Myths about teaching can hold you back


- Year 11•
- Higher
Interpreting and drawing more real-life graphs
I can interpret and draw more real-life graphs.


- Year 11•
- Higher
Interpreting and drawing more real-life graphs
I can interpret and draw more real-life graphs.
These resources were made for remote use during the pandemic, not classroom teaching.
Switch to our new teaching resources now - designed by teachers and leading subject experts, and tested in classrooms.
Lesson details
Key learning points
- Not all real-life graphs can be drawn using sections of different linear graphs.
- The graphs are models, which means that we want them to be useful.
Keywords
Simple interest - Interest is money added to savings or loans. Simple interest is always calculated on the original amount.
Compound interest - Compound interest is calculated on the original amount and the interest accumulated over the previous period.
Exponential - The general form for an exponential equation is $$y = ab^x$$ where $$a$$ is the coefficient, $$b$$ is the base and $$x$$ is the exponent.
Speed - Speed is the rate at which something is moving. It is measured as the distance travelled per unit of time.
Acceleration - Acceleration is the rate of change of speed with respect to time.
Common misconception
Pupils may think the gradient of the line to model simple interest is always the interest rate.
This works when investing £100 but not with other start values. The gradient is the amount of interest added each time which depends on the amount invested and the interest rate. There are examples to show this in the lesson.
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Interpreting and drawing more real-life graphs, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs...
To help you plan your year 11 maths lesson on: Interpreting and drawing more real-life graphs, download all teaching resources for free and adapt to suit your pupils' needs.
The starter quiz will activate and check your pupils' prior knowledge, with versions available both with and without answers in PDF format.
We use learning cycles to break down learning into key concepts or ideas linked to the learning outcome. Each learning cycle features explanations with checks for understanding and practice tasks with feedback. All of this is found in our slide decks, ready for you to download and edit. The practice tasks are also available as printable worksheets and some lessons have additional materials with extra material you might need for teaching the lesson.
The assessment exit quiz will test your pupils' understanding of the key learning points.
Our video is a tool for planning, showing how other teachers might teach the lesson, offering helpful tips, modelled explanations and inspiration for your own delivery in the classroom. Plus, you can set it as homework or revision for pupils and keep their learning on track by sharing an online pupil version of this lesson.
Explore more key stage 4 maths lessons from the Real-life graphs unit, dive into the full secondary maths curriculum, or learn more about lesson planning.

