Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 11•
- Higher
Checking and securing calculating probabilities from tables
I can calculate probabilities from tables and two-way tables.


- Year 11•
- Higher
Checking and securing calculating probabilities from tables
I can calculate probabilities from tables and two-way tables.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- The probability of an outcome can be found by considering a table
- The probability of an event can be found by considering a table showing all possible outcomes
- The probability of an outcome can be found by considering a two-way table showing all possible outcomes for two events
- The probability of an event can be found by considering a two-way table showing all possible outcomes for two events
Keywords
Probability - The probability that an event will occur is the proportion of times the event is expected to happen in a suitably large experiment.
Frequency - The frequency is the number of times an event occurs; or the number of individuals (people, animals etc.) with some specific property.
Common misconception
Pupils may get confused between two-way tables that show outcomes and two-way tables that show frequencies (particularly when the outcomes are numbers, such as the sum of two dice rolls).
Two-way tables can be either used to display the sample space of individual outcomes or the frequencies of outcomes. Therefore, when using a table, it can be helpful to note down what type of data the table shows.
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Checking and securing calculating probabilities from tables, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Checking and securing calculating probabilities from tables, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 maths lessons from the Conditional probability unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
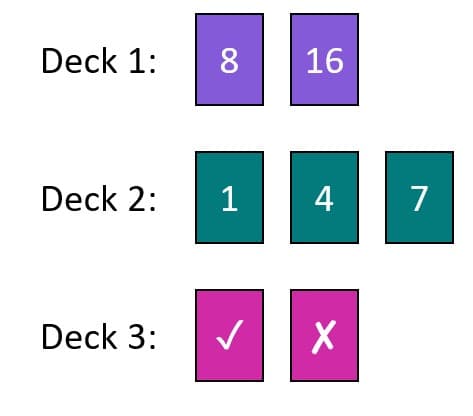
Q1.Here are three decks of cards.
A single card from each of Deck 1, Deck 2, and Deck 3 is drawn to make a trio.
What is the probability that this trio of cards contains a square number?
Q2.Sam plays a video game that can either be won or lost.
The probability that Sam wins the video game is 0.42.
The probability that Sam loses the video game is .
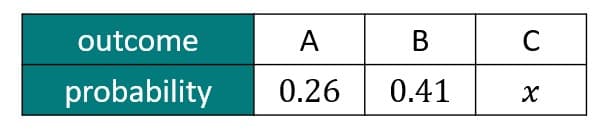
Q3.This table shows the mutually exclusive and exhaustive set of outcomes, and the probability of each outcome, from spinning a spinner once.
The value of $$x$$ is .
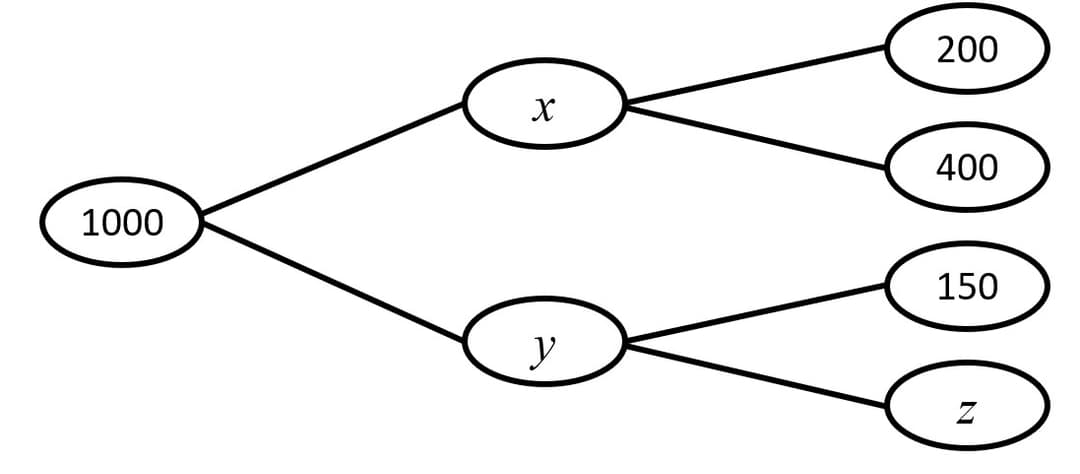
Q4.Which of these statements are correct for this frequency tree?
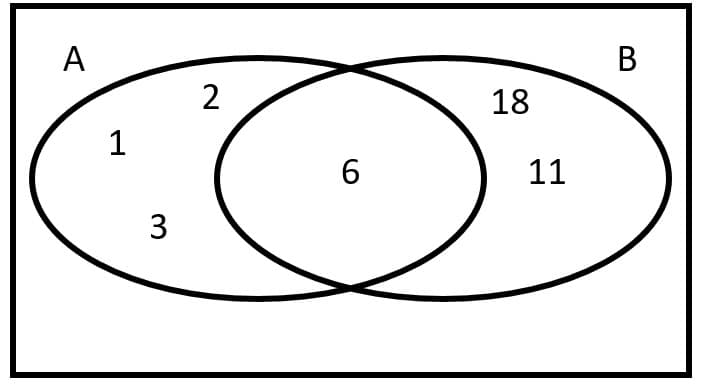
Q5.Each card on a deck of 7 cards has a unique integer written on it. A = {factors of 6}, B = {numbers ≥ 6}.
What positive integer could be on the seventh card for events A and B to not be exhaustive?
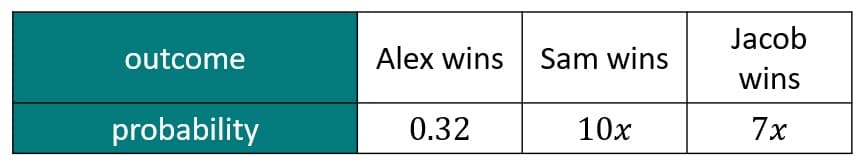
Q6.A game can either be won by either Alex, Sam, or Jacob.
P(Sam wins) = .
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
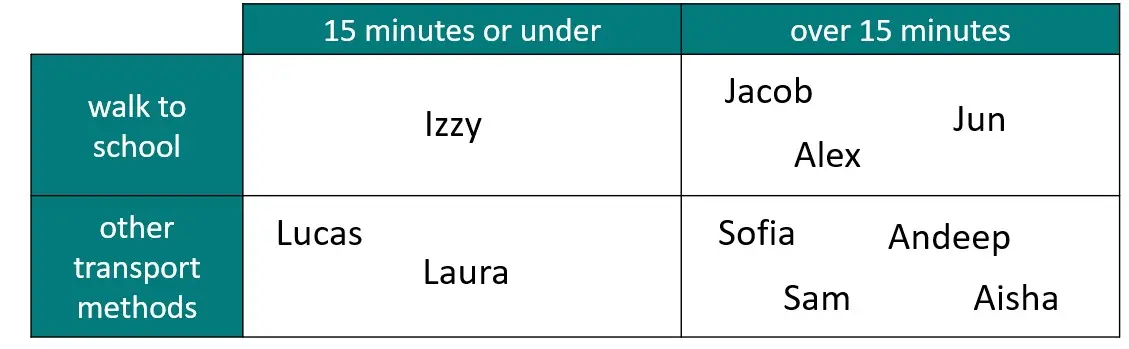
Q1.Students were asked whether they walked to school or used other transport methods, and how long their journey took them. Find the probability a student had a journey of over 15 minutes.
Q2.A spinner with outcomes {1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 15} is spun twice. The outcome of each spin is added together.
Find P(multiple of 10).
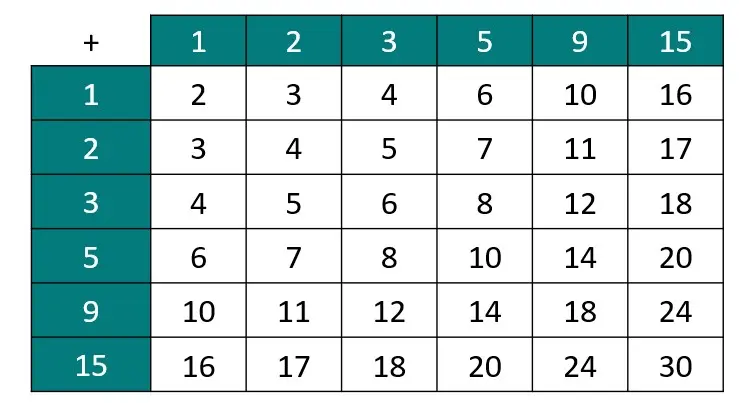
Q3.A spinner with outcomes {1, 2, 3, 5, 9, 15} is spun twice. The outcome of each spin is added together.
Find P(not a prime number).

