Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 11•
- Higher
Experimental vs theoretical probability
I can see the impact of sample size and compare theoretical probabilities to experimental ones.


- Year 11•
- Higher
Experimental vs theoretical probability
I can see the impact of sample size and compare theoretical probabilities to experimental ones.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Different sample sizes can impact the experimental probabilities
- As the sample size increases, the experimental probabilities approach the theoretical probabilities
- A larger sample size is more likely to show a truer estimation of the underlying probability
Keywords
Trial - A trial is a single, pre-defined test.
Experiment - An experiment is a repetition of a trial multiple times in order to observe how often each outcome occurs.
Probability - The probability that an event will occur is the proportion of times the event is expected to happen in a suitably large experiment.
Common misconception
Pupils may assume that it possible to determine whether a coin (or other object/game) is biased by conducting an experiment with a small number of trials.
The greater the number of trial that an experiment contains, the closer the relative frequency of an outcome gets to its theoretical probability.
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Experimental vs theoretical probability, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Experimental vs theoretical probability, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 maths lessons from the Conditional probability unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.__________ probability can be determined by the number of times an event occurred during multiple trials.
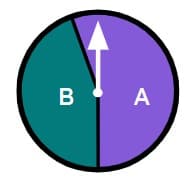
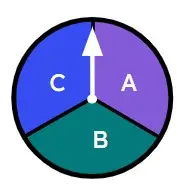
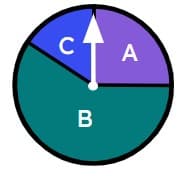
Q2.Select the fair spinners.
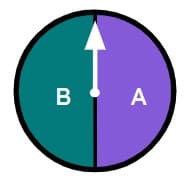
Q3.A toy brick that is dropped could land in one of four possible ways. Jun drops the toy brick multiple times. Starting with the least likely outcome, place the outcomes in order of likelihood.
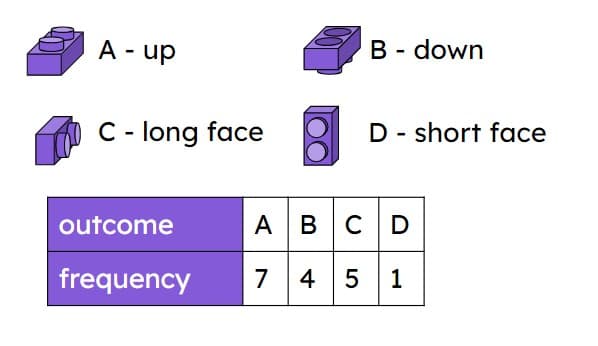
Q4.A toy brick that is dropped could land in one of four possible ways. Sofia and Jun drop the toy brick multiple times. Whose results should be the most reliable? Why?
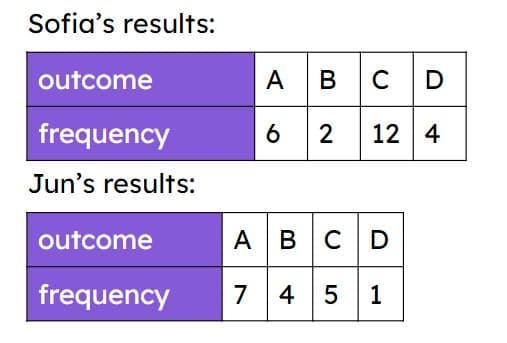
Q5.A dropped cone could land in one of two ways. The bar chart shows the results from an experiment. Which calculation shows how to find the experimental probability of the cone landing curve down?
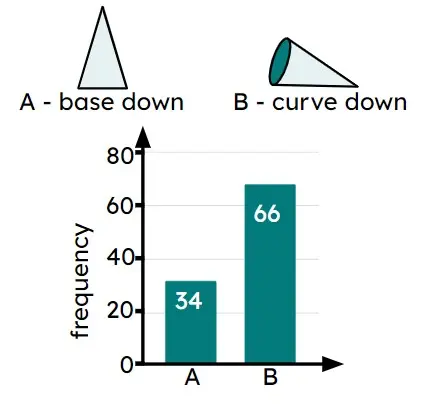
Q6.A dropped cone could land in one of two ways. The bar chart shows the results from an experiment. In an experiment with 800 trials you should expect the cone to land curve down times.

Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.In which of these situations is it possible to work out a theoretical probability?
Q2.Alex flips a coin 4 times. The coin lands heads 3 times. Which of these statements are correct?
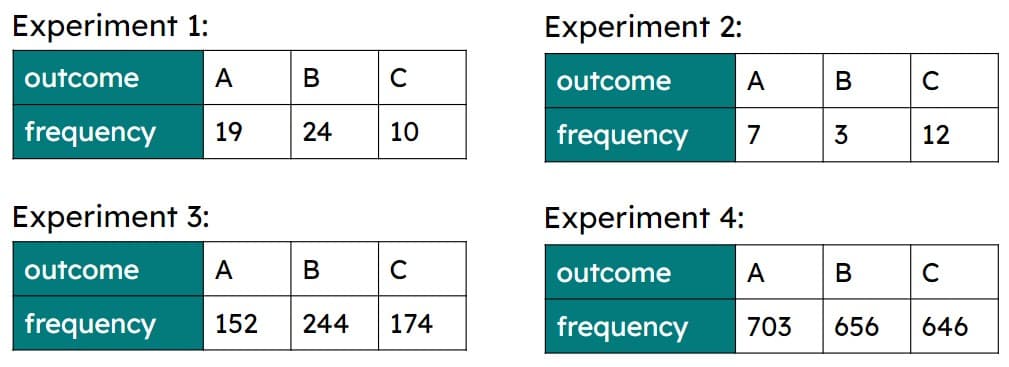
Q3.A spinner contains three letters: A, B and C. The tables show results from four experiments with the spinner. Which experiment will produce the most reliable set of experimental probabilities?
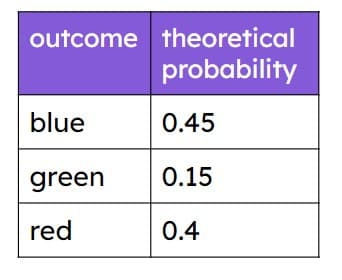
Q4.The table shows the theoretical probabilities of taking a counter of a particular colour out of a bag of counters. In 1000 trials the number of times you should expect to draw a blue counter is .
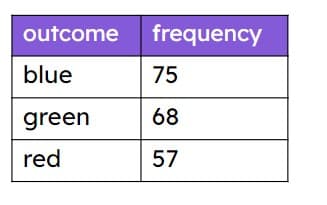
Q5.A box contains 400 counters. A counter is drawn, its colour noted and replaced. The results are in the table. Estimate how many red counters are in the box.
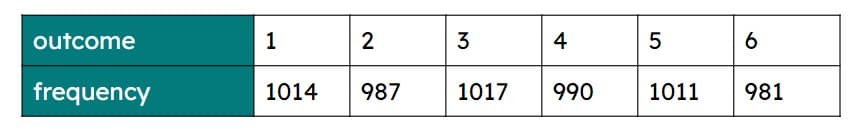
Q6.A class investigates whether a 6-sided die is biased. The table shows the results. Estimate the probability of the die landing on a prime number. P(prime) = (as an unrounded decimal).