Licence
Prior knowledge starter quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Interest which is calculated on the original amount and the interest accumulated over the previous period is called __________.
Q2.£200 is invested into an account with 3% simple interest each year. How much will be in the account after 5 years?
Q3.£200 is invested into an account with 3% compound interest each year. Which of these calculations will give the amount in the account after 5 years?
Q4.£1000 is invested into an account with 2% compound interest paid monthly. How much would be in the account after 1 year? Round to the nearest pence.
Q5.Select the coordinates that lie on the curve $$y=3^x$$
Q6.The general form for an exponential equation is:
Assessment exit quiz
6 Questions
Q1.Which would be the equation of the line if graphing £300 invested at a simple interest rate of 2% per month?
Q2.Which would be the equation of the exponential curve if graphing £500 invested at a simple interest rate of 3% per month?
Q3.Which of these equations could model the value of a car depreciating over time?
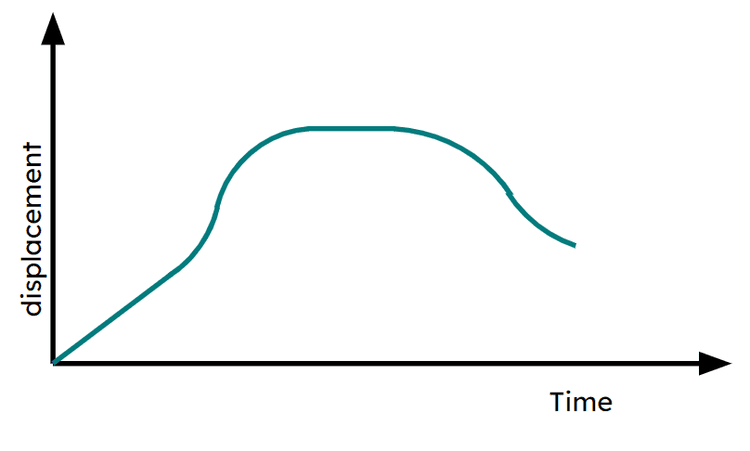
Q4.Which of these journey segments show deceleration on a displacement-time graph?
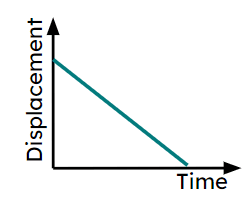
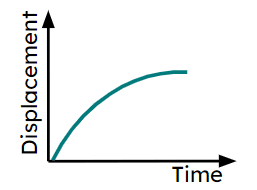
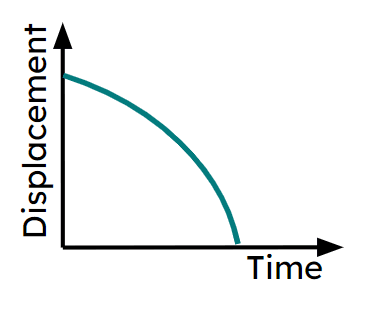
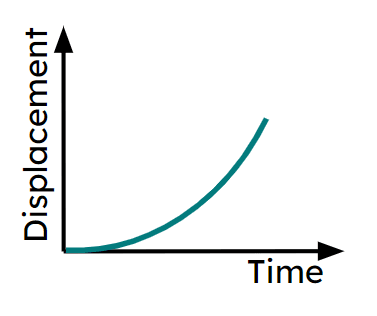
Q5.Match the sections of the graph labelled a)-f) with the correct part of the journey.
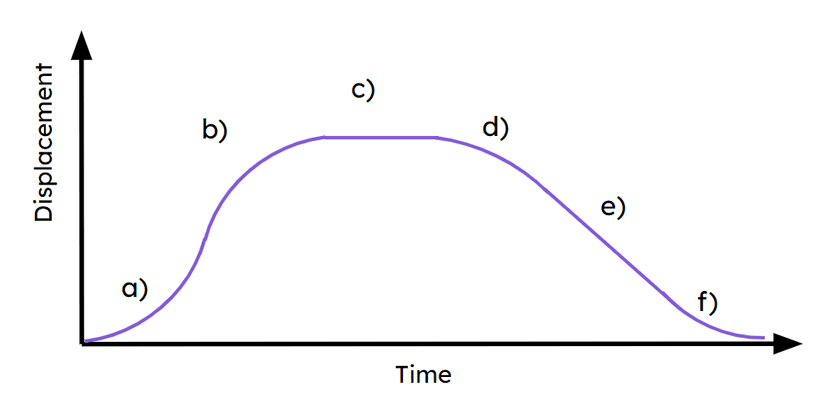
a) -
Increasing in speed moving away from the fixed start point.
b) -
Decelerating moving away from the fixed start point.
c) -
Object is stationary.
d) -
Increasing in speed moving towards the fixed start point.
e) -
Travelling at a constant speed.
f) -
Decelerating moving back towards the fixed start point.
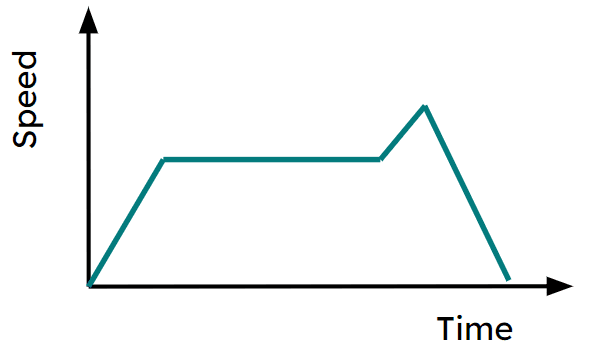
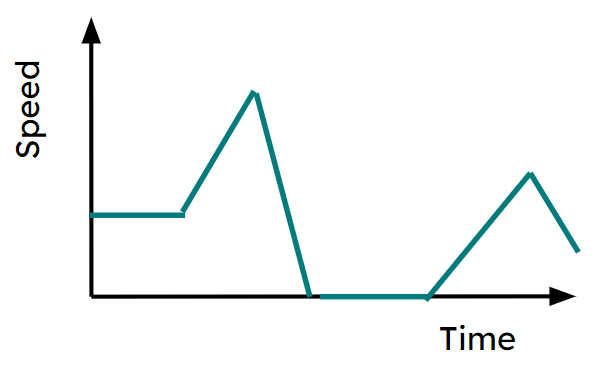
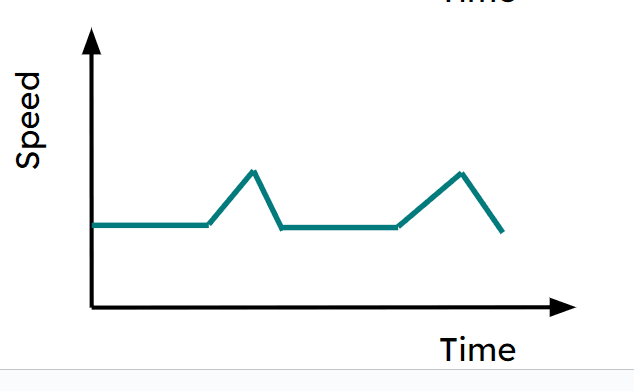
Q6.Here is a displacement-time graph for a journey. Which of these could be a speed-time graph of the same journey?