Q4.People at a bus station were surveyed their age and where their destination was.
Match each frequency from the table to its value.
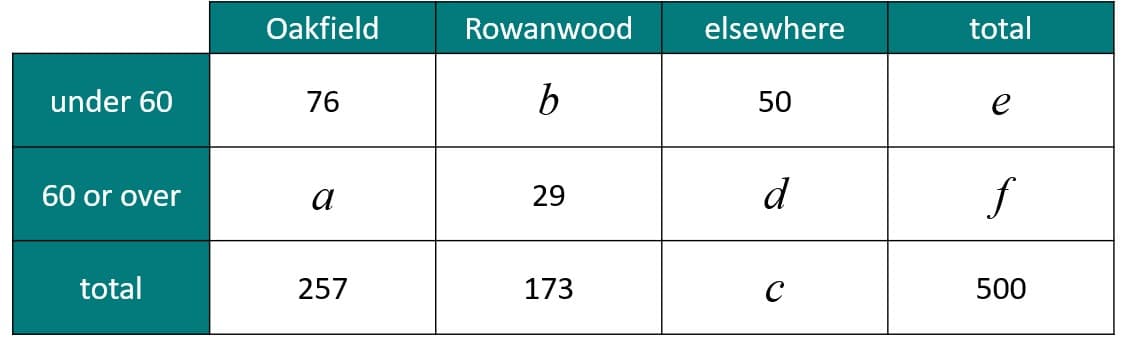
$$a$$ -
181
$$b$$ -
144
$$c$$ -
70
$$d$$ -
20
$$e$$ -
270
$$f$$ -
230
Q5.People at a bus station were surveyed their age and where their destination was.
A person is chosen at random.
Find P(60 or over and going to Rowanwood).

Q6.People at a bus station were surveyed their age and where their destination was.
A person going to Oakfield is chosen at random.
Find P(under 60).


