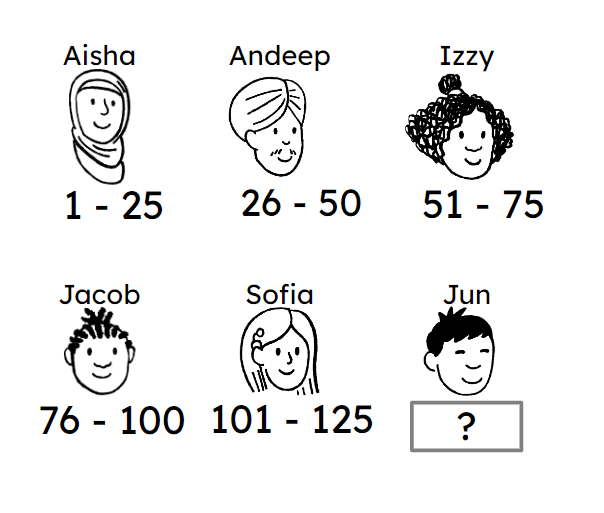
Q6.These six pupils are assigned a range of numbers. A simple random sample of two pupils will be taken using these numbers. What calculation will generate a simple random sample for this population?



